Abstract
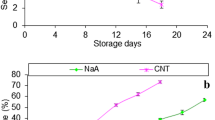
In an attempt to initiate seafood biotechnology in the Sultanate of Oman, Middle East, using underutilized fish, fish burgers from two different formulas were developed and the quality and storage stability were evaluated during storage at −20°C for 3 months. Quality and storage stability were evaluated through total aerobic and coliform bacterial count, peroxide value, protein solubility, and color. Total aerobic bacteria were reduced significantly (P<0.05) by 84% and 97% of the initial load in formulas 1 and 2, respectively, whereas coliforms were completely destroyed in both formulas at the end of storage. Peroxide value increased (P < 0.05) but did not reach detectable levels of rancidity. Salt-soluble protein content decreased remarkably during the storage period. The L value showed good stability during storage, keeping products bright for 3 months. Fish burgers from both formulas were acceptable for 3 months at −20°C. Storage stability was rationalized by the effectiveness of freezing, and antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of food additives.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shewan JM. A review of the microbiology of frozen and cured fishery products. In: Goteborg (eds). Sweden, 1954; No. 100.
Heen E, Karsti O. Fish and shellfish freezing. In: George B (ed). Fish as Food, Academic Press Inc., USA, 1965; IV: 355–418.
Dussault HP. Effect of freezing on coliform bacteria and method of detection in frozen fish fillets and blocks. Fish. Res. Br. Can. 1956; 65: 12–14.
Bank A. The freezing and cold storage of herrings. Gt. Br. Dept. Sci. Ind. Res., Food Inves. Spec. Rept. 1952; 55: 40.
Pj-Ke DMN, Ackman RG. Quality preservation in frozen mackerel. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Tech. J. 1976; 9: 135–138.
Connell JJ. Changes in the actin of cod flesh during storage at −14°C. J. Food Agr. 1960; 11: 515–519.
Haard NF. Biochemical reactions in fish muscle during frozen storage. In: Blight G (ed). Seafood Science and Technology. Fishing News Books. Oxfordshire, UK. 1992; 176–209.
Finn DB. The denaturation of fish muscle proteins by freezing. Contrib. Can. Biol. Fish. 1934; 8: 311–320.
Luijpen AF. Denaturation of fish proteins. Nature 1957; 180: 1422–1423.
Bito M, Honma S. Studies on the retention of meat color of frozen tuna IV. Acceleration of discoloration of tuna meat by freezing and its relation to storage temperatures. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1967; 33: 33–39.
Bito M. Studies on the retention of meat color of frozen tuna II. Effect of storage temperature on preventing discoloration of tuna meat during freezing storage. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1995; 31: 534–545.
Ochiai Y, Chow C, Watabe S, Hashimoto K. Evaluation of tuna meat discoloration by Hunter Color Difference Scale. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1988; 54: 649–653.
Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries. Fisheries Statistics Book. Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, Muscat, Oman. 2003.
Curran C, Nicolaides L, Al Alawi Z. Quality changes during iced storage of three commercial important species of fish in Bahrain. Trop. Sci. 1981; 23: 253–268.
Ministry of Commerce and Industries. Methods of Microbiological Examination of Meat, Fish, Shell-Fish and Their Products. Omani Standard no. 627. Ministry of Commerce and Industries. Muscat, Oman. 1996.
Helrich K (ed). Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemist. Arlington 1990
Egan H, Kirk RS, Sawyer R (eds). Pearsons Chemical Analysis of Foods. Churchil Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK. 1981; 437, 458–459, 499, 533–536.
Rahman SM, Amri OS, Al Bulushi IM. Pores and physico-chemical characteristics of dried tuna produced by different methods of drying. J. Food Eng. 2002; 53: 301–313.
Ironside JI, Love RM. Studies on protein denaturation in frozen fish. I. Biological factors influencing the amount of soluble and insoluble protein present in the muscle of North Sea cod. J. Food Agri. 1958; 2: 597–609.
Lapa-Guimaraea J, Aparecida M, Felicio P, Guzman E. Sensory, color, and psychrotrophic bacterial analysis of squid (Loligo plei) during storage in ice. Lebensm-Wiss. U. Technol. 2002; 35: 21–29.
ICMSE Available at: http://www.fag.org/DOCREP/003/ T1768E/T1768E04.htm 1986.
Chang K, Chang C, Shiau C, Pan B. Biochemical, microbiological and sensory changes of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) under partial freezing and refrigerated storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998; 46: 682–686.
NFI. State Guidelines for Coliforms, Fecal Coliforms, and E. coli. National Fisheries Institute, Arlington, VA, USA, 1998.
Rudolf K (ed). Preezing and Irradiation of Fish. Fishing News (books) Limited. Oxfordshire, UK. 1969.
Vasudevan P, Marek P, Diagle S, Hoagland T, Venkitanarayanan K. Effect of chilling and freezing on survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus on fish fillets. J. Food Safety. 2002; 22: 209.
Digirolamo R, Liston J, Matches J. The effects of freezing on the survival of Salmonella and E. coli in Pacfic oysters. J. Food Sci. 1970; 35: 13–16.
Gopalakrishna ITS, Shrivastava KP. The incidence and low temperature survival of coagulase-positive Staphylococci in fish products. Fish Tech. 1988; 25: 132–138.
Arora D, Kaur J. Antimicrobial activity of spices. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1999; 12: 257–262.
Beuchat LR. Antimicrobial properties of spices and their essential oils. Nat. Antimicrob. Syst. Food Preserv. 1994; 12: 257–262.
Aagaard J. Fryselagring at fed fisk. Konserves 1968; 26: 78–84.
Tanabe H, Yoshida M, Tomita N. Comparison of the antioxidant activities of 22 commonly used culinary herbs and spices on the lipid oxidation of pork meat. Anim. Sci. J. 2002; 73: 389.
Shobana S, Naidu KA. Antioxidant activity of selected Indian spices. Prost. Leuk. Ess. Fatty Acids. 2000; 62: 107–110.
Manoj P, Kasapis S, Chronaskis IS. Gelatin and phase separation in maltodextrin-caseinate system. Food Hydrocoll. 1996; 10: 407–420.
Walkenstrom P, Kidman S, Hermansson A, Rasmussen P, Hoegh L. Microstructure and rheological behaviour of alginate/pectin mixed gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2003; 17: 593–603.
Love RM. Studies on protein denaturation in frozen fish. III: the mechanism and site of denaturation of at low temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1958; 9: 609–617.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Bulushi, I.M., Kasapis, S., Al-Oufi, H. et al. Evaluating the quality and storage stability of fish burgers during frozen storage. Fish Sci 71, 648–654 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01011.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01011.x