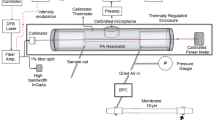
Abstract
Ambient gas phase nitrous acid (HONO) has been measured by Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy with sub-ppbv detection limits. An R-branch line in the 1263.4 cm−1 ν3 band was found tobe free of interference and suitable for ambient HONO measurements. Nitrous acid was measured during the night and early morning at an urban site in Toronto, Canada, during the summer of 1998. Average mixing ratios, integrated over 30 minutes, ranged from below the minimum detection limit of 300 pptv to 1.9 ppbv, with the highest concentrations observed during the early morning hours. During the night of 19 June 1998, the concentration of HONO increased by as much as 0.5 ppbv/hr. The usual decrease in HONO after sunrise was delayed by a few hours, possibly due to a combination of an increase in the production rate of HONO with rush hour, and attenuation of the early morning light by high NO2 within the aerosol fog/haze.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto, H., Takagi, H., and Sakamaki, F., 1987: Photo enhancement of the nitrous acid formation in the surface reaction of nitrogen dioxide and water vapour: Extra radical source in smog chamber experiments, Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 19, 539-551.
Allegrini, I., Desantis, F., Dipalo, V., Febo, A., Liberti, A., Perrino, C., and Possanzini, M., 1987: Annular denuder method for sampling reactive gases and aerosols in the atmosphere, Sci. Total Environ. 67, 1-16.
Ammann, M., Kalberer, M., Jost, D. T., Tobler, L., Rössler, E., Piguet, D., Gäggeler, H. W., and Baltensperger, U., 1998: Heterogeneous production of nitrous acid on soot in polluted air masses, Nature 395, 157-160.
Andrés-Hernández, M. D., Notholt, J., Hjorth, J., and Schrems, O., 1996: A DOAS study on the origin of nitrous acid at urban and non-urban sites, Atmos. Environ. 30, 175-180.
Appel, B. R., Winer, A. M., Tokiwa, Y., and Biermann, H. W., 1990: Comparison of atmospheric nitrous acid measurements by annular denuder and differential optical absorption systems, Atmos. Environ. 24A, 611-616.
Barney, W. S., Wingen, L. M., Lakin, M. J., Brauers, T., Stutz, J., and Finlayson-Pitts, B. J., 2000: Infrared absorption cross-section measurements for nitrous acid (HONO) at room temperature, J. Phys. Chem. A. 104, 1692.
Becker, K. H., Kleffmann, J., Kurtenbach, R., Weisen, P., Febo, A., Gherardi, M., and Sparapani, R., 1995: Line strength measurements of trans-HONO near 1255 cm-1 by tunable diode laser spectrometry, Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 2485-2488.
Berner, A., Sidla, S., Galambos, Z., Kruisz, C., Hitzenberger, R., Tenbrink, H. M., and Kos, G. P. A., 1996: Modal character of atmospheric black carbon size distributions, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 19559-19565.
Brassington, D. J., 1994: Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy for the measurement of atmospheric species, Adv. Spectrosc. 24, 1.
Chan, W. H., Nordstrom, R. J., Calvert, J. G., and Shaw, J. H., 1976: Kinetic study of HONO formation and decay reactions in gaseous mixtures of HONO, NO, NO2, H2O and N2, Environ. Sci. Technol. 10, 674-682.
Collett, J. L. Jr., Bator, A., Rao, X., and Demoz, B., 1994: Acidity variations across the cloud drop size spectrum, and their influence on rates of atmospheric sulfate production, Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 2393-2396.
Febo, A., Perrino, C., and Allegrini, I., 1996: Measurements of nitrous acid in Milan, Italy, by DOAS and diffusion denuders, Atmos. Environ. 30, 3599-3609.
Fried, A., McKeen, S., Sewell, S., Harder, J., Henry, B., Goldan, P., Kuster, W., Williams, E., Baumann, K., Shetter, R., and Cantrell, C., 1997: Photochemistry of formaldehyde during the 1993 Tropospheric OH Photochemistry Experiment, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 6283-6296.
Harris, G. W., Carter, W. P. L., Winer, A. M., Pitts, J. N. Jr., Platt, U., and Perner, D., 1982: Observations of nitrous acid in the Los Angeles atmosphere and the implications for the ozone precursor relationships, Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 414-419.
Harris, G. W., Mackay, G. I., Iguchi, I., Mayne, L. K., and Schiff, H. I., 1989: Measurements of formaldehyde in the troposphere by tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy, J. Atmos. Chem. 3, 119-137.
Harris, G. W., Klemp, D., Zenker, T., Burrows, J. P., and Mathieu, B., 1992: Tunable diode laser measurements of trace gases during the 1988 Polarstern cruise and intercomparisons with other methods, J. Atmos. Chem. 15, 315-326.
Harrison, R. M. and Kitto, A. N., 1994: Evidence for a surface source of atmospheric nitrous acid, Atmos. Environ. 28, 1089-1094.
Henderson, G. S., Evans, W. F. J., McConnell, J. C., and Templeton, E. M. J., 1987: A numerical model for one dimensional simulation of stratospheric chemistry, Atmos. Oceans 25, 427-459.
Jenkin, M. E., Cox, R. A., and Williams, D. J., 1988: Laboratory studies of the kinetics of formation of nitrous acid from the thermal reaction of nitrogen dioxide and water vapour, Atmos. Environ. 22, 487-498.
