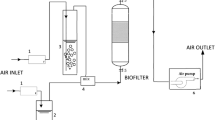
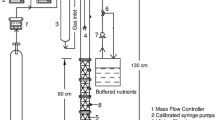
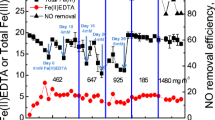
Biofiltration systems utilizing thermophilic (55C) bacteria were constructed and tested for the removal of methanol and α-pinene — two important volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the forest products industry. Thermophilic bacterial mixtures that can degrade both methanol and α-pinene were obtained via enrichment techniques. Two bench-scale thermophilic biofiltration systems (1085 and 1824 cm3) were used to examine compound removals at different residence times, with influent concentrations of 110 ppmv methanol and 15 ppmv α-pinene. At a residence time of 10.85 min, the smaller system had removal efficiencies of >98% for methanol, but only 23% for α-pinene. The larger system was operated with the same parameters to evaluate residence time and surfactant effects on compound removals. At a residence time of 18.24 min, both methanol and α-pinene removal rates were ≥95%. However, α-pinene removal dropped to 26% at a residence time of 6.08 min; methanol removal was not affected. Subsequent addition of a surfactant mixture increased α-pinene removal to 94% at the shortest residence time. No residual α-pinene was detected with the support medium Celite R-635, indicating that the surfactant may increase mass transfer of α-pinene. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2001) 26, 127–133.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 06 June 2000/ Accepted in revised form 09 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhamwichukorn, S., Kleinheinz, G. & Bagley, S. Thermophilic biofiltration of methanol and α-pinene. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 26, 127–133 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000079
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000079