Abstract
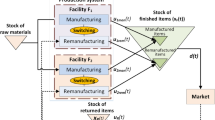
We describe hybrid manufacturing/remanufacturing systems with a long lead time for manufacturing and a short lead time for remanufacturing. We review the classes of inventory strategies for hybrid systems in the literature. These are all based on equal lead times. For systems with slow manufacturing and fast remanufacturing, we propose a new class. An extensive numerical experiment shows that the optimal strategy in the new class almost always performs better and often much better than the optimal strategies in all other classes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thierry M, Salomon M, van Nunenv J and van Wassenhove L. (1995). Strategic issues in product recovery management. Calif Mngt Rev 37(2): 114–135.
Lund R. (1984). Remanufacturing. Technol Rev 87(2): 18–23.
Ayres R, Ferrer G and van Leynselee T. (1997). Eco-efficiency, asset recovery and remanufacturing. Eur Mngt J 15(5): 557–574.
Brayman RB (1992). How to implement MRP II successfully the second time: getting people involved in a remanufacturing environment. In APICS Remanufacturing Seminar Proceedings, Salt Lake City, pp 82–88.
Graedel TE and Allensby BR (1995). Industrial Ecology. Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Guide Jr VDR (1996). Scheduling using drum-buffer-rope in a remanufacturing environment. Int J Prod Res 34(9): 1081–1091.
Sivinski JA and Meegan S (1993). Case study: Abbott labs formalized approach to remanufacturing. In APICS Remanufacturing Seminar Proceedings, Oklahoma City, pp 27–30.
Sprow E (1992). The mechanics of remanufacture. Manuf Engng 108: 38–45.
Vandermerwe S and Oliff MD (1991). Corporate challenges for an age of reconsumption. Columbia J World Bus 26: 7–25.
Teunter RH (1998). Inventory control of service parts in the final phase, PhD thesis, University of Groningen (RUG), the Netherlands.
Teunter RH and Vlachos D (2002). On the necessity of a disposal option for returned products that can be remanufactured. Int J Prod Econ 75: 257–266.
van der Laan E (1997). The effects of remanufacturing on inventory control, PhD thesis, Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
van der Laan EA, Salomon M, Dekker R and van Wassenhove LN (1999). Inventory control in hybrid systems with remanufacturing. Mngt Sci 45(5): 733–747.
Inderfurth K and van der Laan E (1998). Leadtimes effects and policy improvement for stochastic inventory control with remanufacturing, Preprint No. 22, Faculty of Economics and Management, Otto-von-Guericke University of Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany.
Guide Jr VDR (2000). Production planning and control for remanufacturing: industry practise and research needs. J Opns Mngt 18(4): 467–483.
Kiesmüller GP (2001). A new approach for controlling a hybrid stochastic manufacturing/remanufacturing system with inventories and different lead times, Working paper, Eindhoven University of Technology, Faculty of Technology Management, 2001.
Kiesmüller GP and Minner S (2001). Simple expressions for finding recovery system inventory control parameters. Working paper, Eindhoven University of Technology, Faculty of Technology Management.
Teunter RH, van der Laan E and Inderfurth K (2000). How to set the holding cost rates in average cost inventory models with reverse logistics? OMEGA The Int J Mngt Sci 28: 409–415.
Silver EA, Pyke DF and Peterson R (1998). Inventory Management and Production Planning and Scheduling. John Wiley and Sons: New York.
Kiesmüller GP and de Kok AG (2001). Reducing production variability in a hybrid stochastic manufacturing/remanufacturing system. Working paper, Eindhoven University of Technology, Faculty of Technology Management.
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper is part of the research on reuse in the context of the EU sponsored TMR project REVersed LOGistics (ERB 4061 PL 97-5650) in which participate: the Erasmus University Rotterdam (NL), the Eindhoven University of Technology (NL), the Otto-von-Guericke Universitaet Magdeburg (D). INSEAD (F), the Aristoteles University of Thessaloniki (GR) and the University of Piraeus (GR). The research of Dr. Ruud H. Teunter has been made possible by a fellowship of The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teunter, R., Laan, E. & Vlachos, D. Inventory strategies for systems with fast remanufacturing. J Oper Res Soc 55, 475–484 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601687
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601687