Kagann, R. H. and Maki, A. G. J., 1983: Infrared absorption intensities of nitrous acid (HONO) fundamental bands, Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 30, 37.
Kalberer, M., Annann, M., Arens, F., Gaggeler, H. W., and Baltensperger, U., 1999: Heterogeneous formation of nitrous acid (HONO) on soot aerosol particles, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 13825-13832.
Kitto, A.-M. N. and Harrison, R. M., 1992: Nitrous and nitric acid measurements at sites in south-east England, Atmos. Environ. 26A, 235-241.
Koutrakis, P., Brauer, M., Slater, J. L., Stone, C. L., Stevens, R. K. Wolfson, J. M., and Spengler, J. D., 1988: Evaluation of an annular denuder filter pack system to collect acidic aerosols and gases, Environ. Sci. Technol. 22, 1463-1468.
Lammel, G. and Cape, J. N., 1996: A study on the origin of nitrous acid at urban and non-urban sites, Chem. Soc. Rev. 25, 361.
Mackay, G. I., Karecki, D. R., and Schiff, H. I., 1996: Tunable diode laser absorption measurements of H2O2 and HCHO during the Mauna Loa Observatory Photochemistry Experiment, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 14,721-14,728.
Maki, A. G., 1988: High Resolution measurements of the ν 2 band of HNO3 and the ν 3 band of trans-HONO, J. Mol. Spectrosc. 127, 104-111.
National Air Surveillance (NAPS) Sites 1998 data, John Shelton, Environment Canada, Analysis and Air Quality Division, private communication.
Perner, D. and Platt, U., 1979: Detection of nitrous acid in the atmosphere by differential optical absorption, Geophys. Res. Lett. 6, 917-920.
Pitts, J., Sanhueza, E., Atkinson, R., Carter, W. P. L., Winer, A. M., Harris, G. W., and Plum, M. N., 1984: An investigation of the dark formation of nitrous acid in environmental chambers, Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 16, 919-939.
Platt, U., 1996: The origin of nitrous and nitric acid in the atmosphere, in W. Jaeschke (ed.), Chemistry of Multi Phase Atmosphere Systems, Springer, Berlin, NATO-ASI series.
Platt, U., Perner, D., Harris, G., Winer, A. M., and Pitts, J. N. Jr., 1980: Observations of nitrous acid in urban atmospheres by differential optical absorption, Nature 285, 312-314.
Rothman, L. S., Rinsland, C. P., Goldman, A., Massie, S. T., Edwards, D. P., Flaud, J.-M., Perrin, A., Camy-Peyret, C., Dana, V., Mandin, J.-Y.n, Schroeder, J., McCann, A., Gamache, R. R., Wattson, R. B., Yoshino, K., Chance, K. V., Jucks, K. W., Brown, L. R., Nemtchinov, V., and Varanasi, P., 1998: The HITRAN molecular spectroscopic database and HAWKS (HITRAN Atmospheric Workstation): 1996 Edition, J. Quant. Spectro. Rad. Trans. 60, 665.
Saliba, N. A., Mochida, M., and Finlayson-Pitts, B. J., 2000: Laboratory studies of sources of NONO in polluted urban atmospheres, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3229-3232.
Sakamaki, F., Hatakeyama, S., and Akimoto, H., 1983: Formation of nitrous acid and nitric oxide in the heterogeneous dark reaction of nitrogen dioxide and water vapour in a smog chamber, Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 15, 1013-1029.
Schiff, H. I., Hastie, D. R., Mackay, G. I., Iguchi, T., and Ridley, B. A., 1983: Tunable diode laser systems for measuring trace gases in tropospheric air, Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 352-364.
Schiff, H. I., 1992: Ground based measurements of atmospheric gases by spectroscopic methods, in Berichte den Bunsen Gesellschaft fur Physikalishe Cheme-an International J. Phys. Chem. 96, 296-306.
Seinfeld, J. H. and Pandis, S. N., 1998: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley-Interscience, Toronto.
Sickles, J. E. and Hodson, L. L., 1989: Fate of nitrous acid on selected collection surfaces, Atmos. Environ. 23, 2321-2324.
Slemr, F., Harris, G. W., Hastie, D. R., Mackay, G. I., and Schiff, H. I., 1986: Measurements of gas phase hydrogen peroxide in air by tunable diode laser spectroscopy, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 5371-5378.
Sjödin, A. and Ferm, M., 1985: Measurement of nitrous acid in urban air, Atmos. Environ. 19, 985-992.
Sjödin, A., 1988: Studies of the diurnal variation of nitrous acid in urban air, Environ. Sci. Technol. 22, 1086-1089.
Stockwell, W. R. and Calvert, J. G., 1978: The near ultraviolet absorption spectrum of gaseous HONO and N2O3, J. Photochem., 193.
Vecera, D. and Dasgupta, P. K., 1991: Measurement of ambient nitrous acid and a reliable calibration source for gaseous nitrous acid, Environ. Sci. Technol. 25, 255-260.
Wingen, L. M., Barney, W. S., Lakin, M. J., Brauers, T., and Finlayson-Pitts, B. J., 2000: A unique method for Laboratory quantification of gaseous nitrous acid using the reaction HONO + HCl → ClNO + H2O, J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schiller, C.L., Locquiao, S., Johnson, T.J. et al. Atmospheric Measurements of HONO by Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry 40, 275–293 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012264601306
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012264601306