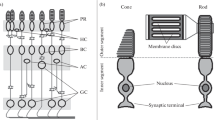
Abstract
At least two independent systems of magnetoreception are currently believed to exist in birds, based on different biophysical principles, located in different parts of their bodies, and with different neuroanatomical mechanisms. One magnetoreceptory system is located in the retina, and may be based on photochemical reactions on the basis of cryptochrome. Information from these receptors is processed in a specialized part of visual Wulst, the so-called Cluster N. There are good reasons to believe that this visual magnetoreceptor processes compass magnetic information necessary for migratory orientation. The second magnetoreceptory system is probably iron-based (biogenic magnetite), located somewhere in the upper beak (its exact location and ultrastructure of receptors remain unknown) and innervated by the ophthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve. It cannot be ruled out that this system participates in spatial representation and helps forming either a kind of map or more primitive signpost sense (identification of specific geographic regions), based on regular spatial variation of the geomagnetic field. The magnetic map probably enables navigation of migrating birds across hundreds and thousands of kilometres. Apart from these two systems, whose existence has been convincingly shown (even if some details are not fully clear yet), there is evidence for the existence of magnetoreceptors based on the vestibular system. It cannot be ruled out that iron-based magnetoreception takes place in lagena (a part of inner ear in fishes, amphibians, reptiles and birds), and the information perceived is processes in vestibular nuclei. The very existence of this magnetoreception system needs verification, and its function remains completely open.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M. and Cashmore, A.R., HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor, Nature, 1993, vol. 366, no. 6451, pp. 162–166.
Azzena, G.B., Mameli, O., and Tolu, E., Distribution of visual input to the vestibular nuclei, Arch. Ital. Biol., 1980, vol. 118, pp. 196–204.
Banerjee, S.K. and Moskowitz, B.M., Ferrimagnetic properties of magnetite, in Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms: A New Biomagnetism, Kirschvink, J.L., Jones, D.S., and McFadden, B.J., Eds., New York: Plenum, 1985, pp. 17–41.
Batchelor, S.N., Kay, C.W.M., McLaughlan, K.A., and Shkrob, I.A., Time-resolved and modulation methods in the study of the effects of magnetic fields on the yields of free radical reactions, J. Phys. Chem., 1993, vol. 97, no. 50, pp. 13250–13258.
Beason, R.C. and Brennan, W.J., Natural and induced magnetization in the bobolink, Dolichonyx oryzivorus (Aves: Icteridae), J. Exp. Biol., 1986, vol. 125, no. 1, pp. 49–56.
Beason, R.C., Dussourd, N., and Deutschlander, M.E., Behavioural evidence for the use of magnetic material in magnetoreception by a migratory bird, J. Exp. Biol., 1995, vol. 198, no. 1, pp. 141–146.
Beason, R.C. and Nichols, J.E., Magnetic orientation and magnetic sensitive material in a trans-equatorial migratory bird, Nature, 1984, vol. 309, no. 5964, pp. 151–153.
Beason, R.C. and Semm, P., Magnetic responses of the trigeminal nerve system of the bobolink (Dolichonyx oryzivorus), Neurosci. Lett., 1987, vol. 80, no. 2, pp. 229–234.
Beason, R.C. and Semm, P., Does the avian ophthalmic nerve carry magnetic navigational information? J. Exp. Biol., 1996, vol. 199, no. 5, pp. 1241–1244.
Beason, R.C., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Pigeon homing: effect of magnetic pulses on initial orientation, Auk, 1997, vol. 114, no. 3, pp. 405–415.
Beck, W. and Wiltschko, W., Magnetic factors control the migratory direction of pied flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca Pallas), in Proc. 19th Int. Ornithol. Congr., 1988, pp. 1955–1962.
Berthold, P., Spatiotemporal programmes and genetics of orientation, Experientia, 1990, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 363–371.
Berthold, P., Spatiotemporal programmes and genetics of orientation, in Orientation in Birds, Berthold, P., Ed., Basel: Birkhauser, 1991, pp. 86–105.
Berthold, P. and Querner, U., Genetic basis of migration behavior on European warblers, Science, 1981, vol. 212, no. 4490, pp. 77–79.
