Abstract
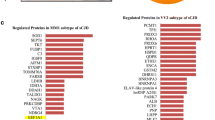
Autism is a severe neurodevelopmental disorder with potential genetic and environmental causes. Cerebellar pathology including Purkinje cell atrophy has been demonstrated previously. We hypothesized that cell migration and apoptotic mechanisms may account for observed Purkinje cell abnormalities. Reelin is an important secretory glycoprotein responsible for normal layering of the brain. Bcl-2 is a regulatory protein responsible for control of programmed cell death in the brain. Autistic and normal control cerebellar corteces matched for age, sex, and post-mortem interval (PMI) were prepared for SDS-gel electrophoresis and Western blotting using specific anti-Reelin and anti-Bcl-2 antibodies. Quantification of Reelin bands showed 43%, 44%, and 44% reductions in autistic cerebellum (mean optical density ± SD per 30 μg protein 4.05 ± 4.0, 1.98 ± 2.0, 13.88 ± 11.9 for 410 kDa, 330 kDa, and 180 kDa bands, respectively; N = 5) compared with controls (mean optical density ± SD per 30 μg protein, 7.1 ± 1.6, 3.5 ± 1.0, 24.7 ± 5.0; N = 8, p < 0.0402 for 180 kDa band). Quantification of Bcl-2 levels showed a 34% to 51% reduction in autistic cerebellum (M ± SD per 75 μg protein 0.29 ± 0.08; N = 5) compared with controls (M ± SD per 75 μg protein 0.59 ± 0.31; N = 8, p < 0.0451). Measurement of β-actin (M ± SD for controls 7.3 ± 2.9; for autistics 6.77 ± 0.66) in the same homogenates did not differ significantly between groups. These results demonstrate for the first time that dysregulation of Reelin and Bcl-2 may be responsible for some of the brain structural and behavioral abnormalities observed in autism.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adams, J. M., & Cory, S. (1998). The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science, 281, 1322–1326.
Bauman, M. L. (1996). Neuroanatomic observations of the brain in pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 26, 199–203.
Bryson, S. E., & Smith, I. M. (1998). Epidemiology of autism: Prevalence, associated characteristics, and implications for research and service delivery. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disorders Research Review, 4, 9–103.
Chan, W. Y., & Yew, I. Y. (1998). Apoptosis and Bcl-2 oncoprotein expression in the human fetal central nervous system. Anatomical Record, 252, 165–175.
Chen, R. W., & Chuang, D. M. (1999). Long-term lithium treatment suppresses p53 and Bax expression but increases Bcl-2 expression: A prominent role in neuroprotection against excitotoxicity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 6039–6042.
DeBergeyck, V., Nakajima, K., Lambert de Roubroit, C., Naerhuyzen, B., Goffinet, A. M., & Miayata, T. et al. (1997). A truncated Reelin protein is produced but not secreted in the ‘Orleans’ reeler mutation (Rein[rl-Orl]). Molecular Brain Research, 50, 85–90.
Falconer, D. S. (1951). Two new mutants, trembler and “Reeler”, with neurological actions in the house mouse. Journal of Genetics, 50, 182–201.
Fatemi, S. H., Emamian, E. S., Kist, D., Sidwell, R. W., Nakajima, K., Akhter, P., et al. (1999). Defective corticogenesis and reduction in Reelin immunoreactivity in the cortex and hippocampus of prenatally infected neonatal mice. Molecular. Psychiatry, 4, 145–154.
Fatemi, S. H., Earle, J., & McMenomy, T. (2000). Reduction in Reelin immunoreactivity in hippocampus of subjects with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depression. Molecular Psychiatry, 5, 654–663.
Fatemi, S. H. (2001). Reelin mutations in mouse and man: from reeler mouse to schizophrenia, mood disorders, autism and lissencephaly. Molecular Psychiatry, 6, 129–133.
Fatemi, S. H., Halt, A. R., Stary, J. M., Realmuto, G. M., & Jalali-Mousavi, M. (2001). Reduction in anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2 in autistic cerebellum. NeuroReport, 12, 929–933.
Fatemi, S. H., Halt, A. R., Earle, J., Kist, D. A., Realmuto, G., Thuras, P. D., & Merz, A. (2000). Reduced Purkinje cell size in autistic cerebellum. Biological Psychiatry, 47, 128S.
