Abstract
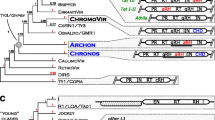
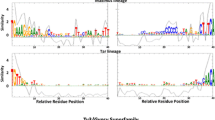
SIRE-1 is a multi-copy, Ty1-copia-like retroelement family found in the genome of Glycine max. A sequenced SIRE-1 genomic copy has an uninterrupted ORF that can be translated into a gag-pol polyprotein, followed by an unprecedented second ORF whose conceptual translation yielded a theoretical protein predicted to possess many of the same secondary structural elements found in mammalian retroviral envelope proteins. Similar, but clearly pseudogenic, envelope-like sequences were recovered from conceptual translations of 10 Arabidopsis Gen-Bank accessions. All were associated with identifiable Ty1-copia-like retroelements. Phylogenetic analysis of the adjacent ribonuclease H regions from these sequences and three similarly endowed elements, two from maize and one from tomato, indicate that the 14 elements constitute a monophyletic group distinct from several closely related plant Ty1-copia-like elements in which polis immediately followed by a downstream LTR. The conservation of identifiable env-like gene features suggests that these plant elements are endogenous retroviruses whose ancestors were acquired from animal vectors. The finding that the env and env-less retroelements identified in this study form distinct lineages does not support the hypothesis that horizontal transmission of retrotransposons is sponsored by ancestral infectious retroviruses that subsequently lost all traces of env genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., T.L. Madden, A.A. Schäffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller & D.J. Lipman, 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389–3402.
Bennetzen, J.L., 1996. The contributions of retroelements to plant genome organization, function and evolution. Trends Microbiol. 4: 347–353.
Bhattacharyya, M.K., R.A. Gonzales, M. Kraft & R.I. Buzzell, 1997. A copia-like retrotransposon Tgmr closely linked to the Rps-k allele that confers race-specific resistance of soybean to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Mol. Biol. 34: 255–264.
Bi, Y.-A. & H.M. Laten, 1996. Sequence analysis of a cDNA containing the gag and prot regions of the soybean retrovirus-like element, SIRE-1. Plant Mol. Biol. 30: 1315–1319.
Boeke, J.D., T. Eickbush, S.B. Sandmeyer & D.F. Voytas, 1999. Metaviridae, In Virus Taxonomy: ICTV VIIth Report, edited by M.H.V. van Regenmortel, C.M. Fauquet, D.H.L. Bishop, E.B. Carstens, M.K. Estes, S.M. Lemon, J. Maniloff, M.S. Mayo, D.J. McGeoch, C.R. Pringle & R.B. Wickner. Academic Press, NY, in press.
Boeke, J.D. & J.P. Stoye, 1997. Retrotransposons, endogenous retroviruses, and the evolution of retroelements, pp. 343–436 in Retroviruses, edited by J.M. Coffin, S.H. Hughes & H.E. Varmus. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Britten, R.J., 1995. Active gypsy/Ty3 retrotransposons or retroviruses in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 599–601.
Britten, R.J., T.J. McCormack, T.L. Mears & E.H. Davidson, 1995. Gypsy/Ty3-class retrotransposons integrated in the DNA of herring, tunicate, and echinoderms. J. Mol. Evol. 40: 13–24.
Brunt, A.A., K. Crabtree, M.J. Dallwitz, A.J. Gibbs, L. Watson & E.J. Zurcher (eds.), 1997. Plant Viruses Online: Descriptions and Lists from the VIDE Database, Version 16.
Bureau, T.E., S.E. White & S.R. Wessler, 1994. Transduction of a cellular gene by a plant retroelement. Cell 77: 479–480.
Carrington, J.C., K.D. Kasschau, S.K. Mahajan & M.C. Schaad, 1996. Cell-to-cell and long-distance transport of viruses in plants. Plant Cell 8: 1669–1681.
Coffin, J.M., 1993. Reverse transcriptase and evolution, pp. 445–479 in Reverse Transcriptase, edited by A.M. Skalka & S.P. Goff. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Ding, B., 1998. Intercellular protein trafficking through plasmodesmata. Plant Mol. Biol. 38: 279–310.
Doolittle, R.F. & D.-F. Feng, 1992. Tracing the origin of retroviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 176: 195–211.
Eickbush, T.H., 1994. Origin and evolutionary relationships of retroelements, pp. 121–157 in The Evolutionary Biology of Viruses, edited by S.S. Morse. Raven Press, NY.
Felder, H., A. Herzceg, Y. deChastonay, P. Aeby, H. Tobler & F. Muller, 1994. Tas, a retrotransposon from the parasitic nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. Gene 149: 219–225.
Flavell, A.J., V. Jackson, M.P. Iqbal, I. Riach & S. Waddell, 1995. Ty1-copia group retrotransposon sequences in amphibia and reptilia. Mol. Gen. Genet. 246: 65–71.
Flavell, A.J. & D.B. Smith, 1992. A Ty1-copia group retro-transposon sequence in a vertebrate. Mol. Gen. Genet. 233: 322–326.