Blakemore, R.P., Magnetotactic bacteria, Science, 1975, vol. 190, no. 4212, pp. 377–379.
Boström, J.E., Åkesson, S., and Alerstam, T., Where on earth can animals use a geomagnetic bi-coordinate map for navigation? Ecography, 2012, vol. 35, no. 11, pp. 1039–1047.
Cadiou, H. and McNaughton, P.A., Avian magnetite-based magnetoreception: a physiologist’s perspective, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, suppl. 2, pp. 193–205.
Chernetsov, N., Kishkinev, D., Gashkov, S., Kosarev, V., and Bolshakov, C.V., Migratory program of juvenile pied flycatchers, Ficedula hypoleuca, from Siberia implies a detour around Central Asia, Anim. Behav., 2008b, vol. 75, no. 2, pp. 539–545.
Chernetsov, N., Kishkinev, D., and Mouritsen, H., A long-distance avian migrant compensates for longitudinal displacement during spring migration, Curr. Biol., 2008a, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 188–190.
Diebel, C.E., Proksch, R., Green, C.R., Neilson, P., and Walker, M.M., Magnetite defines a vertebrate magnetoreceptor, Nature, 2000, vol. 406, no. 6793, pp. 299–302.
Dolnik, V.R., Navigational movements of nocturnal migratory birds, Ornithologia, 1981, vol. 16, pp. 58–63.
Emlen, S.T., Migratory orientation in the Indigo Bunting, Passerina cyanea. Part I: Evidence for use of celestial cues, Auk, 1967a, vol. 84, no. 3, pp. 309–342.
Emlen, S.T., Migratory orientation in the Indigo Bunting, Passerina cyanea. Part II: Mechanism of celestial orientation, Auk, 1967b, vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 463–489.
Falkenberg, G., Fleissner, G., Schuchardt, K., Kuehbacher, M., Thalau, P., Mouritsen, H., Heyers, D., Wellenreuther, G., and Fleissner, G., Avian magnetoreception: elaborate iron mineral containing dendrites in the upper beak seem to be a common feature of birds, PLoS One, 2010, vol. 5, no. 2, p. e9231.
Feenders, G., Liedvogel, M., Rivas, M., Zapka, M., Horita, H., Hara, E., Wada, K., Mouritsen, H., and Jarvis, E.D., Molecular mapping of movement associated areas in the avian brain: a motor theory for vocal learning origin, PLoS One, 2008, vol. 3, no. 3, p. e1768.
Fischer, J.H., Freake, M.J., Borland, S.C., and Phillips, J.B., Evidence for the use of magnetic map information by an amphibian, Anim. Behav., 2001, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 1–10.
Fischer, J.H., Munro, U., and Phillips, J.B., Magnetic navigation by an avian migrant? in Avian Migration, Berthold, P., Gwinner, E., and Sonnenschein, E., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2003, pp. 423–432.
Fleissner, G., Holtkamp-Rötzler, E., Hanzlik, M., Winklhofer, M., Gleissner, G., Petersen, N., and Wiltschko, W., Ultrastructural analysis of a putative magnetoreceptor in the beak of homing pigeons, J. Comp. Neurol., 2003, vol. 458, pp. 350–360.
Fleissner, G., Stahl, B., Thalau, P., Falkenberg, G., and Fleissner, G., A novel concept of Fe-mineral-based magnetoreception: histological and physicochemical data from the upper beak of homing pigeons, Naturwissenschaften, 2007, vol. 94, no. 8, pp. 631–642.
Foley, L.E., Gegear, R.J., and Reppert, S.M., Human cryptochrome exhibits light-dependent magnetosensitivity, Nat. Commun., 2011, vol. 2, no. 6, p. 356.
Fransson, T., Jakobsson, S., Johansson, P., Kullberg, C., Lind, J., and Vallin, A., Magnetic cues trigger extensive refueling, Nature, 2001, vol. 414, no. 6859, pp. 35–36.
Freake, M.J., Muheim, R., and Phillips, J.B., Magnetic maps in animals: a theory comes of age? Quart. Rev. Biol., 2006, vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 327–347.
Freire, R., Dunston, E., Fowler, E.M., McKenzie, G.L., Quinn, C.T., and Michelsen, J., Conditioned response to a magnetic anomaly in the Pekin Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestica) involves the trigeminal nerve, J. Exp. Biol., 2012, vol. 215, no. 14, pp. 2399–2404.
