Abstract
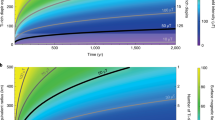
Mars lacks a detectable magnetic field of global scale, but boasts a rich spectrum of magnetic fields at smaller spatial scales attributed to the spatial variation of remanent magnetism in the crust. On average the Mars crust is 10 times more intensely magnetized than that of the Earth. It appears likely that the Mars crust acquired its remanence in the first few hundred million years of evolution when an active dynamo sustained an intense global field. An early dynamo era, ending in the Noachian, or earliest period of Mars chronology, would likely be driven by thermal convection in an early, hot, fluid core. If crustal remanence was acquired later in Mars history, a dynamo driven by chemical convection associated with the solidification of an inner core is likely. Thermal evolution models cannot yet distinguish between these two possibilities. The magnetic record contains a wealth of information on the thermal evolution of Mars and the Mars dynamo, but we have just begun to decipher its message.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M. H. et al.: 1992, ‘Mars Observer Magnetic Fields Investigation’, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 7799-7814.
Acuña, M. H. et al.: 1998, ‘Magnetic Field and Plasma Observations at Mars: Initial Results of the Mars Global Surveyor Mission’, Science 279, 1676-1680.
Acuña, M. H. et al.: 1999, ‘Global Distribution of Crustal Magnetism Discovered by the Mars Global Surveyor MAG/ER Experiment’, Science 284, 790-793.
Acuña, M. H. et al.: 2001, ‘The magnetic Field of Mars: Summary of Results from the Aerobraking and Mapping Orbits’, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 23403-23417.
Albee, A. L., Palluconi, F. D. and Arvidson, R. E.: 1998, ‘Mars Global Surveyor Mission: Overview and Status’, Science 279, 1671-1672.
Albee, A. L., Arvidson, R. E., Palluconi, F. D. and Thorpe, T.: 2001, ‘Overview of the Mars Global Surveyor Mission’, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 23291-23316.
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2001a, ‘A 50-degree Spherical Harmonic Model of the Magnetic Field of Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23197-23208.
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2001b, ‘Paleomagnetic Pole Positions and Pole Reversals on Mars’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28(17), 3409-3412.
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2002a, ‘An Improved 50-degree Spherical Harmonic Model of the Magnetic Field of Mars Derived from Both High-altitude and Low-altitude Data’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E5).
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2002b, ‘Magnetization of the Mars Crust’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E10).
Bertka, C. M. and Fei, Y.: 1997, ‘Mineralogy of the Martian Interior Up to Core-mantle Boundary Pressures’, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 5251-5264.
Blakely, R. J.: 1995, Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 437 pp.
Breuer, D. and Spohn, T.: 1993, ‘Cooling of the Earth, Urey Ratios, and the Problem of Potassium in the Core’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1655-1658.
Breuer, D., Yuen, D. A. and Spohn, T.: 1997, ‘Phase Transitions in the Martian Mantle: Implications for Partially Layered Convection’, Earth Planetary Sci. Lett. 148, 457-469.
Breuer, D. and Spohn. T.: 2003, ‘Early Plate Tectonics vs. Single Plate Tectonics on Mars: Evidence from Magnetic Field History and Crust Evolution’, J. Geophys. Res. submitted.
Braginsky, S. I,: 1964, ‘Magnetohydrodynamics of the Earth's Core’, Geomag. Aeron. 4, 698-712.
Buffett, B. A., Huppert, H. E., Lister, J. R. and Woods, A. W.: 1996, ‘On the Thermal Evolution of the Earth's Core’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 7989-8006.
Cain, J. C., Ferguson, B. and Mozzoni, D.: 2002, ‘An n = 90 Internal Potential Function of the Magnetic Field of the Martian Crustal Magnetic Field’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E10).
Chabot, N. L. and Drake, M. J.: 1999, ‘Potassium Solubility in Metal: The Effects of Composition at 15 kbar and 1900 deg C on Partitioning Between Iron Alloys and Silicate Melts’, Earth Planetary Sci. Lett. 172, 323-335.
Chen, J. H. and Wasserburg, G. J.: 1986, Formation Ages and Evolution of Shergotty and its Parent Planet from U-Th-Pb Systematics', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 955-968.
Christensen, P. R. et al.: 2000, ‘Detection of Crystalline Hematite Mineralization on Mars by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer: Evidence for Near-surface Water’, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 9623-9642.
Cisowski, S.M.: 1986, ‘Magnetic Studies on Shergotty and Other SNC Meteorites’, Geochimica and Cosmochimica Acta. 50, 1043-1048.
Connerney, J. E. P.: 1993, ‘Magnetic Fields of the Outer Planets’, J. Geophys. Res. 98(E10), 18,659-18679.
