Abstract
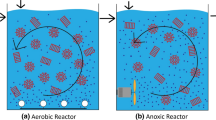
Four moving-medium biofilm reactors treating wastewater were reviewed in this paper: the rotating biological contactor (RBC), the moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR), the vertically moving biofilm reactor (VMBR) and the fluidized-bed reactor (FBR). The RBC process has been applied widely. MBBR is a good process for upgrading current wastewater treatment systems. VMBR is suitable for treating small wastewater flows. FBR can maximize pollutant removals and minimize sludge production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreottola G, Foladori P & Ragazzi M (2000a)Upgrading of a small wastewater treatment plant in a cold climate region using a moving bed bio film reactor (MBBR)system.Water Sci.Technol.41(1):177–185
Andreottola G, Foladori P, Ragazzi M & Tatano F (2000b) Experimental comparison between MBBR and activated sludge system for the treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Sci.Technol.41(4–5):375–382
Banerjee G (1997)Hydraulics of bench-scale rotating biological contactor.Water Res.31:2500–2510
Bosander J & Westlund AD (2000) Operation of full-scale fluidized-bed for denitri fication.Water Sci.Technol. 41 (9): 115–121
Boumansour BE & Vasel JL (1998)A new tracer gas method to measure oxygen transfer and enhancement factor on RBC. Water Res.32:1049–1058
Broch-Due A, Andersen R & Kristoffersen O (1994)Pilot plant experience with an aerobic moving bed bio lm reactor for treatment of NSSC wastewater.Water Sci.Technol.29(5–6): 283–294
Broch-Due A, Andersen R & Opheim B (1997)Treatment of integrated newsprint mill wastewater in moving bed bio film reactors.Water Sci.Technol.35(2–3):173–180
Chen S-D, Chen C-Y, Shen Y-C, Chiu C-M & Cheng H-J (1996)Treatment of high-strength nitrate wastewater by biological methods-operational characteristics study.Water Sci.Technol.34(1–2):269–276
Cheng S-S, Chen W-C & Hwang H-H (1997)Bio film formation:the effects of hydrodynamic and substrate feeding patterns in three phase draft-tubefluidized bed for nitri fication process.Water Sci.Technol.36(12):83–90
de Beer D, Stoodley P & Lewandowski Z (1996)Liquid flow and mass transport in heterogeneous bio films.Water Res.30: 2761–2765
Droste RL (1997)Theory and Practice of Water and Waste-water Treatment,John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Flanagan WP (1998)Biodegradation of dichloromethane in a granular activated carbon fluidized-bed reactor.Water Environ.Res.70:60–66
Galvan A, Urbina P & de Castro F (2000)Characterization of lamentous microorganisms in rotating biological contactor bio lms of wastewater treatment plants.Bioprocess Eng.22: 257–260
Grady CPL,Jr & Lim HC (1980)Biological Wastewater Treatment:Theory and Applications,Marcel Dekker, New York
Green M, Mels A, Lahav O & Tarre S (1996)Biological-ion exchange process for ammonium removal from secondary efluent.Water Sci.Technol.34(1–2):449–458
Green M, Ruskol Y, Tarre S & Loewenthal RE (2002a) Nitri fication utilizing CaCO3 as the buffering agent.Environ. Technol.23:303–308
Green M, Ruskol Y, Shaviv A & Tarre S (2002b)The effect of CO2 concentration on a nitrifying chalk reactor.Water Res. 36:2147–2151
Griffin P & Findlay GE (2000)Process and engineering improvements to rotating biological contactor design.Water Sci.Technol.41(1):137–144
Harremoës P & Henze M (2002)Bio filters.In:Henze M, Harremoës P, la C. Jansen J & Arvin E (Eds)Wastewater Treatment:Biological and Chemical Processes,(pp 157–207). Springer, Heidelberg
Harvey P (2002)Moving bed bio film reactors:a robust solution for wastewater treatment.Chem.Eng.(London)729:33
Helness H & Ødegaard H (1999)Biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch moving bed bio film reactor. Water Sci.Technol.40(4–5):161–168
Hidalgo MD & Garcia-Encina PA (2002)Bio film development and bed segregation in a methanogenic fluidized bed reactor. Water Res.36:3083–3091
Holst TC, Truc A & Pujol R (1997)Anaerobic fluidized beds: ten years of industrial experience.Water Sci.Technol.36(6– 7):415–422 http://wwwny.anox.se/eng/b2 2 barare.htm
Jahren SJ, Rintala JA & Ødegaard H(2002)Aerobic moving bed bio lm reactor treating thermomechanical pulping white-water under thermophilic conditions.Water Res.36:1067–1075
Koran KM, Suidan, MT, Khodadoust AP, Sorial GA & Brenner RC (2001)Effectiveness of an anaerobic granular activated carbonfluidized-bed bioreactor to treat soil wash fluids:a proposed strategy for remediating PCP/PAH contaminated soils.Water Res.35:2363–2370
Lazarova V & Manem J (2000)Innovative bio lm treatment technologies for water and wastewater treatment.In:Bryers JD (Ed)Bio films II:Process Analysis and Applications (pp 159–206).Wiley-Liss, New York