Gagliardo, A., Ioalè, P., Savini, M., and Wild, J.M., Having the nerve to home: trigeminal magnetoreceptor versus olfactory mediation of homing in pigeons, J. Exp. Biol., 2006, vol. 209, no. 15, pp. 2888–2892.
Gagliardo, A., Ioalè, P., Savini, M., and Wild, M., Navigational abilities of homing pigeons deprived of olfactory or trigeminally mediated magnetic information when young, J. Exp. Biol., 2008, vol. 211, no. 13, pp. 2046–2051.
Gagliardo, A., Ioalè, P., Savini, M., and Wild, M., Navigational abilities of adult and experienced homing pigeons deprived of olfactory or trigeminally mediated magnetic information, J. Exp. Biol., 2009, vol. 212, no. 19, pp. 3119–3124.
Gdowski, G.T. and McCrea, R.A., Neck proprioceptive inputs to primate vestibular nucleus neurons, Exp. Brain Res., 2000, vol. 135, no. 4, pp. 511–526.
Gegear, R.J., Casselman, A., Waddell, S., and Reppert, S.M., Cryptochrome mediates light-dependent magnetosensitivity in Drosophila, Nature, 2008, vol. 454, no. 7207, pp. 1014–1018.
Gwinner, E. and Wiltschko, W., Endogenously controlled changes in migratory direction of the garden warbler, Sylvia borin, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 1978, vol. 125, no. 3, pp. 267–273.
Hanzlik, M., Heunemann, C., Holtkamp-Rotzler, E., Winklhofer, M., Petersen, N., and Fleissner, G., Superparamagnetic magnetite in the upper beak tissue of homing pigeons, Biometals, 2000, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 325–331.
Harada, Y., The relation between the magnetic function of birds and fishes and their lagenal function, Acta Otolaryngol., 2008, vol. 128, no. 4, pp. 432–439.
Harada, Y., Taniguchi, M., Namatame, H., and Iida, A., Magnetic materials in otoliths of bird and fish lagena and their function, Acta Otolaryngol., 2001, vol. 121, no. 5, pp. 590–595.
Henshaw, I., Fransson, T., Jakobsson, S., and Kullberg, C., Geomagnetic field affects spring migratory direction in a long distance migrant, Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol., 2010, vol. 64, no. 8, pp. 1317–1323.
Heyers, D., Manns, M., Luksch, H., Güntürkün, O., and Mouritsen, H., A visual pathway links brain structures active during magnetic compass orientation in migratory birds, PLoS One, 2007, vol. 2, no. 9, p. e937.
Heyers, D., Zapka, M., Hoffmeister, M., Wild, J.M., and Mouritsen, H., Magnetic field changes activate the trigeminal brainstem complex in a migratory bird, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, no. 20, pp. 9394–9399.
Hill, E. and Ritz, T., Can disordered radical pair systems provide a basis for a magnetic compass in animals? J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, suppl. 2, pp. 265–271.
Holland, R.A., Differential effects of magnetic pulses on the orientation of naturally migrating birds, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, no. 52, pp. 1617–1625.
Holland, R.A. and Helm, B., A strong magnetic pulse affects the precision of departure direction of naturally migrating adult but not juvenile birds, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2013, vol. 10, no. 81, p. 20121047.
Holland, R.A., Thorup, K., Gagliardo, A., Bisson, I.A., Knecht, E., Mizrahi, D., and Wikelski, M., Testing the role of sensory systems in the migratory heading of a songbird, J. Exp. Biol., 2009, vol. 212, no. 24, pp. 4065–4071.
Ishchenko, L.A., Stolyar, S.V., Ladygina, V.P., Raikher, Yu.L., Balasoiu, M., Bayukov, O.A., Iskhakov, R.S., and Inzhevatkin, E.V., Magnetic properties and application of biomineral particles produced by bacterial culture, Phys. Proc., 2010, vol. 9, pp. 279–282.
Kass, R.E., Ventura, V., and Cai, C., Statistical smoothing of neuronal data, Network: Comput. Neur. Syst., 2003, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 5–15.
