Abstract
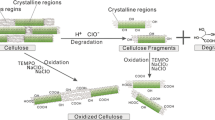
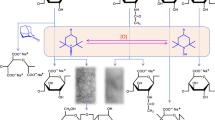
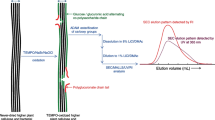
Regenerated cellulose (viscose rayon) was oxidized using NaBr, NaClO and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl radical (TEMPO) or one of ten related nitroxyl radicals in water at pH 10–11. The C6 primary hydroxyl groups in rayon were oxidized to carboxyl groups in most cases, thus giving water-soluble products. However, the oxidation times required for complete dissolution of the products varied substantially, depending on the nitroxyl radical used. Weight average degrees of polymerization (DPw) of the oxidized products were determined by means of high performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) using pullulan standards. All the products had bimodal HPSEC distribution patterns, probably reflected by the solid-state structure of viscose rayon. When 4-acetamido-TEMPO and 4-carboxy-TEMPO were used, cellouronic acids having almost homogeneous chemical structures with higher DPw than for TEMPO were obtained quantitatively within 30 min. The oxidations using 4-amino-TEMPO, 4-carboxy-PROXYL and 4-carbamoyl-PROXYL gave cellouronic acids having the highest DPw, although reaction times of more than 4 h were required, and some side reactions occurred on the products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bragd P.L., Besemer A.C. and van Bekkum H.2000. Bromide-free TEMPO-mediated oxidation of primary alcohol groups in starch and methyl α-D-glucopyranoside. Carbohydr. Res.328: 355–362.
Bragd P.L., Besemer A.C. and van Bekkum H.2001. TEMPO-derivatives as catalysts in the oxidation of primary alcohol groups in carbohydrates. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.170: 35–42.
Bragd P.L., Besemer A.C. and van Bekkum H.2002. Selective oxidation of carbohydrates by 4-AcNH-TEMPO/peracid systems. Carbohydr. Polym.49: 397–406.
de Nooy A.E.J., Besemer A.C. and van Bekkum H.1995. Highly selective nitroxyl radical-mediated oxidation of primary alcohol groups in water-soluble glucans. Carbohydr. Res.269: 89–98.
de Nooy A.E.J., Besemer A.C., van Bekkum H., Van Dijk J.A.P.P. and Smit J.A.M.1996a. TEMPO-mediated oxidation of pullulan and influence of ionic strength and linear charge density on the dimensions of the obtained polyelectrolyte chains. Macromolecules29: 6541–6547.
de Nooy A.E.J., Besemer A.C. and van Bekkum H.1996b. On the use of stable organic nitroxyl radicals for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols. Synthesis1996: 1153–1174.
Ibert M., Marsais F., Merbouh N. and Brückner C.2002. Determination of the side-products formed during the nitroxide-mediated bleach oxidation of glucose to glucaric acid. Carbohydr. Res.337: 1059–1063.
Isogai A. and Kato Y.1998. Preparation of polyglucuronic acid from cellulose by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Cellulose5: 153–164.
Kato Y., Habu N., Yamaguchi J., Kobayashi Y., Shibata I., Isogai A. and Samejima M.2002. Biodegradation of β-1,4-linked polyglucuronic acid (cellouronic acid). Cellulose9: 75–81.
Kato Y., Matsuo R. and Isogai A.2003. Oxidation process of water-soluble starch in TEMPO-mediated system. Carbo-hydr. Polym.51: 69–75.
Merbouh N., Thaburet J.F., Ibert M., Marsais F. and Bobbitt J.M.2001. Facile nitroxide-mediated oxidations of D-glucose to glucaric acid. Carbohydr. Res.336: 75–78.
Potthast A., Röhrling J., Rosenau T. and Kosma P.2002. The “CCOA Method”: A novel method for determination of carbonyl profiles in cellulosic substrates. Proceedings of the ICC2002, Kyoto, Japan, November 6–8, p. 19.
Sharples A.1958. Hydrolysis of cellulose and its relation to structure II. Trans. Faraday Soc.54: 913–917.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibata, I., Isogai, A. Nitroxide-mediated oxidation of cellulose using TEMPO derivatives: HPSEC and NMR analyses of the oxidized products. Cellulose 10, 335–341 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027330409470
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027330409470