Abstract
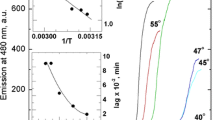
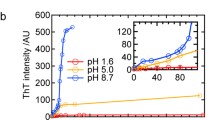
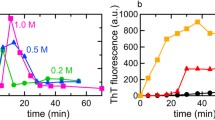
Today, the investigation of the structure of ordered protein aggregates-amyloid fibrils, the influence of the native structure of the protein and the external conditions on the process of fibrillation-is the subject of intense investigations. The aim of the present work is to study the kinetics of formation of insulin amyloid fibrils at low pH values (conditions that are used at many stages of the isolation and purification of the protein) using the fluorescent probe thioflavin T. It is shown that the increase of the fluorescence intensity of ThT during the formation of amyloid fibrils is described by a sigmoidal curve, in which three areas can be distinguished: the lag phase, growth, and a plateau, which characterize the various stages of fibril formation. Despite the variation in the length of the lag phase at the same experimental conditions (pH and temperature), it is seen to drop during solution stirring and seeding. Data obtained by electron microscopy showed that the formed fibrils are long, linear filaments ∼20 nm in diameter. With increasing incubation time, the fibril diameter does not change, while the length increases to 2–3 μm, which is accompanied by a significant increase in the number of fibril aggregates. All the experimental data show that, irrespective of the kinetics of formation of amyloid fibrils, their properties after the completion of the fibrillation process are identical. The results of this work, together with the previous studies of insulin amyloid fibrils, may be important for clarification the mechanism of their formation, as well as for the treatment of amyloidosis associated with the aggregation of insulin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A., DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE of Hsp70 system have differing effects on alpha-synuclein fibrillation involved in Parkinson’s disease, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2010, vol. 4, pp. 275–279.
Ahmad, A., Millett, I.S., Doniach, S., Uversky, V.N., and Fink, A.L., Partially folded intermediates in insulin fibrillation, Biochemistry, 2003, vol. 42, pp. 11404–11416.
Ahmad, A., Muzaffar, M., and Ingram, V.M., Ca(2+), within the physiological concentrations, selectively accelerates Abeta42 fibril formation and not Abeta40 in vitro, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2009, vol. 1794, pp. 1537–1548.
Albert, S.G., Obadiah, J., Parseghian, S.A., Yadira Hurley, M., and Mooradian, A.D., Severe insulin resistance associated with subcutaneous amyloid deposition, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract., 2007, vol. 75, pp. 374–376.
Blundell, T.L., Insulin: the structure in the crystal and its reflection in chemistry and biology, Adv. Protein Chem., 1972, vol. 26, pp. 279–402.
Booth, D.R., Sunde, M., Bellotti, V., Robinson, C.V., Hutchinson, W.L., Fraser, P.E., Hawkins, P.N., Dobson, C.M., Radford, S.E., Blake, C.C., and Pepys, M.B., Instability, unfolding and aggregation of human lysozyme variants underlying amyloid fibrillogenesis, Nature, 1997, vol. 385, pp. 787–793.
Dische, F.E., Wernstedt, C., Westermark, G.T., Westermark, P., Pepys, M.B., Rennie, J.A., Gilbey, S.G., and Watkins, P.J., Insulin as an amyloid-fibril protein at sites of repeated insulin injections in a diabetic patient, Diabetologia, 1988, vol. 31, pp. 158–161.
Goers, J., Permyakov, S.E., Permyakov, E.A., Uversky, V.N., and Fink, A.L., Conformational prerequisites for alpha-lactalbumin fibrillation, Biochemistry, 2002, vol. 41, pp. 12546–12551.
LeVine, H., III, Quantification of beta-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T, Methods Enzymol., 1999, vol. 309, pp. 274–284.
LeVine, H., III, Thioflavine T interaction with synthetic Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides: detection of amyloid aggregation in solution, Protein Sci., 1993, vol. 2, pp. 404–410.
Li, J., Uversky, V.N., and Fink, A.L., Conformational behavior of human alpha-synuclein is modulated by familial Parkinson’s disease point mutations A30P and A53T, Neurotoxicology, 2002, vol. 23, pp. 553–567.
Maskevich, A.A., Stsiapura, V.I., Kuzmitsky, V.A., Kuznetsova, I.M., Povarova, O.I., Uversky, V.N., and Turoverov, K.K., Spectral properties of thioflavin T in solvents with different dielectric properties and in a fibril-incorporated form, J. Proteome Res., 2007, vol. 6, pp. 1392–1401.