Kavokin, K.V., The puzzle of magnetic resonance effect on the magnetic compass of migratory birds, Bioelectromagnetics, 2009, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 402–410.
Keary, N., Ruploh, T., Voss, J., Thalau, P., Wiltschko, R., Wiltschko, W. and Bischof, H.J., Oscillating magnetic field disrupts magnetic orientation in zebra finches, Taeniopygia guttata, Front. Zool., 2009, vol. 6, p. 25. doi:10.1186/1742-9994-6-25
Kirschvink, J.L., Microwave absorption by magnetite: a possible mechanism for coupling non-thermal levels of radiation to biological systems, Bioelectromagnetics, 1996, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 187–194.
Kirschvink, J.L. and Walker, M.M., Particle-size considerations for magnetite-based magnetoreceptors, in Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms: A New Biomagnetism, Kirschvink, J.L., Jones, D.S., and McFadden, B.J., Eds., New York: Plenum, 1985, pp. 243–254.
Kishkinev, D., Chernetsov, N., and Bolshakov, C.V., Migratory orientation of first-year pied flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca) from eastern Baltic, Ornithologia, 2006, vol. 33, pp. 153–160.
Kishkinev, D., Chernetsov, N., Heyers, D., and Mouritsen, H., Migratory reed warblers need intact trigeminal nerves to correct for a 1000 km eastward displacement, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 6, p. e65847.
Klarsfeld, A., Malpel, S., Michard-Vanhée, C., Picot, M., Chélot, E., and Rouyer, F., Novel features of cryptochrome-mediated photoreception in the brain circadian clock of Drosophila, J. Neurosci., 2004, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 1468–1477.
Kramer, G., Eine neue Methode zur Erforschung der Zugorientierung und die bisher damit erzielten Ergebnisse, in Proc. X Ornithol. Congr. Uppsala, 1951, pp. 269–280.
Kramer, G., Die Sonnenorientierung der Vögel, Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges., Zool. Anzeig., 1953, suppl. 16, pp. 72–84.
Kullberg, C., Henshaw, I., Jakobsson, S., Johansson, P., and Fransson, T., Fuelling decisions in migratory birds: geomagnetic cues override the seasonal effect, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2007, vol. 274, no. 1622, pp. 2145–2151.
Kullberg, C., Lind, J., Fransson, T., Jakobsson, S., and Vallin, A., Magnetic cues and time of season affect fuel deposition in migratory thrush nightingales (Luscinia luscinia), Proc. R. Soc. B, 2003, vol. 270, no. 1513, pp. 373–378.
Kuznetsov, A.N. and Vanag, V.K., Mechanism of action of magnetic fields on biological systems, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Biol., 1987, no. 6, pp. 814–827.
Lau, J.C.S., Christopher, T.R., and Hore, P.J., Compass magnetoreception in birds arising from photo-induced radical pairs in rotationally disordered cryptochromes, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2012, vol. 9, no. 77, pp. 3329–3337.
Lauwers, M., Pichler, P., Edelman, N.B., Resch, G.P., Ushakova, L., Salzer, M.C., Heyers, D., Saunders, M., Shaw, J., and Keays, D.A., An iron-rich organelle in the cuticular plate of avian hair cells, Curr. Biol., 2013, vol. 23, no. 10, pp. 924–929.
Liedvogel, M., Feenders, G., Wada, K., Troje, N.F., Jarvis, E.D., and Mouritsen, H., Lateralized activation of cluster N in the brains of migratory songbirds, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2007, vol. 25, pp. 1166–1173.
Liedvogel, M. and Mouritsen, H., Cryptochromes-a potential magnetoreceptor: what do we know and what do we want to know? J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, suppl. 2, pp. 147–162.
Liedvogel, M., Maeda, K., Henbest, K., Schleicher, E., Simon, T., Timmel, C.R., Hore, P.J., and Mouritsen, H., Chemical magnetoreception: bird cryptochrome 1a is excited by blue light and forms long-lived radical-pairs, PLoS One, 2007, vol. 2, no. 10, p. e1106.
Lin, C.T. and Todo, T., The cryptochromes, Genome Biol., 2005, vol. 6, p. 220. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-220
Liu, X. and Chernetsov, N., Avian orientation: multi-cue integration and calibration of compass systems, Chin. Birds, 2012, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1–8.
