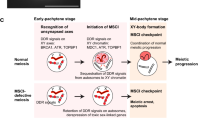
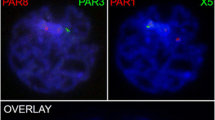
Abstract
During meiosis, heteromorphic mammalian X and Y chromosomes in males undergo transcription silencing and form a compact structure, the XY body, containing specific modifications of the chromatin. In this review, we consider the dynamics of sex chromosome inactivation and discuss the suggestion that the paternally inherited X-chromosome preserves inactivated state in zygote. This state results from meiotic silencing and is prone to imprinted inactivation, which is observed in mammalian females at early embryogenetic stages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly, W.G. and Aramayo, R., Meiotic Silencing and the Epigenetics of Sex, Chromosome Res., 2007, vol. 15, pp. 633–651.
Turner, J.M., Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation, Development, 2007, vol. 134, pp. 1823–1831.
Namekawa, S.H., VandeBerg, J.L., McCarrey, J.R., and Lee, J.T., Sex Chromosome Silencing in the Marsupial Male Germ Line, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, vol. 104, pp. 9730–9735.
Odorisio, T., Rodriguez, T.A., Evans, E.P., et al., The Meiotic Checkpoint Monitoring Synapsis Eliminates Spermatocytes via P53-Independent Apoptosis, Nat. Genet., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 257–261.
Lifschytz, E. and Lindsley, D.L., The Role of X-Chromosome Inactivation during Spermatogenesis (Drosophila-Allocycly-Chromosome Evolution-Male Sterility-Dosage Compensation), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1972, vol. 69, pp. 182–186.
McKee, B.D. and Handel, M.A., Sex Chromosomes, Recombination, and Chromatin Conformation, Chromosoma, 1993, vol. 102, pp. 71–80.
Ayoub, N., Richler, C., and Wahrman, J., Xist RNA Is Associated with the Transcriptionally Inactive XY Body in Mammalian Male Meiosis, Chromosoma, 1997, vol. 106, pp. 1–10.
Turner, J.M., Mahadevaiah, S.K., Benavente, R., et al., Analysis of Male Meiotic “Sex Body” Proteins during XY Female Meiosis Provides New Insights into Their Functions, Chromosoma, 2000, vol. 109, pp. 426–432.
Hoyer-Fender, S., Molecular Aspects of XY Body Formation, Cytogenet. Genome Res., 2003, vol. 103, pp. 245–255.
Handel, M.A., The XY Body: A Specialized Meiotic Chromatin Domain, Exp. Cell Res., 2004, vol. 296, pp. 57–63.
Holstein, A.F., Schulze, W., and Davidoff, M., Under-standing Spermatogenesis Is a Prerequisite for Treatment, Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol., 2003, vol. 1, p. 107.
Bellani, M.A., Romanienko, P.J., Cairatti, D.A., and Camerini-Otero, R.D., SPO11 Is Required for Sex-Body Formation, and Spo11 Heterozygosity Rescues the Prophase Arrest of Atm-/-Spermatocytes, J. Cell Sci., 2005, vol. 118, pp. 3233–3245.
Fernandez-Capetillo, O., Mahadevaiah, S.K., Celeste, A., et al., H2AX Is Required for Chromatin Remodelling and Inactivation of Sex Chromosomes in Male Mouse Meiosis, Dev. Cell, 2003, vol. 4, pp. 497–508.
Khalil, A.M., Boyar, F.Z., and Driscoll, D.J., Dynamic Histone Modifications Mark Sex Chromosome Inactivation and Reactivation during Mammalian Spermatogenesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, vol. 101, pp. 16583–16587.
Godmann, M., Auger, V., Ferraroni-Aguiar, V., et al., Dynamic Regulation of Histone H3 Methylation at Lysine 4 in Mammalian Spermatogenesis, Biol. Reprod., 2007, vol. 77, pp. 754–764.
van der Heijden, G.W., Derijck, A.A., Posfai, E., et al., Chromosome-Wide Nucleosome Replacement and H3.3 Incorporation during Mammalian Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation, Nat. Genet., 2007, vol. 39, pp. 251–258.
Greaves, I.K., Rangasamy, D., Devoy, M., et al., The X and Y Chromosomes Assemble into H2A.Z-Containing Facultative Heterochromatin Following Meiosis, Mol. Cell Biol., 2006, vol. 26, pp. 5394–5405.
Turner, J.M., Aprelikova, O., Xu, X., et al., BRCA1, Histone H2AX Phosphorylation, and Male Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation, Curr. Biol., 2004, vol. 14, pp. 2135–2142.