Connerney, J. E. P. et al.: 1999, ‘Magnetic Lineations in the Ancient Crust of Mars’, Science 284, 794-798.
Connerney, J. E. P. et al.: 2001, ‘The Global Magnetic Field of Mars and Implications for Crustal Evolution’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 4015-4018.
Davaille, A. and Jaupart, C.: 1993, ‘Transient High-Rayleigh-number Thermal Convection with Large Viscosity Variations’, J. Fluid Mech. 253, 141-166.
Dolginov, Sh. Sh. and Zhuzgov, L. N.: 1991, ‘The Magnetic Field and Magnetosphere of the Planet Mars’, Planetary Space Sci. 39, 1493-1510.
Ernst, R. E., Grosfils, E.B. and Mege, D.: 2001, ‘Giant Dike Swarms: Earth, Venus, and Mars’, Ann. Rev. Earth Planetary Sci. 29, 489-534.
Fairen, A. G., Ruiz, J. and Anguita, F.: 2002, ‘An Origin for the Linear Magnetic Anomalies on Mars Through Accretion of Terranes: Implications for Dynamo Timing’, Icarus 160, 220-223.
Frey, H. and Schultz, R. A.: 1988, ‘Large Impact Basins and the Mega-impact Origin for the Crustal Dichotomy on Mars’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 15, 229-232.
Frey, H. V., Roark, J. H., Shockey, K. M., Frey, E. L. and Sakimoto, S. E. H.: 2002, ‘Ancient Lowlands on Mars’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29.
Gessmann, C. K. and Wood, B. J.: 2002, ‘Potassium in the Earth's Core?’, Earth Planetary Sci. Lett. 200, 63-78.
Glatzmeier, G. A. and Roberts, P. H. ‘Simulating the Geodynamo’, Contemp. Phys. 38, 269-288.
Goettel, K. A.: 1981, ‘Density of the Mantle of Mars’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 497-500.
Goldstein, M. L.: 1975, ‘Lunar Magnetism’, Nature 258, 175.
Grasset, O. and Parmentier, E. M.: 1998, ‘Thermal Convection in a Volumetrically Heated, Infinite Prandtl Number Fluid With Strongly Temperature-Dependent Viscosity: Implications for Planetary Thermal Evolution’, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 18171-18181.
Gringauz, K. I., Verigin, M., Luhmann, J., Russell, C. T. and Mihalov, J. D.: 1993, ‘On the Compressibility of the Magnetic Tails of Mars and Venus’, in Plasma Environments of Non-magnetic Planets, Pergammon, New York, pp. 265-270.
Hauck, S. A. and Phillips, R. J.: 2002, ‘Thermal and Crustal Evolution of Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 107.
Head, J. W., Kreslavsky, M. A. and Pratt, S.: 2002, ‘Northern Lowlands of Mars: Evidence for Widespread Volcanic Flooding and Tectonic Deformation in the Hesperian Period’, J. Geophys. Res. 107.
Hood, L. L. and Zakharian, A.: 2001, ‘Mapping and Modeling of Magnetic Anomalies in the Northern Polar Region of Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E7), 14601-14619.
Jault, D.: 1996, ‘Magnetic Field Generation Impeded by Inner Cores of Planets’, Cr. Acad. Sci. II A 323, 451-458.
Kellog, O. D.: 1929, Foundations of Potential Theory, Frederick Ungar Publishers, New York.
Kleine, T., Münker, C., Metzger and Palme, H.: 2002, ‘Rapid Accretion and Core Formation on Asteroids and the Terrestrial Planets from Hf-W Chronometry’, Nature 418, 952-955.
Kletetschka, G., Wasilewski, P. J. and Taylor, P. T.: 2000, ‘Hematite vs. Magnetite as the Signature for Planetary Magnetic Anomalies?’, Earth Planetary Sci. Lett. 176, 469-479.
Langel, R. A.: 1987, in J. A. Jacobs (ed.), ‘The Main Field’, Geomagnetism Academic Press, London, pp. 249-512.
Langel, R. A., Schnetzler, C. C., Phillips, J. D. and Horner, R. J.: 1982, ‘Initial Vector Magnetic Anomaly Map from MAGSAT’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 273-276.
Langel, R. A. and Estes, H.: 1982, ‘A Geomagnetic Field Spectrum’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 250-253.
Lee, D. C. and Halliday, A. N.: 1997, ‘Core Formation on Mars and Differentiated Asteroids’, Nature 388, 854-857.
Leweling, M. and Spohn, T.: 1997, ‘Mars: a Magnetic Field Due to Thermoremanence?’, Planetary Space Sci. 45, 1389-1400.
