Abstract
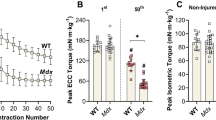
The primary purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between myosin heavy chain (MHC) and actin contents and maximum isometric tetanic force (Po) in mouse extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles following eccentric contraction-induced injury. Po and protein contents were measured in injured (n=80) and contralateral control (n = 80) EDL muscles at the following time points after in vivo injury: sham, 0, 0.25, 1, 3, 5, 14, and 28 days. Po was reduced by 37 ± 2.3% to 49 ± 3.8% (p ≤ 0.05), while MHC and actin contents were unaltered from 0 to 3 days after injury. Whereas Po partially recovered between 3 and 5 days (from −49 ± 3.8% to −35 ± 3.6%), MHC and actin contents in the injured muscles declined by 19 ± 4.9% and 20 ± 5.3%, respectively, by 5 days compared with control muscles. Decrements in Po were similar to the reductions in MHC and actin contents at 14 (∼24%) and 28 (∼11%) days. Evaluation of myofibrillar and soluble protein fractions indicated significant reductions in the content of major proteins at 5 and 14 days. Immunoblots of heat shock protein 72 revealed elevations starting at 0.25 days, peaking during 1–3 days, and declining after 5days. These findings indicate that decreased contractile protein content is not related to the initial decrease in Po. However, decreased MHC and actin contents could account for 58% of the Po reduction at 5 days, and for nearly all the decrements in Po from 14 to 28 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anathan, J., Goldberg, A. L. & Voellmy, R. (1986) Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science 232, 522–4.
Armstrong, R. B., Ogilvie, R. W. & Schwane, J. A. (1983) Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 54, 80–93.
Balnave, C. D. & Allen, D. G. (1995) Intracellular calcium and force in single mouse muscle fibres following repeated contractions with stretch. J. Physiol. Lond. 488, 25–36.
Beckman, R. P., Mizzen, L. A. & Welch, W. J. (1990) Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science 248, 850–54.
Belcastro, A. N. (1993) Skeletal muscle calcium-activated neutral protease (calpain) with exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 74, 1381–6.
Bornman, L., Polla, B. S., Lotz, B. P. & Gericke, G. S. (1995) Expression of heat-shock/stress proteins in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle and Nerve 18, 23–31.
Brooks, S. V. & Faulkner, J. A. (1990) Isometric, shortening, and lengthening contractions of muscle fiber segments from adult and old mice. Am. J. Physiol. 267, C507–13.
Close, R. I. (1972) Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev. 52, 129–97.
Doherty, F. J. & Mayer, R. J. (1992) The mechanismspathways of intracellular proteolysis. In Intracellular Protein Degradation (edited by Rickwood, D. & Male, D.) pp. 15–32. New York: Oxford University Press.
Evans, W. J., Meredith, C. N., Cannon, J. G., Dinarello, C. A., Frontera, W. R., Hughes, W. A., Jones, B. H. & Knuttgen, H. G. (1986) Metabolic changes following eccentric exercise in trained and untrained men. J. Appl. Physiol. 61, 1864–8.
Everett, A. W., Prior, G., Clark, W. A. & Zak, R. (1983) Quantitation of myosin in muscle. Anal. Biochem. 30, 102–7.
Fielding, R. A., Meredith, C. N., O'Reilly, K. P., Frontera, W. R., Cannon, J. G. & Evans, W. J. (1991) Enhanced protein breakdown after eccentric exercise in young and older men. J. Appl. Physiol. 71, 674–9.
FridÉn, J., Seger, J., SjÖstrÖm, M. & Ekblom, B. (1983) Adaptive response in human skeletal muscle subjected to prolonged eccentric training. Int. J. Sports Med. 4, 177–83.
Goldberg, A. & Rock, K. (1992) Proteolysis, proteosomes and antigen presentation. Nature 357, 375–9.
Goldberg, A. & St John, A. (1976) Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 45, 747–803.
Ingalls, C. P., Warren, G. L., Lowe, D. A., Boorstein, D. B. & Armstrong, R. B. (1996) Differential effects of anesthetics on in vivo skeletal muscle contractile function in the mouse. J. Appl. Physiol. 80, 332–40.
Kantengwa, S., Capponi, A. M., Bonventre, J. V. & Polla, B. S. (1990) Calcium and the heat shock response in the human monocytic line U-937. Am. J. Physiol. 259, C77–83.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–85.
Lowe, D. A., Warren, G. L., Hayes, D. A., Farmer, M. A. & Armstrong, R. B. (1994) Eccentric contractioninduced injury of mouse soleus muscle: effect of varying [Ca2+]o. J. Appl. Physiol. 76, 1445–53.