Mahadevaiah, S.K., Turner, J.M., Baudat, F., et al., Recombinational DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Mice Precede Synapsis, Nat. Genet., 2001, vol. 27, pp. 271–276.
Solari, A.J., The Behavior of the XY Pair in Mammals, Int. Rev. Cytol., 1974, vol. 38, pp. 273–317.
Costa, Y., Speed, R.M., Gautier, P., et al., Mouse MAELSTROM: The Link between Meiotic Silencing of Unsynapsed Chromatin and microRNA Pathway?, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2006, vol. 15, pp. 2324–2334.
Meistrich, M.L., Bucci, L.R., Trostle-Weige, P.K., and Brock, W.A., Histone Variants in Rat Spermatogonia and Primary Spermatocytes, Dev. Biol., 1985, vol. 112, pp. 230–240.
Wolfe, S.A. and Grimes, S.R., Histone H1t: A Tissue-Specific Model Used to Study Transcriptional Control and Nuclear Function during Cellular Differentiation, J. Cell Biochem., 1993, vol. 53, pp. 156–160.
Baarends, W.M., Wassenaar, E., van der Laan, R., et al., Silencing of Unpaired Chromatin and Histone H2A Ubiquitination in Mammalian Meiosis, Mol. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 25, pp. 1041–1053.
de Vries, F.A., de Boer, E., Bosch, M., et al., Mouse Sycp1 Functions in Synaptonemal Complex Assembly, Meiotic Recombination, and XY Body Formation, Genes Dev., 2005, vol. 19, pp. 1376–1389.
van der Laan, R., Uringa, E.J., Wassenaar, E., et al., Ubiquitin Ligase Rad18Sc Localizes to the XY Body and to Other Chromosomal Regions That Are Unpaired and Transcriptionally Silenced during Male Meiotic Prophase, J. Cell Sci., 2004, vol. 117, pp. 5023–5033.
Baarends, W.M., Hoogerbrugge, J.W., Roest, H.P., et al., Histone Ubiquitination and Chromatin Remodeling in Mouse Spermatogenesis, Dev. Biol., 1999, vol. 207, pp. 322–333.
Metzler-Guillemain, C., Luciani, J., Depetris, D., et al., HP1beta and HP1gamma, but not HP1alpha, Decorate the Entire XY Body during Human Male Meiosis, Chromosome Res., 2003, vol. 11, pp. 73–81.
Ooi, S.L., Priess, J.R., and Henikoff, S., Histone H3.3 Variant Dynamics in the Germline of Caenorhabditis elegans, PLoS Genet., 2006, vol. 2, p. e97.
van der Heijden, G.W., Derijck, A.A., Ramos, L., et al., Transmission of Modified Nucleosomes from the Mouse Male Germline to the Zygote and Subsequent Remodeling of Paternal Chromatin, Dev. Biol., 2006, vol. 298, pp. 458–469.
Turner, J.M., Burgoyne, P.S., and Singh, P.B., M31 and macroH2A1.2 Colocalise at the Pseudoautosomal Region during Mouse Meiosis, J. Cell Sci., 2001, vol. 114, pp. 3367–3375.
Hoyer-Fender, S., Czirr, E., Radde, R., et al., Localisation of Histone macroH2A1.2 to the XY-Body Is not a Response to the Presence of Asynapsed Chromosome Axes, J. Cell Sci., 2004, vol. 117, pp. 189–198.
Namekawa, S.H., Park, P.J., Zhang, L.F., et al., Postmeiotic Sex Chromatin in the Male Germline of Mice, Curr. Biol., 2006, vol. 16, pp. 660–667.
Chen, H.Y., Sun, J.M., Zhang, Y., et al., Ubiquitination of Histone H3 in Elongating Spermatids of Rat Testes, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, vol. 273, pp. 13165–13169.
Wang, P.J., Page, D.C., and McCarrey, J.R., Differential Expression of Sex-Linked and Autosomal Germ-Cell-Specific Genes during Spermatogenesis in the Mouse, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2005, vol. 14, pp. 2911–2918.
Hornecker, J.L., Samollow, P.B., Robinson, E.S., et al., Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation in the Marsupial Monodelphis domestica, Genesis, 2007, vol. 45, pp. 696–708.
Mueller, J.L., Mahadevaiah, S.K., Park, P.J., et al., The Mouse X Chromosome Is Enriched for Multicopy Testis Genes Showing Postmeiotic Expression, Nat. Genet., 2008, vol. 40, pp. 794–799.
Khil, P.P., Smirnova, N.A., Romanienko, P.J., and Camerini-Otero, R.D., The Mouse X Chromosome Is Enriched for Sex-Biased Genes not Subject to Selection by Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation, Nat. Genet., 2004, vol. 36, pp. 642–646.