Lu C, Li H-C, Lee LY & Lin M-R (1997)Effects of disc rotational speed and submergence on the performance of an anaerobic rotating biological contactor.Environ.Int.23: 253–263
Maloney SW, Adrian NR, Hickey RF & Heine RL (2002) Anaerobic treatment of pinkwater in afluidized bed reactor containing GAC.J.Hazard.Mater.92:77–88
Martin-Cereceda M, Alvarez AM, Serrano S & Guinea A (2001)Confocal and light microscope examination of protozoa and other microorganisms in the bio films from a rotating biological contactor wastewater treatment plant.Acta Protozool.40:263–272
Mba D, Bannister RH & Findlay GE (1999)Mechanical redesign of the rotating biological contactor.Water Res.33: 3679–3688
Moteleb MA, Suidan MT, Kim J, Davel JL & Adrian NR (2001)Anaerobic degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in granular activated carbonfluidized bed and batch reactors. Water Sci.Technol.43(1):67–75
Ødegaard H (2000)Advanced compact wastewater treatment based on coagulation and moving bed bio film processes. Water Sci.Technol.42(12):33–48
Ødegaard H, Rusten B & Badin H (1993)Small wastewater treatment plants based on moving bed bio film reactors. Water Sci.Technol.28(10):351–359
Ødegaard H, Rusten B & Westrum T (1994)A new moving bed bio lm reactor-applications and results.Water Sci.Technol. 29(10–11):157–165
Okabe S, Hiratia K, Ozawa Y & Watanabe Y (1996)Spatial microbial distributions of nitri ers and heterotrophs in mixed-population bio films.Biotechnol.Bioeng.50:24–35
Pastorelli G, Andreottola, G, Canziani R, de Fraja E, de Pascalis F, Gurrieri G & Rozzi A (1997)Pilot-plant experiments with moving-bed bio lm reactors.Water Sci.Technol. 36(1):43–50
Rodgers M (1999)Organic carbon removal using a new bio lm reactor.Water Res.33:1495–1499
Rodgers M & Burke D (2001)Carbonaceous oxidation using a new vertically moving bio lm system.Environ.Technol.22: 673–678
Rodgers M & Burke D (2002)Nitrogen removal using a vertically moving bio lm system.Water Sci.Technol.47(1): 71–76
Rodgers M, Zhan X-M & Gallagher B (2003a)A pilot plant study using a vertically moving bio lm process to treat municipal wastewater.Biore.Technol.89:139–143
Rodgers M, Zhan X-M & Casey A (2003b)Ammonium removal using a vertically moving bio lm system.J Environ. Sci.Health Part A 38:2483–2494
Rodgers M, Zhan X-M & Casey A (2004)Oxygen transfer and industrial wastewater treatment effciency of a vertically moving bio lm system.Water Air Soil Pollut 151:165–178
Rusten B, Ødegaard H & Lundar A (1992)Treatment of dairy wastewater in a novel moving bed bio lm reactor.Water Sci. Technol.26(3–4):703–711
Rusten B, Siljudalen JG & Strand H (1996)Upgrading of a biological-chemical treatment plant for cheese factory waste-water.Water Sci.Technol.34(11):41–49
Rusten B, McCoy M, Proctor R & Siljudalen JG (1998)The innovative moving bed bio lm reactor/solids contact reaeration process for secondary treatment of municipal waste-water.Water Environ.Res.70:1083–1089
Rusten B, Johnson CH, Devall S, Davoren D & Cashion BS (1999)Biological pretreatment of a chemical plant wastewater in high-rate moving bed bio lm reactors.Water Sci.Technol.39(10–11):257–264
Rusten B, Hellstrom BG, Hellstrom F, Sehested O, Skjelfoss E & Svendsen B (2000)Pilot testing and preliminary design of moving bed bio lm reactors for nitrogen removal at the FREVAR wastewater treatment plant.Water Sci.Technol. 41(4):13–20
Surampalli RY & Baumann ER (1997)Role of supplemental aeration in improving overloaded first-stage RBC performance.Water Air Soil Pollut.98:1–15
Sutton PM, Hurvid J & Hoeksema M (1999)Biological fluidized-bed treatment of wastewater from byproduct coking operations:full-scale case history.Water Environ.Res.71: 5–9
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL & Stensel MD (2003) Wastewater Engineering:Treatment and Reuse, Metcalf & Eddy, New York
Teixeira P & Oliveira R (2001)Denitri cation in a closed rotating biological contactor:effect of disk submergence. Process Biochem.37:345–349
Trulear MG & Characklis WG (1982)Dynamics of bio lm processes.J.Water Pollut.Control Fed.54:1288–1301
USEPA (1993)Nitrogen Removal,Technomic Publishing Company, Pennsylvania,USA
WEF (Water Environment Federation)& ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) (1998) Design of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants,WEF and ASCE, Alexandria and Reston,USA
Winkler MA (1981)Biological Treatment of Wastewater,John Wiley & Sons, New York
Zhu S & Chen S (2001)Impacts of Reynolds number on nitri cation bio lm kinetics.Aquacult.Eng.24:213–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodgers, M., Zhan, XM. Moving-Medium Biofilm Reactors. Re/Views in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 2, 213–224 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RESB.0000040467.78748.1e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RESB.0000040467.78748.1e