Flavell, A.J., D.B. Smith & A. Kumar, 1992. Extreme heterogeneity of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in plants. Mol. Gen. Genet. 231: 233–242.
Goldbach, R. & D. Peters, 1996. Molecular and biological aspects of tospoviruses, pp. 129–157 in The Bunyaviridae, edited by R.M. Elliott. Plenum Press, NY.
Inouye, S., S. Yuki & K. Saigo, 1986. Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a Drosophila transposable genetic element, 297. Eur. J. Biochem. 154: 417–425.
Jin, Y.-K. & J.L. Bennetzen, 1994. Integration and nonrandom mutation of a plasma membrane proton ATPase gene fragment within the Bs1 retroelement in maize. Plant Cell 6: 1177–1186.
Kim, A., C. Terzian, P. Santamaria, A. Pelisson, N. Prud'homme & A. Bucheton, 1994. Retroviruses in invertebrates: the gypsy retrotransposon is apparently an infectious retrovirus of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1285–1289.
Kumar, A., 1996. The adventures of the Ty1-copia family of retrotransposons in plants. Trends Genet. 12: 41–43.
Kumar, A., 1998. The evolution of plant retroviruses: moving to greener pastures. Trends Plant Sci. 3: 371–374.
Laten, H.M. & R.O. Morris, 1993. SIRE-1, a long interspersed repetitive DNA element from soybean with weak sequence similarity to retrotransposons: initial characterization and partial sequence. Gene 133: 153–159.
Laten, H.M., A. Majumdar & E.A. Gaucher, 1998. SIRE-1, a copia/Ty1-like retroelement from soybean, encodes a retroviral envelope-like protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6897–6902.
Leblanc, P., S. Deswset, B. Dastugue & C. Vaury, 1997. Invertebrate retroviruses — Zam, a new candidate in D. melanogaster. EMBO J. 16: 7521–7531.
Lerat, E. & P. Capy, 1999. Retrotransposons and retroviruses: Analysis of the envelope gene. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16: 1198–1207.
Mumford, R.A., I. Barker & K.R. Wood, 1996. The biology of tospoviruses. Ann. Appl. Biol. 128: 159–183.
Nault, L.R., 1994. Transmission biology, vector specificity and evolution of planthopper-transmitted plant viruses, pp.429–448 in Planthoppers: Their Ecology and Management, edited by R.F. Denno & T.J. Perfect. Chapman and Hall, NY.
Ozers, M.S. & P.D. Friesen, 1996. The Env-like open reading frame of the baculovirus-integrated retrotransposon TED encodes a retrovirus-like envelope protein. Virology 226: 252–259.
Pardue, M.L., N. Danilevskaya, K. Lowenhaupt, F. Slot & K.L. Traverse, 1996. Drosophila telomeres: new views on chromosome evolution. Trends Gent. 12: 48–52.
Patience, C., D.A. Wilkenson & R.A. Weiss, 1997. Our retroviral heritage. Trends Genet. 13: 116–120.
Peterson-Burch, B.D., D.A. Wright, H.M. Laten & D.F. Voytas, 2000. Retroviruses in Plants? Trends Genet. 16: 151–152.
Petropoulos, C., 1997. Retroviral taxonomy, protein structures, sequences, and genetic maps, pp. 757–805 in Retroviruses, edited by J.M. Coffin, S.H. Hughes & H.E. Varmus, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Saigo, K., W. Kugimiya, Y. Matsuo, S. Inouye, K. Yoshioka & S. Yuki, 1984. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 312: 659–661.
SanMiguel, P., A. Tikhonov, Y.-K. Jin, N. Motchoulskaia, D. Zakharov, A. Melake-Berhan, P.S. Springer, K.J. Edwards, M. Lee, Z. Avramova & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Nested retrotransposons in the intergenic regions of the maize genome. Science 274: 765–768.
Song, S.U., T. Gerasimova, M. Kurkulos, J.D. Boeke & V.G. Corces, 1994. An Env-like protein encoded by a Drosophila retroelement: evidence that gypsy is an infectious retrovirus. Genes Dev. 8: 2046–2057.
Suoniemi, A., J. Tanskanen & A.H. Schulman, 1998. Gypsy-like retrotransposons are widespread in the plant kingdom. Plant J. 13, 699–705.
Tanda, S., J.L. Mullor & V.G. Corces, 1994. The Drosophila tom retrotransposon encodes an envelope protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 5392–5401.
Temin, H.M., 1992. Origin and general nature of retroviruses, pp. 1–18 in The Retroviridae, Vol 1, edited by J.A. Levy. Plenum Press, NY.
Voytas, D.F., M.P. Cummings, A. Konieczny, F.M. Ausubel & S.R. Rodermel, 1992. copia-like retrotransposons are ubiquitous among plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 7124–7128.
Wright, D.A. & D.F. Voytas, 1998. Potential retroviruses in plants: Tat1 is related to a group of Arabidopsis thaliana Ty3/gypsy retrotransposons that encode envelope-like proteins. Genetics 149: 703–715.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laten, H.M. Phylogenetic evidence for Ty1-copia-like endogenous retroviruses in plant genomes. Genetica 107, 87–93 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003901009861
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003901009861