Munishkina, L.A., Ahmad, A., Fink, A.L., and Uversky, V.N., Guiding protein aggregation with macromolecular crowding, Biochemistry, 2008, vol. 47, pp. 8993–9006.
Nielsen, L., Khurana, R., Coats, A., Frokjaer, S., Brange, J., Vyas, S., Uversky, V.N., and Fink, A.L., Effect of environmental factors on the kinetics of insulin fibril formation: elucidation of the molecular mechanism, Biochemistry, 2001, vol. 40, pp. 6036–6046.
Sahoo, S., Reeves, W., and DeMay, R.M., Amyloid tumor: a clinical and cytomorphologic study, Diagn. Cytopathol., 2003, vol. 28, pp. 325–328.
Shikama, Y., Kitazawa, J., Yagihashi, N., Uehara, O., Murata, Y., Yajima, N., Wada, R., and Yagihashi, S., Localized amyloidosis at the site of repeated insulin injection in a diabetic patient, Intern. Med., 2010, vol. 49, pp. 397–401.
Sluzky, V., Tamada, J.A., Klibanov, A.M., and Langer, R., Kinetics of insulin aggregation in aqueous solutions upon agitation in the presence of hydrophobic surfaces, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1991, vol. 88, pp. 9377–9381.
Souillac, P.O., Uversky, V.N., Millett, I.S., Khurana, R., Doniach, S., and Fink, A.L., Elucidation of the molecular mechanism during the early events in immunoglobulin light chain amyloid fibrillation. Evidence for an off-pathway oligomer at acidic pH, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, pp. 12666–12679.
Storkel, S., Schneider, H.M., Muntefering, H., and Kashiwagi, S., Iatrogenic, insulin-dependent, local amyloidosis, Lab. Invest., 1983, vol. 48, pp. 108–111.
Sulatskaya, A.I. and Kuznetsova, I.M., Thioflavin T interaction with amyloid fibrils as an instrument for their studying, Tsitologiia, 2010, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 955–959.
Sulatskaya, A.I., Kuznetsova, I.M., and Turoverov, K.K., Interaction of thioflavin T with amyloid fibrils: stoichiometry and affinity of dye binding, absorption spectra of bound dye, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2011, vol. 115, pp. 11519–11524.
Sulatskaya, A.I., Kuznetsova, I.M., and Turoverov, K.K., Interaction of thioflavin T with amyloid fibrils: fluorescence quantum yield of bound dye, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, vol. 116, pp. 2538–2544.
Sulatskaya, A.I., Maskevich, A.A., Kuznetsova, I.M., Uversky, V.N., and Turoverov, K.K., Fluorescence quantum yield of thioflavin T in rigid isotropic solution and incorporated into the amyloid fibrils, PLoS One, 2010, vol. 5, p. e15385.
Swift, B., Examination of insulin injection sites: an unexpected finding of localized amyloidosis, Diabet. Med., 2002, vol. 19, pp. 881–882.
Uversky, V.N., Li, J., and Fink, A.L., Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 10737–10744.
Vladimirov, Yu.A., and Litvin, F.F., Fotobiologiya i spektral’nye metody issledovaniya (Photobiology and Spectral Research Methods), Moscow: Vysshaya shkola, 1964.
Wild, S., Roglic, G., Green, A., Sicree, R., and King, H., Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030, Diabetes Care, 2004, vol. 27, pp. 1047–1053.
Yumlu, S., Barany, R., Eriksson, M., and Rocken, C., Localized insulin-derived amyloidosis in patients with diabetes mellitus: a case report, Hum. Pathol., 2009, vol. 40, pp. 1655–1660.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.I. Sulatskaya, E.A. Volova, Ya.Yu. Komissarchik, E.S. Snigirevskaya, A.A. Maskevich, E.A. Drobchenko, I.M. Kuznetsova, K.K. Turoverov, 2013, published in Tsitologiya, 2013, Vol. 55, No. 11, pp. 809–814.
The article was translated by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sulatskaya, A.I., Volova, E.A., Komissarchik, Y.Y. et al. Investigation of the kinetics of insulin amyloid fibrils formation. Cell Tiss. Biol. 8, 186–191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X14020114
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X14020114