Lohmann, K.J., Cain, S.D., Dodge, S.A., and Lohmann, C.M.F., Regional magnetic fields as navigational markers for sea turtles, Science, 2001, vol. 294, no. 5541, pp. 364–366.
Lohmann, K.J., Hester, J.T., and Lohmann, C.M.F., Longdistance navigation in sea turtles, Ethol. Ecol. Evol., 1999, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–23.
Lohmann, K.J., Lohmann, C.M.F., Ehrhart, L.M., Bagley, D.A., and Swing, T., Geomagnetic map used in sea-turtle navigation, Nature, 2004, vol. 428, no. 6986, pp. 909–910.
Lowenstam, H.A., Magnetite in denticle capping in recent chitons (Polyplacophora), Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1962, vol. 73, no. 4, pp. 435–438.
Maeda, K., Henbest, K.B., Cintolesi, F., Kuprov, I., Rodgers, C.T., Liddell, P.A., Gust, D., Timmel, C.R., and Hore, P.J., Chemical compass model of avian magnetoreception, Nature, 2008, vol. 453, no. 7183, pp. 387–390.
Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms: A New Biomagnetism, Kirschvink, J.L., Jones, D.S., and McFadden, B.J., Eds., New York: Plenum, 1985.
Möller, A., Sagasser, S., Wiltschko, W. and Schierwater, B., Retinal cryptochrome in a migratory passerine bird: a possible transducer for the avian magnetic compass, Naturwissenschaften, 2004, vol. 91, no. 12, pp. 585–588.
Mora, C.V., Davison, M., Wild, J.M., and Walker, M.M., Magnetoreception and its trigeminal mediation in the homing pigeon, Nature, 2004, vol. 432, no. 7016, pp. 508–511.
Mora, C.V. and Walker, M.M., Do release-site biases reflect response to the Earth’s magnetic field during position determination by homing pigeons? Proc. R. Soc. B, 2009, vol. 276, no. 1671, pp. 3295–3302.
Mora, C.V. and Walker, M.M., Consistent effect of an attached magnet on the initial orientation of homing pigeons, Columba livia, Anim. Behav., 2012, vol. 84, no. 2, pp. 377–383.
Mouritsen, H., Search for the compass needles, Nature, 2012, vol. 484, no. 7394, pp. 320–321.
Mouritsen, H. and Hore, P.J., The magnetic retina: light-dependent and trigeminal magnetoreception in migratory birds, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2012, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 343–352.
Mouritsen, H., Feenders, G., Liedvogel, M., and Kropp, W., Migratory birds use head scans to detect the direction of the earth’s magnetic field, Curr. Biol., 2004a, vol. 14, no. 21, pp. 1946–1949.
Mouritsen, H., Feenders, G., Liedvogel, M., Wada, K., and Jarvis, E.D., Night-vision brain area in migratory songbirds, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2005, vol. 102, no. 23, pp. 8339–8344.
Mouritsen, H., Janssen-Bienhold, U., Liedvogel, M., Feenders, G., Stalleicken, J., Dirks, P., and Weiler, R., Cryptochrome and neuroactivity markers co-localize in bird retina during magnetic orientation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004b, vol. 101, no. 39, pp. 14294–14299.
Muheim, R., Bäckman, J., and Åkesson, S., Magnetic compass orientation in European robins is dependent on both wavelength and intensity of light, J. Exp. Biol., 2002, vol. 205, no. 24, pp. 3845–3856.
Muheim, R., Moore, F.R., and Phillips, J.B., Calibration of magnetic and celestial compass cues in migratory birds-a review of cue-conflict experiments, J. Exp. Biol., 2006, vol. 209, no. 1, pp. 2–17.
Munro, U., Munro, J.A., Phillips, J.B., and Wiltschko, W., Effect of wavelength of light and pulse magnetisation on different magnetoreception systems in a migratory bird, Aust. J. Zool., 1997a, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 189–198.
Munro, U., Munro, J.A., Phillips, J.B., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Evidence for a magnetite-based navigational ‘map’ in birds, Naturwissenschaften, 1997b, vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 26–28.