Longhi, J., Knittle, E., Holloway, J. R. and Wanke, H.: 1992, in Kieffer, Hugh H., Jakosky, Bruce, M., Snyder, Conway W., Matthews, Mildred S., (Eds), ‘The Bulk Composition, Mineralogy, and Internal Structure of Mars’, Mars, University of Arizona Press, Tucson, AZ, pp. 184-208.
Maus, S., Rother, M., Holme, R., Luhr, H., Olsen, N. and Haak, V.: 2002, ‘First Scalar Magnetic Anomaly Map from CHAMP Satellite Data Indicates Weak Lithospheric Field’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(14).
Maus, S. and Haak, V.: 2002, ‘Is the Long Wavelength Crustal Magnetic Field Dominated by Induced or Remanent Magnetization?’, Geophys. Res. Lett. in press.
Mayhew, M. A. and Galliher, S. C.: 1982, ‘An Equivalent Source Magnetization Model for the United States Derived from MAGSAT Data’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 311-313.
McSween, H. Y., Jr. et al.: 2001, ‘Geochemical Evidence Magmatic Water Within Mars from Pyroxenes in the Shergotty Meteorite’, Nature, 409, 487-490.
Mitchell, D. L. et al.: 2001, ‘Probing Mars' Crustal Magnetic Field and Ionosphere with the MGS Electron Reflectometer’, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23419-23427.
Mohlmann, D. et al.: 1991, ‘The Question of an Internal Martian Magnetic Field’, Planetary Space Sci. 39, 83.
Ness, N. F.: 1979, ‘The Magnetic Fields of Mercury, Mars and Moon’, Ann. Rev. Earth Planetary Sci. 7, 248-288.
Nimmo, F.: 2000, ‘Dike Intrusion as a Possible Cause of Linear Martian Magnetic Anomalies’, Geology 28, 391-394.
Nimmo, F. and Stevenson, D.: 2000, ‘Influence of Early Plate Tectonics on the Thermal Evolution and Magnetic Field of Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 11969-11979.
Ochadlick, A. R., Jr.: 1991, ‘Magnetic Exploration of Ocean Crust for Craters of Impact Origin’, Geophysics 56(6), 1153-1157.
Olsen, N.: 2002, ‘A Model of the Geomagnetic Field and its Secular Variation for Epoch 2000’, Geophys. J. Int. 149, 454-462.
Parker, R. L.: 2003, ‘Ideal Bodies for Mars Magnetics’, J. Geophys. Res. 108(E1).
Purucker, M. et al.: 2000, ‘An Altitude-normalized Magnetic Map of Mars and Its Interpretation’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 2449-2452.
Riedler, W. et al.: 1989, ‘Magnetic Fields Near Mars: First Results’, Nature 341, 604-607.
Roberts, P. H. and Glatzmeier, F. A.: 2000, ‘Geodynamo Theory and Ssimulation’, Rev. Modern Physics 72, 1081-1123.
Runcorn, S. K.: 1975, ‘An Ancient Lunar Magnetic Dipole Field’, Nature 253, 701-703.
Runcorn, S. K.: 1975, ‘On the Interpretation of Lunar Magnetism’, Phys. Earth planetary Int. 10, 327-335.
Russell, C. T.: 1978a, ‘The Magnetc Field of Mars: Mars 3 Evidence Re-examined’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 81-84.
Russell, C. T.: 1978b, ‘The Magnetic Field of Mars: Mars 5 Evidence Re-examined’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 85-88.
Russell, C. T.: 1979, in C. F. Kennel (ed.), ‘The Interaction of the Solar Wind With Mars, Venus and Mercury’, Solar System Plasma Physics, North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 208-252.
Russell, C. T. et al.: 1995, ‘A Simple Test of the Induced Nature of the Martian Tail’, Planetary Space Sci. 43(7), 875-879.
Schubert, G. and Spohn. T.: 1990, ‘Thermal History of Mars and the Sulfur Content of Its Core’, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14095-14104.
Schubert, G, Solomon, S. C., Turcotte, D. L., Drake, M. J. and Sleep,: 1992, in Kieffer, Hugh, H., Jakosky, Bruce M., Snyder, Conway, W., Matthews, Mildred S. (ed.), ‘Origin and Thermal Evolution of Mars’, Mars University of Arizona Press, Tucson, AZ, pp. 147-183.
Schubert, G., Russell, C. T. and Moore, W. B.: 2000, ‘Geophysics-Timing of the Martian dynamo’, Nature 408, 666-667.
Senshu, H., Kuramoto, K. and Matsui, T.: 2002, ‘Thermal Evolution of a Growing Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E12), 5118.
Slavin, J. A., Schwingenschuh, K., Riedler, W. and Yeroshenko, Y.: 1991, ‘The Solar Wind Interaction With Mars: Mariner 4, Mars 2, Mars 3, Mars 5, and Phobos 2 Observations of Bow Shock Position and Shape’, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 11235-11241.
