Abstract
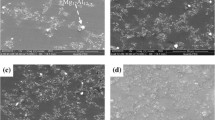
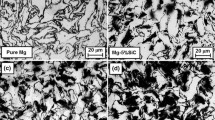
In the present study, elemental and silicon carbide reinforced magnesium materials were synthesized using an innovative disintegrated melt deposition method followed by hot extrusion. Microstructural characterization studies revealed the presence of minimal porosity and completely recrystallized matrix in all the unreinforced and reinforced samples. In the case of reinforced magnesium samples, a fairly uniform distribution of SiC particulates and good SiC-Mg interfacial integrity was realized. The results of microhardness measurements revealed an increase in the brittleness of the SiC-Mg interfacial region with an increase in the amount of SiC particulates. Results of physical and mechanical properties characterization revealed that the increasing presence of SiC particulates led to an increase in hardness and elastic modulus, does not affect 0.2% yield strength and reduces the ultimate tensile strength, ductility, work for fracture and coefficient of thermal expansion. An attempt is made to correlate the results of physical and mechanical properties testing with that of the microstructural characterization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Lloyd, Int. Mat. Reviews 39(1) (1994) 1.
D. M. Lee, B. K. Suh, B. G. Kim, J. S. Lee and C. H. Lee, Mat. Sci. Tech. 13 (1997) 590.
A. Luo, Metall. Mater. Trans. A26 (1995) 2445.
J. Lo and G. Carpenter, in “Conf. Proceedings of ICCE/5,” edited by D. Hui (Las Vegas, July 5-11, 1998) p. 526.
V. Laurent, P. Jarry, G. Regazzoni and D. Apelian, J. Mat. Sci. 27 (1992) 4447.
M. Gupta, M. O. Lai and C. Y. Soo, Mat. Sci. and Eng. A210 (1996) 114.
Powder Diffraction File, International Center for Diffraction Data, 1601 Park Lane, Swarthmore, PA, USA, 1991.
V. C. Nardone and K. W. Prewo, Scr. Metall. 20 (1986) 43.
W. S. Miller and F. J. Humphreys, Scr. Metall. et Mater. 25 (1991) 2623.
P. G. Shewmon, “Transformation in Metals” (McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, USA, 1969) p. 69.
R. E. Reed-Hill, “Physical Metallurgy Principles,” 2nd ed. (D. Van Nostrand Company, New York, USA, 1964) pp. 267, 753.
M. Gupta, F. Mohamed, E. Lavernia and T. S. Srivatsan, J. Mat. Sci. 28 (1993) 2245.
M. Gupta, F. A. Mohamed and E. J. Lavernia, Metall. Trans. 23A (1992) 845.
M. Gupta, R. Sikand and A. K. Gupta, Scr Met et Mater. 30(10) (1994) 1343.
Z. G. Wang, S. Li and L. Sun, Key Eng. Mater. 104-107 (1995) 729.
M. K. Surappa, J. Mat. Sci. Lett. 12 (1993) 1272.
M. Gupta, I. A. Ibrahim, F. Mohamed and E. Lavernia, J. Mat. Sci. 26 (1991) 6673.
B. Inem and G. Pollard, ibid. 28 (1993) 4427.
A. L. Geiger and M. Jackson, Adv. Mat. Proc. 136(7) (1989) 23.
C. J. Smithells, “Metals Reference Book,” 5th ed. (Butterworths & Co. Ltd, London, 1976).
J. F. Shackelford, W. Alexander and J. S. Park, “CRC Materials Science and Engineering Handbook” (CRC Press Inc., 1994) p. 304.
M. Gupta and S. Ling, Mater. and Design 18(3) (1997) 139.
N. Christman and S. Suresh, Acta. Metall. 36 (1988) 1691.
G. E. Fougere, L. Riester, M. Ferber, J. R. Weertman and R. W. Siegel, Mater. Sci. and Eng. A, 204 (1995) 1.
A. R. Boccaccini, G. Ondracek, P. Mazilu and D. Windelberg, J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 4 (1993) 119.
M. Gupta and M. K. Surappa, Key Eng. Mater. 104-107, Part 1 (1995) 259.
ASM Handbook, “Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-purpose Materials, Vol. 2” (ASM International, 1990) p. 1132.
G. F. Bocchini, Int. J. of Powder Metallurgy 22(3) (1986) 185.
R. D. Payne, A. L. Moran and R. C. Cammarata, Scr. Metall. et Mater. 29 (1993) 907.
D. L. MCDanels, Metall. Trans. A16 (1985) 1105.
M. R. Krishnadev, R. Angers, C. G. Krishnadas Nair and G. Huard, J. Met. 45(8) (1993) 52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, M., Lai, M. & Saravanaranganathan, D. Synthesis, microstructure and properties characterization of disintegrated melt deposited Mg/SiC composites. Journal of Materials Science 35, 2155–2165 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004706321731
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004706321731