Abstract
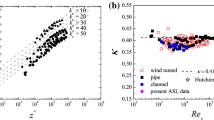
The structures of mean flow and turbulence in the atmospheric surface boundary layer have been extensively studied on Earth, and to a far less extent on Mars, where only the Viking missions and the Pathfinder mission have delivered in-situ data. Largely the behaviour of surface-layer turbulence and mean flow on Mars is found to obey the same scaling laws as on Earth. The largest micrometeorological differences between the two atmospheres are associated with the low air density of the Martian atmosphere. Together with the virtual absence of water vapour, it reduces the importance of the atmospheric heat flux in the surface energy budget. This increases the temperature variation of the surface forcing the near-surface temperature gradient and thereby the diabatic heat flux to higher values than are typical on the Earth, resulting in turn in a deeper daytime boundary layer. As wind speed is much like that of the Earth, this larger diabatic heat flux is carried mostly by larger maximal values of T*, the surface scale temperature. The higher kinematic viscosity yields a Kolmogorov scale of the order of ten times larger than on Earth, influencing the transition between rough and smooth flow for the same surface features.The scaling laws have been validated analysing the Martian surface-layer data for the relations between the power spectra of wind and temperature turbulence and the corresponding mean values of wind speed and temperature. Usual spectral formulations were used based on the scaling laws ruling the Earth atmospheric surface layer, whereby the Earth's atmosphere is used as a standard for the Martian atmosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchvarova, E. and Gryning, S. E.: 1991, 'Applied Model for the Growth of the Daytime Mixed Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 56, 261–274.
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1982, 'Exchange Processes at the Earth-Atmosphere Interface', in E. Plate (ed.), Engineering Meteorology, Elsevier pp. 319-369.
Champerlain, T. E., Cole, H. L., Dutton, R. G., Green, G. C., and Tillman, J. E.: 1976, 'Atmospheric Measurements on Mars - the Viking Meteorological Experiment', Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 57, 1094–1099.
Colburn, D. S., Pollack, J. B., and Haberle, R. M.: 1989, 'Diurnal Variations in Optical Depth at Mars', Icarus 79, 159–189.
Emeis, S., Frank, H. P., and Friedler, F.: 1995, 'Modification of Air Flow Over an Escarpment -Results from the Hjardemål Experiment', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 74, 161–161.
Etling, D. and Brown, R. A.: 1993, 'Roll Vortices in the Planetary Boundary Layer: A Review', Boundary-Layer Meteorol.65, 215–248.
Frank, H.: 1996, 'A Simple Spectral Model for the Modification of Turbulence in Flow Over Hills', Boundary-Layer Meteorol.79, 345–373.
Golitsyn, G. S.: 1969, 'Estimates of Boundary-Layer Parameters in the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets', Izv., Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics 5(8), 775–781.
Gryning, S.-E. and Batchvarova, E.: 1999, 'Regional Heat Flux Over the NOPEX Area Estimated from the Evolution of the Mixed-Layer', Agric. For. Meteorol. 98-99, 159–167.
Højstrup, J., Larsen, S. E., and Madsen, P. H.: 1990, 'Power Spectra of HorizontalWind Components in the Neutral Atmospheric Surface Layer', in Ninth Symposium on Turbulence and Diffusion. Amer. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, Mass. 305–308.
Kaimal, J. C.: 1973, 'Turbulence Spectra, Length Scales and Structure Parameters in the Stable Surface Layer', Boundary-Layer. Meteorol. 4, 289–309.
Kaimal, J. C., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Coté, O. R.: 1972, 'Spectral Characteristics of Surface Layer Turbulence', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 563–589.
Kieffer, H. H., Christensen, P. R., Martin, T. Z., Miner, E. D., and Palluconi, F. D.: 1976, 'Temperatures of the Martian Surface and Atmosphere: Viking Observation of Diurnal and Geometric Variations', Science 194, 1306–1351.
Larsen, S. E., Olesen, H. R., and Håjstrup, J.: 1985, 'Parameterisation of the Low Frequency Part of the Spectra of Horizontal Velocity Components in the Stable Surface Boundary Layer', in J.C. R. Hunt (ed.), Turbulence and diffusion in stable environments, Oxford University Press, pp. 181-204.
Lettau, H.: 1969, 'Note on Aerodynamic Roughness-Parameter Estimation on the Basis of Roughness-Element Distribution', J. Appl. Meteorol. 8, 820–832.
Mann, J.: 1999, 'Modeling of the Spectral Velocity Tensor in Complex Terrain', in Larsen, Larosse & Livesy (eds.), Wind Engineering into the 21st Century, Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 257–264.
Murphy, J. R., Conway, B., Leovy, C., and Tillman, J. E.: 1990, 'Observations of Martian Surface Winds at the Viking Lander 1 Site', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14555–14576.
Savijärvi, H.: 1999, 'A Model Study of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer in the Mars Pathfinder Lander Condition', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 125, 438–493.
Schofield, J. T., Barnes, J. R., Crisp, D., Haberle, R. M., Larsen, S., Magalhaes, J. A., Murphy, J. R., Seiff, A., Wilson, G.: 1997, 'The Mars Pathfinder Atmospheric Structure Investigation/ Meteorology (ASI/MET) Experiment', Science 278, 1752–1758.
Science:1997, 'Mars Parthfinder-Images', Science 278, 1734–1742.
Seiff, A and Kirk, D. B.: 1976, 'Structure of Mars's Atmosphere Up to 100 Kilometres from the Entry Measurements of Viking 2', Science 194, 1300–1303.
Siili, T. and Tillman, J.: 2000, 'Martian Atmosphere', in E. Pellinen and P. Raudsepp (eds.), Towards Mars, Oy Raud Publishing, Helsinki, Finland, pp. 201–216.
Stull, R. B.: 1988, An Introduction to Boundary-Layer Meteorology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 670 pp.
Sutton, J. L., Leovy, C. B., and Tillman, J. E.: 1978, 'Diurnal Variations of theMartian Surface Layer Meteorological Parameters During the First 45 Sols of the Two Viking Lander Sites', J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 2346–2355.
TLL: 1994: Tillman, J. E., Landberg, L., and Larsen, S. E.: 1994, 'The Boundary Layer of Mars: Fluxes, Ftability, Turbulence Fpectra and Growth of the Mixed Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 1709–1727.
TLL: 1995: Landberg, L., Larsen, S. E., and Tillman, J. E.: 1995, The Boundary Layer of Mars: Fluxes, Stability, Turbulent Spectra and the Growth of the Mixed Layer, Risø-R-701(EN), 54 pp.
Tillman, J. E., Harri, A.-M., and Larsen, S. E.: 1999, 'Martian climate variability: Multi-Year, in-situObservations and Requirements', in The Fifth International Conference on Mars, July 18-23, Pasadena, CA (unpublished, copy available from the first author).
Troen, I. and Lundtang Petersen, E.: 1989, European Wind Atlas, European Community Publication, Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, Denmark, 656 pp.
Ye, Z. Y., Segal, M., and Pielke, R. A.: 1990, 'A Comparative Study of Daytime Thermally Induced Up-Slope Flow on Mars and Earth', J. Atmos. Sci. 47, 612–628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, S.E., Jørgensen, H.E., Landberg, L. et al. Aspects Of The Atmospheric Surface Layers On Mars And Earth. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 105, 451–470 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020338016753
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020338016753