Abstract
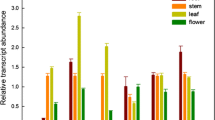
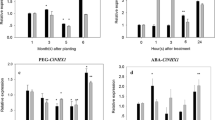
A family of AtNHX1-like genes of Arabidopsis thaliana, coding for vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters, was cloned and functionally characterized by their heterologous expression in yeast mutants lacking an endosomal vacuolar antiporter. The expression of all of the AtNHX members of the family provided a recovery of the salt sensitive yeast mutant, supporting their role in Na+/H+ exchange. RT-PCR, used to determine the relative abundance of the AtNHX transcripts, showed that while AtNHX1 and AtNHX2 transcripts were abundant and widely distributed in all tissues, AtNHX3 and AtNHX4 transcripts were almost exclusively detected in flower and root tissues, respectively. AtNHX5 transcripts were observed at very low levels in all tissues. The potential for the use of these genes for the engineering of salt tolerance in crop plants is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apse M P, Aharon G S, Snedden W A and Blumwald E 1999 Overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport confers salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Science 285, 1256–1258.
Blumwald E and Poole R J 1985 Na+/H+ antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 78, 163–167.
Blumwald E 1987 Tonoplast vesicles for the study of ion transport in plant vacuoles. Physiol. Plant. 69, 731–734.
Blumwald E, Aharon G S and Apse M P 2000 Na+ transport in plant cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1465, 140–151.
Bowers K, Levi B P, Patel F I and Stevens T H 2000 The sodium/proton exchanger Nhx1p is required for endosomal protein trafficking in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 4277–4294.
Clough S J and Bent A F 1998 Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–43.
Darley C P, van Wuytswinkel O CM, van derWoude K, Mager WH and de Boer A H 2000 Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae NHX1 genes encode amiloride sensitive electroneutral Na+/H+ exchangers. Biochem. J. 351, 241–249.
Flowers T, Troke P F and Yeo A R 1977 The mechanisms of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 89–121.
Gaxiola R A, Rao R, Sherman A, Grisafi P, Alper S L and Fink G R 1999 The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1480–1485.
Gaxiola R A, Li J, Undurraga S, Dang L M, Allen G J, Alper S L and Fink G R 2001 Drought-and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+-pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11444–11449.
Glenn E, Brown J J and Blumwald E 1999 Salt-tolerant mechanisms and crop potential of halophytes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 18, 227–255.
Greenway H and Munns R 1980 Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalohytes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 149–190.
Kieber J J, Rothenberg M, Roman G, Feldmann K A and Ecker J R 1993 CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the raf family of protein kinases. Cell 72, 427–41.
Long J A, Moan, E I, Medford J I and Barton M K 1996 A member of the KNOTTED class of homeodomain proteins encoded by the STM gene of Arabidopsis. Nature 379, 66–69.
Maathuis F J M and Amtmann A 1999 K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: The basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann. Bot. 84, 123–133.
Maser P, Thomine S, Schroeder J I, Ward J M, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke I N, Amtmann A, Maathuis F J M, Sanders D, Harper J F, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans M W, Salt D E, Kim S A and Guerinot M L 2001 Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 126, 1646–1667.
Mumberg D, Muller R and Funk M 1994 Regulatable promoters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Comparison of transcriptional activity and their use for heterologous expression. Nucl. Acids Res. 22, 5767–5768.
Nass R, Cunningham K W and Rao R 1997 Intracellular sequestration of sodium by a novel Na+/H+ exchanger in yeast is enhanced by mutations in the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Insights into mechanisms of sodium tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26145–26152.
Nass R and Rao R 1998 Novel localization of a Na+/H+ exchanger in a late endosomal compartment of yeast. Implications for vacuole biogenesis J Biol. Chem. 273, 21054–21060.
Paulsen I T, Sliwinski M K and Saier M H 1998 Microbial genome analyses: global comparisons of transport capabilities based on phylogenies, bioenergetics and substrate specificities. J. Mol. Biol. 277, 573–592.
Quintero F J, BlattMR and Pardo JM 2000 Functional conservation between yeast and plant endosomal Na+/H+ antiporters. FEBS Lett. 471, 224–228.
Shi H, Quintero F J, Pardo J M and Zhu J K 2002 The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14, 465–477.
Shi H and Zhu J K 2002 Regulation of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 expression by salt stress and ABA. Plant Mol. Biol. 50, 543–550.
Spalding E P, Hirsch R E, Lewis D R, Qi Z, Sussman M R and Lewis B D 1999 Potassium uptake supporting plant growth in the absence of AKT1 channel activity-Inhibition by ammonium and stimulation by sodium. J. Gen. Physiol. 113, 909–918.
Venema K, Quintero F J, Pardo J M and Donaire J P 2002 The Arabidopsis Na+/H+ exchanger AtNHX1 catalyzes low affinity Na+ and K+ transport in reconstituted liposomes J. Biol. Chem. 277, 2413–2418.
Yamaguchi T, Fukada-Tanaka S, Inagaki Y, Saito N, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Tanaka Y, Kusumi T and Iida S 2001 Genes encoding the vacuolar Na+/H+ exchanger and flower coloration. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 451–61.
Yokoi S, Quintero F J, Cubero B, Ruiz MT, Bressan R A, Hasegawa P M and Pardo J M 2002 Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J. 30, 529–539.
Zhang H X, Hodson J, Williams J P and Blumwald E 2001 Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica Plants: Characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12832–12836.
Zhang H X and Blumwald E 2001 Transgenic salt tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in the foliage but not in the fruits. Nat. Biotech. 19, 765–768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aharon, G.S., Apse, M.P., Duan, S. et al. Characterization of a family of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant and Soil 253, 245–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024577205697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024577205697