Newton, A., A Dictionary of Birds, London: A & C Black, 1896.
Nieβner, C., Denzau, S., Gross, J.C., Peichl, L., Bischof, H.J., Fleissner, G., Wiltschko, W. and Wiltschko, R., Avian ultraviolet/violet cones identified as probable magnetoreceptors, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 5, p. e20091.
Partch, C.L. and Sancar, A., Photochemistry and photobiology of cryptochrome bluelight photopigments: the search for a photocycle, Photochem. Photobiol., 2005, vol. 81, no. 6, pp. 1291–1304.
Phillips, J.B., Freake, M.J., Fischer, J.H., and Borland, S.C., Behavioral titration of a magnetic map coordinate, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 2002, vol. 188, no. 2, pp. 157–160.
Putman, N.F., Endres, C.S., Lohmann, C.M.F., and Lohmann, K.J., Longitude perception and bicoordinate magnetic maps in sea turtles, Curr. Biol., 2011, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 463–466.
Putman, N.F., Lohmann, K.J., Putman, E.M., Quinn, T.P., Klimley, A.P., and Noakes, D.L.G., Evidence for geomagnetic imprinting as a homing mechanism in Pacific salmon, Curr. Biol., 2013, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 312–316.
Rappl, R., Wiltschko, R., Weindler, P., Berthold, P., and Wiltschko, W., Orientation behavior of garden warblers, Sylvia borin, under monochromatic light of various wavelengths, Auk, 2000, vol. 117, no. 1, pp. 256–260.
Ritz, T., Ahmad, M., Mouritsen, H., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Photoreceptor-based magnetoreception: optimal design of receptor molecules, cells, and neuronal processing, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, suppl. 2, pp. 135–146.
Ritz, T., Adem, S., and Schulten, K., A model for photoreceptor-based magnetoreception in birds, Biophys. J., 2000, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 707–718.
Ritz, T., Thalau, P., Phillips, J.B., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Resonance effects indicate a radicalpair mechanism for avian magnetic compass, Nature, 2004, vol. 429, no. 6988, pp. 177–180.
Rodgers, C.T. and Hore, P.J., Chemical magnetoreception in birds: the radical pair mechanism, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2009, vol. 106, no. 2, pp. 353–360.
Sancar, A., Structure and function of DNA photolyase and cryptochromes blue-light photoreceptors, Chem. Rev., 2003, vol. 103, no. 6, pp. 2203–2237.
Schmidt-Koenig, K., The sun compass, Experientia, 1990, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 336–342.
Schneider, T., Thalau, H.P., Semm, P., and Wiltschko, W., Melatonin is crucial for the migratory orientation of pied flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca Pallas), J. Exp. Biol., 1994, vol. 194, no. 1, pp. 255–262.
Schulten, K., Magnetic field effects in chemistry and biology, in Festkörperprobleme, Treusch, J., Ed., Braunschweig: Vieweg, 1982, vol. 22, pp. 61–83.
Schulten, K., Swenberg, C.E., and Weller, A., A biomagnetic sensory mechanism based on magnetic field modulated coherent electron spin motion, Z. Phys. Chem. (NF), 1978, vol. 111, no. 1, pp. 1–5.
Schulten, K. and Windemuth, A., Model for a physiological magnetic compass, in Biophysical Effects of Steady Magnetic Fields, Maret, G., Boccara, N., and Kiepenheuer, J., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1986, vol. 11, pp. 99–106.
Shcherbakov, V.P. and Winklhofer, M., Theoretical analysis of flux amplification by soft magnetic material in a putative biological magnetic-field receptor, Phys. Rev. E, 2010, vol. 81, no. 3, p. 031921.
Semm, P. and Beason, R.C., Responses to small magnetic variations by the trigeminal system of the bobolink, Brain Res. Bull., 1990, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 735–740.
Solov’yov, I.A. and Greiner, W., Theoretical analysis of an iron-mineral-based magnetoreceptor model in birds, Biophys. J., 2007, vol. 93, no. 5, pp. 1493–1509.
Solov’yov, I., Mouritsen, H., and Schulten, K., Acuity of a cryptochrome and vision-based magnetoreception system in birds, Biophys. J., 2010, vol. 99, no. 1, pp. 40–49.