Slavin, J. A. and Holzer, R. E.: 1994, ‘The Solar Wind Interaction With Mars Revisited’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 10285-10296.
Sleep, N. H.: 1994, ‘Martian Plate Tectonics’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5639-5655.
Smith, D. E. et al.: 1999, ‘The Global Topography of Mars and Implications for Surface Evolution’, Science 284, 1495-1503.
Smith, D. E., Zuber, M. T. and Neumann, G. A.: 2001, ‘Seasonal Variations of Snow Depth on Mars’, Science 294(5549), 2141-2146.
Smith, E. J., Davis, L. Jr., Coleman, P. J. and Jones, D. E.: 1965, ‘Magnetic Field Measurements Near Mars’, Science 149, 1241-1242.
Sohl, F. and Spohn, T.: 1997, ‘The Structure of Mars: Implications from SNC-Meteorites’, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 1613-1635.
Solomatov, V. S.: 1995, ‘Scaling of Temperature-and Stress-Dependent Viscosity’, Phys. Fluids 7, 266-274.
Spohn, T.: 1991, ‘Mantle Differentiation and Thermal Evolution of Mars, Mercury, and Venus’. Icarus 90(2), 222-236.
Spohn T., Acuña, M. A., Breuer, D., Golombek, M., Greeley, R., Halliday, A., Hauber, E., Jaumann, R. and Sohl, F.: 2001, ‘Geophysical Constraints on the Evolution of Mars’, Space Sci. Rev. 96, 231-262.
Spohn, T., Sohl, F. and Breuer, D.: 1998, ‘Mars’, Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 8, 181-235.
Sprenke, K. F. and Baker, L. L.: 2000, ‘Magnetization, Paleomagnetic Poles, and Polar Wander on Mars’, Icarus 147, 26-34.
Stevenson, D. J., Spohn, T. and Schubert, G.: 1983, ‘Magnetism and Thermal Evolution of the Terrestrial Planets’, Icarus 54, 466-489.
Stevenson, D. J.: 1990, in Newsom, H. E., Jones, J. H. (eds), ‘Fluid dynamics of core formation’. Origin of the Earth Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 231-249.
Stevenson, D. J.: 2001, ‘Mars Core and Magnetism’, Nature 412, 214-219.
Stevenson, D. J.: 2000, ‘Core Superheat’, EOS Trans. AGU 81(48).
Telford, W. M., Geldart, L. P., Sheriff, R. E. and Keys, D. A.: 1976, Applied Geophysics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Verigin, M. I. et al.: 1991, ‘Ions of Planetary Origin in Martian Magnetosphere’, Planetary Space Sci. 39(1–2), 131-137.
Voorhies, C. V., Sabaka, T. J. and Purucker, M.: 2002, ‘On Magnetic Spectra of Earth and Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E6).
Wadhwa, M.: 2000, ‘Redox State of Mars' Upper Mantle and Crust From Eu Anomalies in Shergottite Pyroxenes’, Science 291, 1527-1530.
Wihelms, D. E. and Squyres, S. W.: 1984, ‘The Martian Hemispheric Dichotomy May be Due to a Giant Impact’, Nature 309, 138-140.
Williams, Q. and Jeanloz, R.: 1990, ‘Melting Relations in the Iron Sulfur System at Ultra-high Pressures: Implications For the Thermal State of the Earth’, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 19299-19310.
Wise, D. U., Golombeck, M. P. and McGill, G. E.: 1979, ‘Tectonic Evolution on Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 7934-7939.
Zindler, A. and Hart, S.: 1986, ‘Chemical Geodynamics’, Ann. Rev. Earth Planetary Sci. 14, 493-571.
Yoder, C. F., Konopliv, A. S., Yuan, D. N., Standish, E. M. and Folkner, W. M.: 2003, ‘Fluid Core Size of Mars from Detection of the Fluid Tide’, Science.
Zuber, M. T.: 2001, ‘The Crust and Mantle of Mars’, Nature 412, 220-227.
Zuber, M. T., Solomon, S. C., Phillips, R. J., Smith, D. E., Tyler, G. L., Aharonson, O., Balmino, G., Banerdt, W. B., Head, J.W., Lemoine, F. G., McGovern, P. J., Neumann, G. A., Rowlands, D. D. and Zhong, S.: 2000, ‘Internal Structure and Early Thermal Evolution of Mars from Mars Global Surveyor Topography and Gravity’, Science 287, 1788-1793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Connerney, J., Acuña, M., Ness, N. et al. Mars Crustal Magnetism. Space Science Reviews 111, 1–32 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SPAC.0000032719.40094.1d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SPAC.0000032719.40094.1d