Abstract
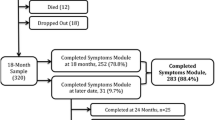
This study examined the reliability and construct validity of a modified version of the Colorado Symptom Index (MCSI), a brief, self-report measure of psychological symptomatology, in a study of interventions to prevent homelessness. Eight projects in a national, cooperative study collected new data at baseline, 6, and 12 months using a set of common measures as well as site-specific instruments. The pooled sample consisted of 1,381 persons in treatment for mental illness or substance abuse (or both), of which 84% had a history of homelessness. The analyses employed classical and Rasch methods to examine the MCSI's content validity, internal consistency and item quality, test/retest reliability, dimensionality, appropriateness for the sample, construct validity, and responsiveness to change. This 14-item scale was found to be a reliable and valid measure of psychological symptoms in this sample. Its content was consistent with other symptom measures, its high internal consistency and test-retest coefficients supported its reliability, its relationships to other measures indicated that it had good construct validity, and it was responsive to change. We conclude that the MCSI performed similarly to longer, more widely used measures of psychological symptomatology and could be useful in other studies targeting homeless adults with severe mental illness, substance use disorders, or both.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bassuk, E. L., Rubin, L., & Lauriat, M. A. (1984). Is homelessness a mental health problem? American Journal of Psychiatry, 141, 1546–1550.
Campbell, D. T., & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56(2), 81–105.
Cattell, R. B. (1966). The meaning and strategic use of factor analysis. In R. B. Cattell (ed.), Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology. Chicago: Rand McNally.
Ciarlo, J. A., Edwards, D. W., Kiresuk, T. J., Newman, F. L., & Brown, T. R. (1981). The assessment of client /patient outcome techniques for use in mental health.Washington, DC: National Institute of Mental health. (Contract No. 278-80-0005)
Ciarlo, J. A., & Riehman, J. (1977). The Denver Community Mental Health Questionnaire: Development of a multidimensional program evaluation instrument. In R. Coursey, G. Spector, S. Morell, & D. Hunt (Eds.), Program evaluation for mental health: Methods, strategies and participants. New York: Grune and Stratton.
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral science. New York: Academic Press.
Conrad, K. J., Matters, M. D., Hanrahan, P., & Luchins, D. J. (Eds.). (1999). Homelessness prevention in treatment of substance abuse and mental illness: Logic models and implementation of eight American projects. New York: Haworth Press. (Co-published as Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly, 17(1/2))
Conrad, K. J., Quasius, D. L., Matters, M. D., Hanrahan, P., & Luchins, D. J. (in press). A money management outcome measure. Chicago, IL: University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health.
Derogatis, L.R. (1993). Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) administration, scoring, and procedures manual (3rd ed.). Minneapolis: National Computer Systems.
Derogatis, L.R. (1994). SCL-90-R administration, scoring, and procedures manual. Minneapolis: National Computer Systems.
Green, R. S., & Gracely, E. J. (1987). Selecting a rating scale for evaluation services to the chronically mentally ill. Community Mental Health Journal, 23(2), 91–102.
Hedges, L. V., & Olkin, I. (1985). Statistical methods for metaanalysis. Orlando, FL: Academic Press.
Hedlund, J. L., & Vieweg, B.W. (1980). The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS): A comprehensive review. Journal of Operational Psychiatry, 11(1), 48–65.
Jennrich, R. I., & Sampson, P. F. (1966). Rotation for simple loadings. Psychometrika, 31, 313–323.
Kaiser, H. F. (1958). The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 23, 187–200.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational Psychological Measurement, 20, 141–151.
Koegel, P., Burnam, A., & Farr, R. K. (1988). The prevalence of specific psychiatric disorders among homeless individuals in the inner city of Los Angeles. Archives of General Psychiatry, 45, 1085–1092.
Lee, B., Shern, D., & Coen, A. (1999). Reliability, stability, and sensitivity of the Colorado Symptom Index. Unpublished manuscript.
Lehman, A. F. (1991). Quality of life interview core version. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University.