Stapput, K., Thalau, P., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Orientation of birds in total darkness, Curr. Biol., 2008, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 602–606.
Steiner, U. and Ulrich, T., Magnetic field effects in chemical kinetics and related phenomena, Chem. Rev., 1989, vol. 89, no. 1, pp. 51–147.
Thalau, P., Ritz, T., Stapput, K., Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Magnetic compass orientation of migratory birds in the presence of a 1.315 MHz oscillating field, Naturwissenschaften, 2005, vol. 92, no. 2, pp. 86–90.
Thienemann, J., Rossitten, Neumann: Neudamm, 1927.
Timmel, C.R. and Hore, P.J., Oscillating magnetic field effects on the yields of radical pair reactions, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1996, vol. 257, nos. 3–4, pp. 401–408.
Treiber, C.D., Salzer, M.C., Riegler, J., Edelman, N., Sugar, C., Breuss, M., Pichler, P., Cadiou, H., Saunders, M., Lythgoe, M., Shaw, J., and Keays, D.A., Clusters of iron-rich cells in the upper beak of pigeons are macrophages not magnetosensitive neurons, Nature, 2012, vol. 484, no. 7394, pp. 367–370.
Walcott, C., Anomalies in the earth’s magnetic field increase the scatter of pigeon’s vanishing bearings, in Animal Migration, Navigation, and Homing, Schmidt-Koenig, K. and Keeton, W.T., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978, pp. 143–151.
Walcott, C., Magnetic maps in pigeons, in Orientation in Birds, Berthold, P., Ed., Basel: Birkhauser, 1991, pp. 38–51.
Walcott, C., Gould, J.L., and Kirschvink, J.L., Pigeons have magnets, Science, 1979, vol. 205, no. 4410, pp. 1027–1029.
Walker, M.M., A model for encoding of magnetic-field intensity by magnetite-based magnetoreceptor cells, J. Theor. Biol., 2008, vol. 250, no. 1, pp. 85–91.
Wallraff, H.G., The magnetic map of the homing pigeon, an evergreen phantom, J. Theor. Biol., 1999, vol. 197, no. 2, pp. 265–269.
Wallraff, H.G., Avian Navigation: Pigeon Homing as a Paradigm, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2005.
Wallraff, H.G., Kiepenheuer, J., Neumann, M.F., and Streng, A., Homing experiments with starlings deprived of the sense of smell, Condor, 1995, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 20–26.
Weber, S., Light-driven enzymatic catalysis of DNA repair: a review of recent biophysical studies on photolyase, BBA-Bioenergetics, 2005, vol. 1707, no. 1, pp. 1–23.
Williams, M.N. and Wild, J.M., Trigeminally innervated iron-containing structures in the beak of homing pigeons, and other birds, Brain Res., 2001, vol. 889, nos. 1–2, pp. 243–246.
Wiltschko, W., Further analysis of the magnetic compass of migratory birds, in Animal Migration, Navigation, and Homing, Schmidt-Koenig, K. and Keeton, W.T., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978, pp. 301–310.
Wiltschko, W., Daum, P., Fergenbauer-Kimmel, A., and Wiltschko, R., The development of the star compass in garden warblers, Sylvia borin, Ethology, 1987, vol. 74, no. 4, pp. 285–292.
Wiltschko, W., Gesson, M., and Wiltschko, R., Magnetic compass orientation of European robins under 565 nm green light, Naturwissenschaften, 2001, vol. 88, no. 9, pp. 387–390.
Wiltschko, W., Munro, U., Beason, R.C., Ford, H., and Wiltschko, R., A magnetic pulse leads to a temporary deflection in the orientation of migratory birds, Experientia, 1994, vol. 50, no. 7, pp. 697–700.
Wiltschko, R., Munro, U., Ford, H., Stapput, K., and Wiltschko, W., Light-dependent magnetoreception: orientation behavior of migratory birds under dim red light, J. Exp. Biol., 2008, vol. 211, no. 20, pp. 3344–3350.
Wiltschko, W., Munro, U., Ford, H., and Wiltschko, R., Red light disrupts magnetic orientation of migratory birds, Nature, 1993, vol. 364, no. 6437, pp. 525–527.
