Abstract
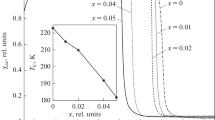
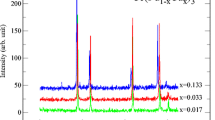
The structure of the Ce(Fe1 − x Si x )2 compounds (with x ≤ 0.075) has been studied and, magnetic susceptibility, heat capacity, and Mössbauer effect have been measured. The compounds with x ≥ 0.05 are antiferromagnetic at low temperatures; as the temperature increases, the compounds become, at first, ferromagnetic and next paramagnetic. The temperatures of magnetic phase transitions have been determined using data on the magnetic susceptibility, and the magnetic phase diagram of the system has been constructed. The heat capacity has been measured and the data were used to calculate the entropy change upon magnetic phase transitions; it is 7.9 and 6.0 J/kg K for CeFe2 and Ce(Fe0.93Si0.07)2, respectively. An analysis of Mössbauer spectra for the alloys in the paramagnetic state allowed us to find that silicon atoms statistically substitute for iron atoms in the crystal lattice intermetallic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Eriksson, L. Nordstrom, M. S. S. Brooks, and B. Johansson, “4f-band magnetism in CeFe2,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2523–2526 (1988).
A. V. Deryagin, A. A. Kazakov, N. V. Kudrevatykh, V. N. Moskalev, N. V. Mushnikov, and S. V. Terent’ev, “Magnetic moment, magnetostriction and effective field at Fe nuclei in CeFe2, LuFe2 and their hydrides,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved. 60, 295–300 (1985).
L. Paolasini, B. Ouladdiaf, N. Bernhoeft, J-P. Sanchez, P. Vulliet, G. H. Lander, and P. Canfield, “Magnetic ground state of pure and doped CeFe2,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 057201 (2003).
D. Braithwaite, G. Lapetrol, B. Salce, A. M. Cumberlige, and P. L. Alireza, “Antiferromagnetic order in pure CeFe2 under pressure,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 76, 224427 (2007).
S. B. Roy and B. R. Coles, “Magnetic behavior of CeFe2: Effects of Ru, Rh, and Pd substitutions,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 39, 9360–9367 (1989).
S. J. Kennedy and B. R. Coles, “The magnetic phases of pseudobinary Ce(Fe1 − x M x)2 intermetallic compounds; M = Al, Co, Ru,” J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2, 1213–1222 (1990).
A. Haldar, N. K. Singh, Ya. Mudryk, K. G. Suresh, A. K. Nigam, and V. K. Pecharsky, “Temperature and magnetic field induced structural transformation in Sidoped CeFe2: An in-field X-ray diffraction study,” Solid State Commun. 150, 879–883 (2010).
L. Paolasini, S. Di Matteo, P. P. Deen, S. Wilkins, C. Mazzoli, B. Detlefs, G. Lapertot, and P. Canfield, “Resonant magnetic X-ray scattering in the antiferromagnet Ce(Fe− x Cox)2,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 77, 094433 (2008).
L. A. Stashkova, V. S. Gaviko, N. V. Mushnikov, and P. B. Terent’ev, “Hydrogen ordering in rare-earth intermetallic (Er, Tb)Fe2 compounds with giant spontaneous magnetostriction,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 985–991 (2013).
A. Haldar, K. G. Suresh, and A. K. Nigam, “Magnetism in gallium-doped CeFe2: Martensitic scenario,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 78, 144429 (2008).
A. Haldar, K. G. Suresh, and A. K. Nigam, “Martensitic features in Si doped CeFe2 revealed by magnetization and transport study,” Intermetallics 18, 1772–1778 (2010).
S. B. Roy, “First order magneto-structural phase transition and associated multi-functional properties in magnetic solids,” J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 183201 (2013).
M. K. Chattopadhyay, M. A. Manekar, and S. B. Roy, “Magnetocaloric effect in CeFe2 and Ru-doped CeFe2 alloys,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 1006–1011 (2006).
A. Haldar, K. G. Suresh, and A. K. Nigam, “Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Ce1−x RxFe2 and Ce(Fe1−x Mx)2 compounds,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 43, 285004 (2010).
U. Atzmony and M. P. Dariel, “Magnetic anisotropy and hyperfine interactions in CeFe2, GdFe2, and LuFe2,” Phys. Rev. B: Solid State 10, 2060–2067 (1974).
X. B. Liu, Z. Altounian, and D. H. Ryan, “Structure and magnetic transition of LaFe13 − x Six compounds,” J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, 7385–7394 (2003).
M. Polcarova, S. Kadeckova, J. Brandler, K. Godwod, and J. Bank-Misiuk, “Lattice parameters of Fe-Si alloy single crystals,” Phys. Status Solidi A 106, 17–23 (1988).
A. K. Grover, R. G. Pillay, V. Balasubramanian, and P. N. Tandon, “Magnetic behavior of Ce(Fe1 − x Alx)2 and Ce(Fe1 − x Six)2,” J. Phys. Paris 49(Suppl. 12), Colloq. C8, 281–282 (1988).
A. K. Grover, R. G. Pillay, V. Balasubramanian, and P. N. Tandon, “Frustration of Fe moments in CeFe2 Matrix,” Solid State Commun. 67, 1223–1227 (1988).
J. Deportes, D. Givord, and K. R. A. Ziebeck, “Evidence of short range magnetic order at four times TC in a metallic compound containing Fe: Susceptibility and paramagnetic scattering in CeFe2,” J. Appl. Phys. 52, 2074–2076 (1981).
H. Wada, M. Nishigori, and M. Shiga, “Magnetic entropy of ferro- and antiferromagnetic Ce(Fe1 − x Cox)2,” J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 62, 1337–1345 (1993).
L. Paolasini, P. Dervenagas, P. Vulliet, J-P. Sanchez, G. H. Lander, A. Hiess, A. Panchula, and P. Canfield, “Magnetic response function of the itinerant ferromagnet CeFe2,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 58, 12117–12124 (1998).
H. Wada, T. Harada, and M. Shiga, “The magnetic field dependence of the electronic specific heat of Ce(Fe1 − x Cox)2,” J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 9347–9352 (1997).
N. Pillmayr, G. Schaudy, T. Holubar, and G. Hilscher, “Specific heat measurements of Ce(Fe1 − x Mx)2 compounds (M = Al, Si; Co, Ni, Cu; In, Sn),” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 104-107, 881–882 (1992).
V. V. Serikov, N. M. Kleinerman, A. V. Vershinin, and N. V. Mushnikov, “Mössbauer studies of the magnetic phase transition in La(Fe0.88SixAl0.12 − x )13 compounds,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 113, 855–861 (2012).
V. V. Serikov, N. M. Kleinerman, A. V. Vershinin, V. S. Gaviko, and N. V. Mushnikov, “Structure of La(Fe0.88SixAl0.12 − x )13 compounds in the paramagnetic state,” Phys. Solid State 55, 495–501 (2013).
W. H. Tang, J. K. Liang, X. L. Chen, and G. X. Rao, “Structure of LaFe9Si4 intermetallic compound,” J. Appl. Phys. 76, 4095–4098 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Vershinin, V.V. Serikov, N.M. Kleinerman, N.V. Mushnikov, E.G. Gerasimov, V.S. Gaviko, A.V. Proshkin, 2014, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2014, Vol. 115, No. 12, pp. 1276–1283.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vershinin, A.V., Serikov, V.V., Kleinerman, N.M. et al. Magnetic phase transitions in the Ce(Fe1 − x Si x )2 compounds. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 115, 1208–1215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14120096
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14120096