Wang, P.J., McCarrey, J.R., Yang, F., and Page, D.C., An Abundance of X-Linked Genes Expressed in Spermatogonia, Nat. Genet., 2001, vol. 27, pp. 422–426.
Wang, P.J., X-chromosomes, Retrogenes and Their Role in Male Reproduction, Trends Endocrinol. Metab., 2004, vol. 15, pp. 79–83.
McCarrey, J.R. and Thomas, K., Human Testis-Specific PGK Gene Lacks Introns and Possesses Characteristics of a Processed Gene, Nature, 1987, vol. 326, pp. 501–505.
Heard, E. and Disteche, C.M., Dosage Compensation in Mammals: Fine-Tuning the Expression of the X-chromosome, Genes Dev., 2006, vol. 20, pp. 1848–1867.
McCarrey, J.R., Watson, C., Atencio, J., et al., X-Chromosome Inactivation during Spermatogenesis Is Regulated by an Xist/Tsix-Independent Mechanism in the Mouse, Genesis, 2002, vol. 34, pp. 257–266.
Turner, J.M., Mahadevaiah, S.K., Elliott, D.J., et al., Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation in Male Mice with Targeted Disruptions of Xist, J. Cell Sci., 2002, vol. 115, pp. 4097–4105.
Shevchenko, A.I., Pavlova, S.V., Dementyeva, E.V., et al., Chromatin Modifications during X-Chromosome Inactivation in Female Mammals, Russ. J. Genet., 2006, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 1225–1234.
van Attikum, H. and Gasser, S.M., The Histone Code at DNA Breaks: A Guide to Repair?, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 6, pp. 757–765.
Vigodner, M., Sumoylation Precedes Accumulation of Phosphorylated H2AX on Sex Chromosomes during Their Meiotic Inactivation, Chromosome Res., 2009, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 37–45.
Turner, J.M., Mahadevaiah, S.K., Fernandez-Capetillo, O., et al., Silencing of Unsynapsed Meiotic Chromosomes in the Mouse, Nat. Genet., 2005, vol. 37, pp. 41–47.
Burgoyne, P.S., Mahadevaiah, S.K., and Turner, J.M., The Consequences of Asynapsis for Mammalian Meiosis, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2009, vol. 10, pp. 207–216.
Lyon, M.F. and Rastan, S., Parental Source of Chromosome Imprinting and Its Relevance for X-chromosome Inactivation, Differentiation, 1984, vol. 26, pp. 63–67.
McLaren, A. and Monk, M., X-Chromosome Activity in the Germ Cells of Sex-Reversed Mouse Embryos, J. Reprod. Fertil., 1981, vol. 63, pp. 533–537.
Ooi, S.L. and Henikoff, S., Germline Histone Dynamics and Epigenetics, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2007, vol. 19, pp. 257–265.
Goto, T. and Kinoshita, T., Maternal Transcripts of Mitotic Checkpoint Gene, Xbub3, Are Accumulated in the Animal Blastomeres of Xenopus Early Embryo, DNA Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 18, pp. 227–234.
Goto, Y. and Takagi, N., Tetraploid Embryos Rescue Embryonic Lethality Caused by an Additional Maternally Inherited X-chromosome in the Mouse, Development, 1998, vol. 125, pp. 3353–3363.
Okamoto, I. and Arnaud, D., Le Baccon P., et al., Evidence for de novo Imprinted X-Chromosome Inactivation Independent of Meiotic Inactivation in Mice, Nature, 2005, vol. 438, pp. 369–373.
Govin, J., Caron, C., Lestrat, C., et al., The Role of Histones in Chromatin Remodelling during Mammalian Spermiogenesis, Eur. J. Biochem., 2004, vol. 271, pp. 3459–3469.
Churikov, D., Zalenskaya, I.A., and Zalensky, A.O., Male Germline-Specific Histones in Mouse and Man, Cytogenet. Genome Res., 2004, vol. 105, pp. 203–214.
Trostle-Weigem P.K., Meistrich, M.L., Brock, W.A., et al., Isolation and Characterization of TH2A, a Germ Cell-Specific Variant of Histone 2A in Rat Testis, J. Biol. Chem., 1982, vol. 257, pp. 5560–5567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.A. Vaskova, S.V. Pavlova, A.I. Shevchenko, S.M. Zakian, 2010, published in Genetika, 2010, Vol. 46, No. 4, pp. 437–447.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaskova, E.A., Pavlova, S.V., Shevchenko, A.I. et al. Meiotic inactivation of sex chromosomes in mammals. Russ J Genet 46, 385–393 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410040010
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410040010