Wiltschko, W., Munro, U., Ford, H., and Wiltschko, R., Effect of a magnetic pulse on the orientation of silvereyes, Zosterops l. lateralis, during spring migration, J. Exp. Biol., 1998, vol. 201, no. 23, pp. 3257–3261.
Wiltschko, W., Munro, U., Ford, H., and Wiltschko, R., Avian orientation: the pulse effect is mediated by the magnetite receptors in the upper beak, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2009, vol. 276, no. 1665, pp. 2227–2232.
Wiltschko, R., Ritz, T., Stapput, K., Thalau, P., and Wiltschko, W., Two different types of light-dependent responses to magnetic fields in birds, Curr. Biol., 2005, vol. 15, no. 16, pp. 1518–1523.
Wiltschko, R., Schiffner, I., Fuhrmann, P., and Wiltschko, W., The role of the magnetite based receptors in the beak in pigeon homing, Curr. Biol., 2010, vol. 20, no. 17, pp. 1534–1538.
Wiltschko, R., Schiffner, I., and Wiltschko, W., A strong magnetic anomaly affects pigeon navigation, J. Exp. Biol., 2009, vol. 212, no. 18, pp. 2983–2990.
Wiltschko, R., Stapput, K., Ritz, T., Thalau, P., and Wiltschko, W., Magnetoreception in birds: different physical processes for two types of directional responses, HFSP J., 2007, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 41–48.
Wiltschko, W. and Wiltschko, R., Magnetic compass of European robins, Science, 1972, vol. 176, no. 4030, pp. 62–64.
Wiltschko, W. and Wiltschko, R., Migratory orientation of European robins is affected by the wavelength of light as well as by a magnetic pulse, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 1995, vol. 177, no. 3, pp. 363–369.
Wiltschko, W. and Wiltschko, R., The effect of yellow and blue light on magnetic compass orientation in European robins, Erithacus rubecula, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 1999, vol. 184, no. 3, pp. 295–299.
Wiltschko, W. and Wiltschko, R., Light-dependent magnetoreception in birds: the behavior of European robins, Erithacus rubecula, under monochromatic light of various wavelengths and intensities, J. Exp. Biol., 2001, vol. 204, no. 19, pp. 3295–3302.
Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., Avian navigation, Auk, 2009a, vol. 126, no. 4, pp. 717–743.
Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., ’Fixed direction’responses of birds in the geomagnetic field, Commun. Integr. Biol., 2009b, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 100–103.
Wiltschko, R., and Wiltschko, W., The magnetite-based receptors in the beak of birds and their role in avian navigation, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 2013, vol. 199, no. 2, pp. 89–98.
Wiltschko, W., Wiltschko, R., and Munro, U., Light-dependent magnetoreception in birds: the effect of intensity of 565 nm green light, Naturwissenschaften, 2000, vol. 87, no. 8, pp. 366–369.
Winklhofer, M. and Kirschvink, J.L., A quantitative assessment of torque-transducer models for magnetoreception, J. R. Soc. Interface, 2010, vol. 7, suppl. 2, pp. 273–289.
Wu, L.-Q. and Dickman, J.D., Magnetoreception in an avian brain in part mediated by inner ear lagena, Curr. Biol., 2011, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 418–423.
Wu, L.-Q. and Dickman, J.D., Neural correlates of a magnetic sense, Science, 2012, vol. 336, no. 6084, pp. 1054–1057.
Zapka, M., Heyers, D., Hein, C.M., Engels, S., Schneider, N.-L., Hans, J., Weiler, S., Dreyer, D., Kishkinev, D., Wild, M., and Mouritsen, H., Visual, but not trigeminal, mediation of magnetic compass information in a migratory bird, Nature, 2009, vol. 461, no. 7268, pp. 1274–1277.
Zapka, M., Heyers, D., Liedvogel, M., Jarvis, E.D., and Mouritsen, H., Night-time neuronal activation of cluster N in a day- and night-migrating songbird, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 619–624.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Zhurnal Obshchei Biologii, 2014, Vol. 75, No. 2, pp. 104–123.
The article was translated by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kishkinev, D.A., Chernetsov, N.S. Magnetoreception systems in birds: A review of current research. Biol Bull Rev 5, 46–62 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086415010041
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086415010041