Guidotti, A., Auta, J., Davis, J., Dwivedi, Y., Grayson, D., Impagnatiello, F., et al. (2000). Decrease in Reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: A post-mortem brain study. Archives in General Psychiatry, 57, 1061–1069
Hong, S. E., Shugart, Y. Y., Huang, D. T., Shahwan, S. A., Grant, P. E., Hourihane, J. O. B., et al. (2000). Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations. Nature Genetics, 20, 93–96.
Impagnatiello, E., Guidotti, A. R., Pesold, O., Dwivedi, Y., Caruncho, H., Pisu, M. G., et al. (1998). A decrease of Reelin expression as a putative vulnerability factor in schizophrenia. Proceedings of National Academic Science USA, 95, 15718–15723.
Ingram, J. L., Stodgell, C. J., Hyman, S. L., Figlewicz, D. A., Weitkamp, L. R., & Rodier, P. M. (2000). Discovery of allelic variants of HOXA1 and HOXB1: Genetic susceptibility to autism spectrum disorders. Teratology, 62, 393–405.
Jarskog, L. F., & Gilmore, J. H. (2000). Developmental expression of Bcl-2 protein in human cortex. Brain Research Developmental Brain Research, 119(2), 225–230.
Jarskog, L. F., Gilmore, J. H., Selinger, E. S., & Lieberman, J. A. (2000). Cortical Bcl-2 protein expression and apoptotic regulation in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 48, 641–650.
Keller, E., Persico, A. M., Zelante, L., Gasparini, P., D'Agruma, N., Maiorano, N., et al. (2000). Reelin gene alleles and haplotypes are associated with autistic disorder. Society of Neuroscience, 26, 77 (31.11).
Lacor, P., Grayson, D. R., Auta, J., Sugaya, I., Costa, E., & Guidotti, A. (2000). Reelin secretion from glutamatergic neurons in culture is independent from neurotransmitter regulation. Proceedings of National Academic Science USA, 97, 3556–3561.
Margolis, R. L., Chuang, D. M., & Post, R. M. (1994). Programmed cell death: Implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 35, 946–956.
Marshall, K. A., Daniel, S. E., Cairns, N., Jenner, P., & Halliwell, B. (1997). Upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 may be an early event in neurodegenerate studies on Parkinson's and incidental Lewy body disease. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 240, 84–87.
Ogawa, M., Miyata, T., Nakajima, K., Yagyu, K., Selke, M., Ikenake, K., et al. (1995). The reeler gene-associated antigen on Cajal-Retzius neurons is a crucial molecule for laminar organization of cortical neurons. Neuron, 14, 800–912.
Persico, A. M., Agruma, L. D., Maiorano, N., Totaro, A., Militerni, R., Bravaccio, C., et al. (2001) Reelin gene alleles and haplotypes as a factor predisposing to autistic disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 6, 150–159.
Ritvo, E. R., Freeman, B. J., Schweibel, A. B., Duong, T., Robinson, H., Guthrie, D., & Ritvo, A. (1986). Lower Purkinje cell counts in the cerebella of four autistic subjects: Initial findings of the UCLA-NSAC autopsy research report. American Journal Psychiatry, 143, 862–866.
Smallheiser, N. R., Costa, E., Guidotti, A., Impagnatiello, F., Auta, J., Lacor, P., et al. (2000). Expression of Reelin in adult mammalian blood, liver, pituitary pars intermedia, and adrenal chromoffin cells. Proceedings of National Academic Science USA, 97, 1281–1285.
Tueting, P., Costa, E., Dwivedi, Y., Guidotti, A., et al. (1999). The phenotypic characteristics of heterozygous reeler mouse. NeuroReport, 10, 1327–1334.
Vyas, S., Javoy-Agid, F., Herrero, M. T., Strada, O., Boissiere, F., Hibner, U., & Agid, Y. (1997). Expression of Bcl-2 in adult human brain regions with special reference to neurodegenerate disorders. Journal of Neurochemistry, 69, 223–231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemi, S.H., Stary, J.M., Halt, A.R. et al. Dysregulation of Reelin and Bcl-2 Proteins in Autistic Cerebellum. J Autism Dev Disord 31, 529–535 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013234708757
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013234708757