Abstract
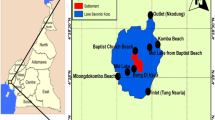
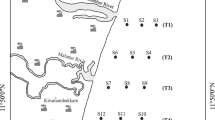
Lake Umbozero (the second largest in the area and the deepest in Murmansk province) was studied with the aim to establish the biogeochemical features of the distribution of chalcophile elements (Hg, Cd, Pb, As) in water, bottom sediments, and whitefish organs and tissues. Lake Umbozero is subject to the effect of emissions and effluents of mining-and-metallurgical plants in Murmansk province, as well as airborne anthropogenic pollution of global character. Surface and near-bed peaks were recorded in the distribution of Pb and Cd in water mass. Those peaks can be due to phytoplankton development in surface layers and the precipitation of dead organisms and mechanical suspension into bed layers. The mean Pb and Cd concentrations in Umbozero water mass exceed the mean for lake water in taiga zone. Water body pollution manifests itself in an increase in concentrations of elements, such as heavy metals, in the surface layers of bottom sediments. The largest contamination factors were recorded for Cd and Pb. Lake pollution by highly toxic chalcophile elements also caused their accumulation in whitefish organs and tissues: the biological accumulation coefficient is >1 for Cd in kidneys (5.8) and for Hg in kidneys, liver, and muscles (3.6, 3.3, and 2.2, respectively).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alferovskaya, M.M., Thermal and Hydrochemical Regime of Umbozero, in Ryby Murmanskoi oblasti (Fish of Murmansk Province), Murmansk, 1966, pp. 37–48.
Vrednye khimicheskie veshchestva. Neorganicheskie soedineniya elementov V-VIII grupp (Hazardous Chemical Substances: Inorganic Compounds of Elements of the V-VIII Group), Leningrad: Khimiya, 1988.
Doklad po okhrane okruzhayushchei sredy i ratsional’nomu ispol’zovaniyu prirodnykh resursov Murmanskoi oblasti v 2004 godu (Report on the Environmental Protection and Rational Use of Natural Resources in Murmansk Province), Murmansk: Komitet po prirodnym resursam i okhrane okruzhayushchei sredy Murmanskoi oblasti, 2005.
Dauvalter, V.A., Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments of the Inari-Pasvik Lake-River System, Vodn. Resur., 1998, vol. 25, no. 4 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 451–457].
Dauvalter, V.A., Regularities in Sedimentation in Water Bodies of European Subarctic Region: Nature Protection Aspects of the Problem, Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Geogr.) Dissertation, Apatity: Izd. Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 1999.
Dauvalter, V.A., Assessment of Toxicity of Metals Accumulated in Bottom Deposits of Lakes, Vodn. Resur., 2000, vol. 27, no. 4 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 424–431].
Dauvalter, V.A. and Il’yashuk, B.P., Conditions of Formation of Ferromanganese Nodules in the Bottom Sediments of Lakes in the Baltic Shield, Geokhimiya, 2007, no. 6 [Geochem. Int. (Engl. Transl.), no. 6, pp. 615–619].
Dauvalter, V.A., Moiseenko, T.I., Rodyushkin, I.V., et al., Sulfur Migration and Cycle in a Subarctic Lake Contaminated by Wastes of a Mining Complex: A Case Study of Lake Imandra, Geokhimiya, 1999, no. 6 [Geochem. Int. (Engl. Transl.), no. 6, pp. 541–551].
Kashulin, N.A., Ryby malykh ozer Severnoi Fennoskandii v usloviyakh aerotekhnogennogo zagryazneniya (Fish of Small Lakes in Northern Fennoscandia under Anthropogenic Pollution), Apatity: Izd. Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 2004.
Kashulin, N.A., Dauvalter, V.A., Kashulina, T.G, et al., Antropogennye izmeneniya loticheskikh ekosistem Murmanskoi oblasti (TRANSLATION), Apatity: Izd-vo Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 2005, vol. 1.
Kashulin, N.A., Lukin, A.A., and Amundsen, P.-A, Ryby presnykh vod subarktiki kak bioindikatory tekhnogennogo zagryazneniya (Fish of Subarctic Freshwater Lakes as Indicators of Technogenic Pollution), Apatity: Izd. Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 1999.
Krokhin, E.M., Materials for Studying Lake Umbozero, Izv. Vsesoyuzn. Geograf. Obshch., 1936, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 12–135.
