Abstract
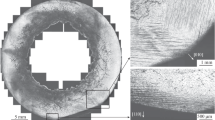
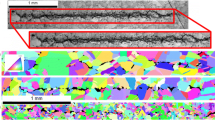
Results of experiments on shock-wave deformation of M2 copper under uniaxial loading are presented. Light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy methods are used to reveal specific features of mechanisms of deformation and fracture of copper during the formation of a main spall crack. The parameters of spall strength, damage, and self-similarity of the spall crack contour are determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. K. Barakhtin, Yu. I. Meshcheryakov, and G. G. Savenkov, “Statistical Characteristics of Multiple Fracture of Metal Targets under Dynamic Loading and Their Relationship with Mechanical Parameters of Materials,” Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 80(1), 79–84 (2010).
Yu. V. Bat’kov, O. N. Ignatova, I. N. Kondrokhina, et al., “Specific Features of Damage Generation under Intense Loading of Copper,” Fiz. Tverd. Tela 53(4), 716–720 (2011).
A. G. Ivanov, “On Possible Causes of Brittle Fracture,” Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 29(3), 137–141 (1988) [J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 29 (3), 439–443 (1988)].
S. A. Atroshenko, S. A. Gladyshev, and Yu. I. Meshcheryakov, “Study of the Mechanisms of Changing the Scale of Structural Levels of Fracture of Dynamically Loaded Media,” in Report of the 4th All-Union Conference on Detonation (Telavi, 1988), Vol. 1, pp. 286–292.
Physical Mesomechanics and Computational Design of Materials, Ed. by V. E. Panin (Nauka, Sib. Izdat. Firma, Novosibirsk, 1995), Vol. 1 [in Russian].
Yu. I. Meshcheryakov and A. K. Divakov, Interference Method for Detecting the Particle Velocity Heterogeneousity in Elastoplastic Loading Waves in Solids (Leningrad, 1989) [in Russian].
B. Mandelbrot, The Fractal Geometry of Nature (W. H. Freeman and Co., 1982).
G. G. Savenkov, “Fractal-Cluster Model of Spall Fracture,” Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 72(12), 44–48 (2002).
B. K. Barakhtin and G. G. Savenkov, “Relationship Between Spall Characteristics and the Dimension of Fractal Fracture Structures,” Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 50(6), 61–69 (2009) [J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 50 (6), 965–971 (2009)].
B. L. Glushak, I. R. Trunin, S. A. Novikov., and A. I. Ruzanov, “Numerical Simulation of Spall Fracture of Metals,” in Fractals in Applied Physics (All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Physics, Arzamas-16, 1995), pp. 59–123.
G. I. Kanel’, S. G. Sugak, and V. E. Fortov, “Spall Fracture Models,” Probl. Prochn., No. 8, 40–44 (1983).
G. G. Savenkov and N. N. Vasil’ev, “Plasticity and Strength of Copper in High-Rate Deformation,” Probl. Prochn., No. 10, 47–52 (1993).
Yu. I. Meshcheryakov, N. I. Zhigacheva, A. K. Divakov, I. P. Makarevich, and B. K. Barakhtin, “Transition of Metals into a Structurally Unstable State under Shock-Wave Loading,” Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 51(5), 132–146 (2010) [J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 51 (5), 732–743 (2010)].
B. K. Barakhtin, Yu. I. Meshcheryakov, and G. G. Savenkov, “Dynamic and Fractal Properties of SP-28 Steel under High-Rate Loading,” Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 68(10), 43–52 (1998).
Fracture of Multiscale Objects under Explosion, Ed. by A. G. Ivanov. (Institute of Experimental Physics, Sarov, 2001) [in Russian].
G. G. Savenkov, “Mechanisms of Deformation and Fracture of Plastic Bodies and Solids in High-Rate Interaction” Doct. Disseration in Tech. Sci. (St. Petersburg, 2003) [in Russian].
Sh. Kh. Khannanov, “Structural Turbulence in Amorphous and Crystalline Solids,” in Disclinations and Rotational Deformation of Solids, Ed. by A. E. Romanov (Ioffe Phys. Tech. Inst., Leningrad, 1990) [in Russian]
A. Carpinteri, N. Pugno, and S. Puzzi, “Strength vs. Toughness Optimization of Microstructured Composities,” Chaos, Solitons Fractals 39, 1210–1223 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.G. Savenkov, Yu.I. Meshcheryakov, B.K. Barakhtin, N.V. Lebedeva.
__________
Translated from Prikladnaya Mekhanika i Tekhnicheskaya Fizika, Vol. 55, No. 5, pp. 195–203, September–October, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savenkov, G.G., Meshcheryakov, Y.I., Barakhtin, B.K. et al. Deformation and fracture mechanisms and structural changes in coarse-grained copper under shock-wave loading. J Appl Mech Tech Phy 55, 896–903 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894414050198
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894414050198