Linacre, J. M., & Wright, B.D. (1998).Auser's guide to WINSTEPS, BIGSTEPS, and MINISTEPS. Chicago: Mesa Press.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (1996). Toolkit for practical metaanalysis. Boston: HSRI.
Lyons, J. S., Coleta, J., Devens, M., & Finkel, S. I. (1995). The validity of the Severity of Psychiatric Illness in a sample of psychogeriatric patients. International Journal of Psychogeriatrics, 7, 407–412.
Lyons, J. S., O'Mahoney, M. T., Doheny, K. M., Dworkin, L. N., & Miller, S. I. (1995). The prediction of short stay psychiatric inpatients. Administration and Policy in Mental Health, 23, 17–25.
Lyons, J. S., O'Mahoney, M. T., Miller, S. I., Neme, J., Kabat, J., & Miller, F. (1997). Predicting readmission to the psychiatric hospital in a managed care environment: Implications for quality indicators. American Journal of Psychiatry, 154, 337–340.
Lyons, J. S., Stutesman, J., Neme, J., Vessey, J. T., O'Mahoney, M. T., & Camper, J. (1997). Predicting psychiatric emergency admissions and hospital outcomes. Medical Care, 35(8), 792–800.
McLellan, A. T., Alterman, A. I., Woody, G. E., & Metzer, D. (1992). Treatment services review. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania.
Mercer-McFadden, C., & Drake, R.E. (1992).AReview of outcome measures for assessing homeless populations with severe mental illness and co-occurring substance abuse. Dartmouth, NH: New Hampshire-Dartmouth Psychiatric Research Center. (NIMH Contract Order No. 91MF45295301D)
New Hampshire-Dartmouth Psychiatric Research Center. (1995). Residential follow-back calendar, version - 6/1/95. Lebanon, NH: Dartmouth Medical School.
Overall, J. E., & Gorham, D. R. (1962).The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports, 10, 799–812.
Policy Research Associates. (2000). Draft final report on the crosssite evaluation of the collaborative program to prevent homelessness. Delmar, NY. Author. (DRAFT)
Reckase, M. (1979). Unifactor latent trait models applied to multifactor tests: Results and implications. Journal of Educational Statistics, 4, 207–230.
Rich, A., & Clark, C. (1997).Treatment services needed and received. Tampa, (FL): Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Center.
Rickards, L. D., Leginski, W., Randolph, F. L., Oakley, D., Herrell, J. M., & Gallagher, C. (1999). Cooperative agreements for CMHS/CSATcollaborative program to prevent homelessness: An overview. In K. J. Conrad, M. D. Matters, P. Hanrahan, & D. J. Luchins (Eds.), Homelessness prevention in treatment of substance abuse and mental illness: Logic models and implementation of eight American projects (pp. 1–15). New York: Haworth Press. (Co-published as Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly, 17, (1/2))
Rosenberg, M. (1989). Society and the adolescent self-image. Middleton, CT: Wesleyan University Press.
Shern, D. L., Wilson, N. Z., & Coen, A. S. (1994). Client outcomes II: Longitudinal client data from the Colorado treatment outcome study. Milbank Quarterly, 72(1), 123–148.
Shorkey, C. T., & Whiteman, V. L. (1978). Correlations between standard English and dialectical Spanish versions of five personality tests. Psychological Reports, 4(3), 910.
Silber, E., & Tippett, J. (1965). Self-esteem: Clinical assessment and measurement validation. Psychological Reports, 16, 1017–1071.
Toro, P. A., & Wall, D.D. (1991). Research on homeless persons: Diagnostic comparisons and practice implications. Professional Psychology: Research and practice, 22(6), 479–488.
Wilcoxon, F. (1945). Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biometrics, 1, 80–83.
Wright, B. D., & Masters, G. N. (1982). Rating scale analysis: Rasch measurement. Chicago: Mesa Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conrad, K.J., Yagelka, J.R., Matters, M.D. et al. Reliability and Validity of a Modified Colorado Symptom Index in a National Homeless Sample. Ment Health Serv Res 3, 141–153 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011571531303
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011571531303