Moiseenko, T.I., Dauvalter, V.A., Lukin, A.A., et al., Antropogennye modifikatsii ekosistemy ozera Imandra (Anthropogenic Modifications of Lake Imandra Ecosystem), Moiseenko, T.I., Ed., Moscow: Nauka, 2002.
Moiseenko, T.I., Dauvalter, V.A., and Rodyushkin, I.V., Geokhimicheskaya migratsiya elementov v subarkticheskom vodoeme (na primere ozera Imandra) (Geochemical Migration of Elements in a Subarctic Water Body: Case Study of Lake Imandra), Apatity: Izd. Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 1997.
Moiseenko, T.I., Dauvalter, V.A., and Rodyushkin, I.V., Mechanisms of the Cycle of Natural and Human-introduced Metals in Surface Waters of the Arctic Basin, Vodn. Resur., 1998, vol. 25, no. 2 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 212–224].
Moiseenko, T.I., Kudryavtseva, L.P., and Gashkina, N.A., Rasseyannye elementy v poverkhnostnykh vodakh sushi: Tekhnofil’nost’, bioakkumulyatsiya i ekotoksikologiya (Dispersed Elements in Continental Surface Waters: Technophilicity, Bioaccumulation, and Ecotoxicology), Moscow: Nauka, 2006.
Moiseenko, T.I., Rodyushkin, I.V., Dauvalter, V.A., and Kudryavtseva, L.P., Formirovanie kachestva vod i donnykh otlozhenii v usloviyakh antropogennykh nagruzok na vodoemy arkticheskogo basseina (na primere Kol’skogo Severa) (Formation of Quality of Water and Bottom Sediments under Anthropogenic Load onto Water Bodies of the Arctic Basin: Case Study of Kola North), Apatity: Izd. Kol’sk. NTs RAN, 1996.
Moiseenko, T.I. and Yakovlev, V.A., Antropogennye preobrazovaniya vodnykh ekosistem Kol’skogo Severa (Anthropogenic Transformations of Aquatic Ecosystems of Northern Part of Kola Peninsula), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Rikhter, G.D., Physicogeographic Description, Geologiya SSSR, 1958, vol. 27,P. 1, pp. 20–41.
Dauvalter, V., and Sandimirov, S., Pollution of the Sediments of the Paz River Basin, In: State of the Environment in the Norwegian, Finnish, and Russian Border Area, Stebel, K., Chritinsen, G., Derome, J., and Crekela, I., The Fin. Environ., 2007, no. 6.
Goldberg, E.D., Geochronology with Lead-210 // Radioactive Dating, Vienna: IAEA, 1963, pp. 145–157.
Håkanson, L., An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control—A Sedimentological Approach, Water Res., 1980, vol. 14, no. 8, p. 975–1001.
Häsänen, E., Dating of Sediments, Based on 210Pb Measurements, Radiochemical and Radioanalytical Letters, 1977, vol. 31, no. 2, p. 207–214.
Iivonen, P., Pipponen, S., and Verta, M., Factors Affecting Trace-Metal Bioaccumulation in Finnish Headwater Lakes, Environ. Pollut., 1992, vol. 78, no. 1, p. 87–95.
Jernström J., Lehto J., Dauvalter V.A. et al. Heavy metals in bottom sediments of Lake Umbozero in Murmansk Region, Russia // Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, vol. 161, nos. 1–4, p. 93–105.
Kock, G. and Triendi, M., and Hofer. R. Seasonal Patterns of Metal Accumulation in Arctic Char (Salvelinus Alpinus) from an Oligotrophic Alpine Lake Related to Temperature, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1996, vol. 53, no. 6, p. 780–786.
Skogheim, O.K., Rapport Fra Arungenprosjektet, Oslo: As-NLH, 1979, no. 2.
Wicklund, A. and Ruun, P., Calcium Effects on Cadmium Uptake, Redistribution and Elimination in Minnows, Phoxinus Phoxinus, Acclimated to Different Calcium Concentrations, Aquat. Toxicol, 1988, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 109–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Dauvalter, N.A. Kashulin, 2010, published in Vodnye Resursy, 2010, Vol. 37, No. 4, pp. 461–476.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dauvalter, V.A., Kashulin, N.A. Chalcophile elements (Hg, Cd, Pb, As) in Lake Umbozero, Murmansk province. Water Resour 37, 497–512 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807810040093
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807810040093