Lowe, D. A., Warren, G. L., Ingalls, C. P., Boorstein, D. B. & Armstrong, R. B. (1995) Muscle function and protein metabolism after initiation of eccentric contraction-induced injury. J. Appl. Physiol. 79, 1260–70.
Mair, J., Koller, A., Artner-Dworzak, E., Haid, C., Wicke, K., Judmaier, W. & Puschendoef, B. (1992) Effects of exercise on plasma heavy chain fragments and MRI of skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 72, 656–63.
Mair, J., Mayr, M., Muller, E., Koller, A., Haid, C., Artner-Dworzak, E., Calzolari, C., Larue, C. M. & Puschendoef, B. (1995) Rapid adaptation to eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Int. J. Sports Med. 16, 352–6.
Mccully, K. K. & Faulkner, J. A. (1985) Injury to skeletal muscle fibers of mice following lengthening contractions. J. Appl. Physiol. 59, 119–26.
Mccully, K. K. & Faulkner, J. A. (1986) Characteristics of lengthening contractions associated with injury to skeletal muscle fibers. J. Appl. Physiol. 61, 293–9.
Morimoto, K. & Harrington, W. F. (1974) Substructure of the thick filament of vertebrate striated muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 83, 83–97.
Newham, D. J., Mcphail, G., Mills, K. R. & Edwards, R. H. T. (1983) Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions of human muscle. J. Neurol. Sci. 61, 109–22.
Ogilvie, R. W., Armstrong, R. B., Baird, K. E. & Bottoms, C. L. (1988) Lesions in the rat soleus muscle following eccentrically biased exercise. Am. J. Anat. 182, 335–46.
Raboy, B., Sharon, G., Parag, H. A., Shocat, Y. & Kulka, R. G. (1991) Effect of stress on protein degradation: role of the ubiquitin system. Acta Biol. Hung. 42, 3–20.
Rechsteiner, M. (1987) Ubiquitin-mediated pathways for intracellular proteolysis. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 3, 1–30.
Rock, K. L., Gramm, C., Rothstein, L., Clark, K., Stein, R., Dick, L., Hwang, H. & Goldberg, A. L. (1994) Inhibitors of the proteosome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC Class I molecules. Cell 78, 761–71.
Solaro, R. J., Pang, D. C. & Briggs, F. N. (1971) The purification of cardiac myofibrils with Triton X-100. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 245, 259–62.
Taylor, J. A. & Kandarian, S. C. (1994) Advantage of normalizing force production to myofibrillar protein in skeletal muscle cross-sectional area. J. Appl. Physiol. 76, 974–8.
Thompson, H. S. & Scordilis, S. P. (1994) Ubiquitin changes in human biceps muscle following exerciseinduced damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 204, 1193–8.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. & Gordon, J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4350–54.
Tsika, R. W., Herrick, R. E. & Baldwin, K. M. (1987) Time course adaptations in rat skeletal muscle isomyosins during compensatory growth and regression. J. Appl. Physiol. 63, 2111–21.
van Remmen, H., Ward, W. F., Sabia, R. V. & Richardson, A. (1995) Gene expression and protein degradation. In Handbook of Physiology-Aging (edited by MASORO, E. J.) pp. 211–34. New York: Oxford University Press.
Warren, G. L., Hayes, D. A., Lowe, D. A., Williams, J. H. & Armstrong, R. B. (1994) Eccentric contractioninduced injury in normal and hindlimb-suspended mouse soleus and EDL muscles. J. Appl. Physiol. 77, 1421–30.
Warren, G. L., Lowe, D. A., Hayes, D.A., Farmer, M. A. & Armstrong, R. B. (1995) Redistribution of cell membrane probes following contraction-induced injury of mouse soleus muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 282, 311–20.
Warren, G. L., Lowe, D. A., Hayes, D. A., Karwoski, C. J., Prior, B. M. & Armstrong, R. B. (1993) Excitation failure in eccentric contraction-induced injury of mouse soleus muscle. J. Physiol. Lond. 468, 487–99.
Warren, G. L., Lowe, D. A., Inman, C. L., Orr, O. M., Hogan, H. A., Bloomfield, S. A., & Armstrong, R. B. (1996) Estradiol effects on anterior crural muscles: tibial bone relationship and susceptibility to injury. J. Appl. Physiol. 80, 1660–65.
Yates, L. D. & Greaser, M. L. (1983) Quantitative determination of myosin and actin in rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 168, 123–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingalls, C.P., Warren, G.L. & Armstrong, R.B. Dissociation of force production from MHC and actin contents in muscles injured by eccentric contractions. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19, 215–224 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005368831198
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005368831198