Abstract
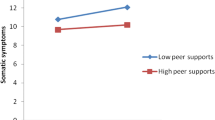
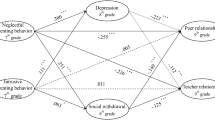
The purpose of this study was to fill up a research gap by examining the relationship of particular daily hassles and specific social support with regard to parent, peer, and teacher relationship to depression and antisocial behavior among early adolescents. Three-hundred and thirty-eight 5th and 6th graders were examined for depression and 360 for antisocial behavior through self-report questionnaires. Findings showed that except for parental support, hassles alone affected the level of maladjustment. Social support had no main effects except for parental support. Early adolescents who perceived high parental support reported less maladjustment. Social support did not moderate daily hassles in emotional and behavioral adjustment. Additionally, hassles with friends and parents were the best predictors of depression whereas hassles with parents were the best predictor of antisocial behavior. These findings suggest that Korean early adolescents were having more daily hassles that contributed to maladjustment than they had social support from significant others.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Benson, L. T., and Deeter, T. E. (1992). Moderator of the relation between stress and depression in adolescents. Sch. Counsel. 39: 189–194.
Cohen, S., and Wills, T. A. (1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychol. Bull. 98(2): 310–357.
Compas, B. E., Davis, G. E., and Forsythe, C. J. (1985). Characteristics of life events during adolescence. Am. J. Community Psychol. 13(6): 677–691.
Compas, B. E., Howell, D. C., Phares, V., Williams, R. A., and Giunta, C. T. (1989). Risk factors for emotional/behavioral problems in young adolescents: Prospective analysis of adolescent and parental stress and symptoms. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 57(6): 732–740.
Compas, B. E., Slavin, L. S., Wagner, B. M., and Vannatta, K. (1986). Relationship of life events and social support with psychological dysfunction among adolescents. J. Youth Adolesc. 15: 205–221.
DeLongis, A., Coyne, J. C., Dakof, G., Folkman, S., and Lazarus, R. S. (1982). Relationship of daily hassles, uplifts, and major life events to health status. Health Psychol. 1(2): 119–136.
DuBois, D. L., Felner, R. D., Brand, S., Adan, A. M., and Evans, E. G. (1992). A prospective study of life stress, social support, and adaptation in early adolescence. Child Dev. 63(3): 542–557.
Eccles, J. S., Midgley, C., Wigfield, A., Buchanan, C. M., Reuman, D., Flanagan, C., and Iver, D. M. (1993). Development during adolescence: The impact of stage-environment fit on young adolescents' experiences in schools and in families. Am. Psychol. 48(2): 90–101.
Furman, W., and Buhmester, D. (1992). Age and sex differences in perceptions of networks of personal relationships. Child Dev. 63(1): 103–115.
Gad, M. T., and Johnson, J. H. (1980). Correlates of adolescent life stress as related to race, sex, and levels of perceived social support. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 9: 13–16.
Greene, A. L. (1988). Early adolescents' perceptions of stress. J. Early Adolesc. 8(4): 391–403.
Han, Mi-hyun, and Yoo, An-jin (1995). Development of daily hassles scale for children in Korea. J. Korean Home Econ. Assoc. 33(4): 49–64.
Harris, J. R., and Liebert, R. M. (1992). Infant & Child: Development from Birth Through Middle Childhood. Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Harter, S. (1986). Manual: Social Support Scale for Children. University of Denver.
Kanner, A. D., Coyne, J. C., Schaefer, C., and Lazarus, R. S. (1981). Comparison of two modes of stress measurement: Daily hassles and uplifts versus major life events. J. Behav. Med. 4(1): 1–39.
Kwak, K. J., and Mun, E. Y. (1993). The relationships of psychological characteristics and depression and antisocial behavior among adolescents. Korean J. Psychol.: Dev. 6(2): 29–43.
Larson, R., and Ham, M. (1993). Stress and “Storm and Stress” in early adolescence: The relationship of negative events with dysphoric affect. Dev. Psychol. 29(1): 130–140.
Levitt, M. J., Guacci-France, N., Levitt, J. L. (1993). Convoys of social support in childhood and early adolescence: Structure and function. Dev. Psychol. 29(5): 811–818.
Monroe, A. M. (1983). Major and minor life events as predictors of psychological distress: Further issues and findings. J. Behav. Med. 6(2): 189–205.
Nor, S., Avison, W., and Kasper, V. (1992). Depression symptoms among Korean immigrants: Assessment of a translation of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scales. Psychol. Assess. 4: 84–91.
Rowlison, R. T., and Felner, R. D. (1988). Major life events, hassles, and adaptation in adolescence: Confounding in the conceptualization and measurement of life stress and adjustment revisited. J. Person. Soc. Psychol. 55(3): 432–444.
Simmons, R. G., Burgeson, R., Carlton-Ford, S., Blyth, D. A. (1987). The impact of cumulative change in early adolescence. Child Dev. 58: 1220–1234.
Thoits, P. A. (1982). Conceptual, methodological, and theoretical problems in studying social support as a buffer against life stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 23: 145–159.
Wagner, B. M., Compas, B. E., and Howell, D. C. (1988). Daily and major life events: A test of an integrative model of psychosocial stress. Am. J. Commun. Psychol. 16(2): 189–205.
Windle, M. (1992). A longitudinal study of stress buffering for adolescent problem behaviors. Dev. Psychol. 28(3): 522–530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, Ho. Relationship of Daily Hassles and Social Support to Depression and Antisocial Behavior Among Early Adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 29, 647–659 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026451805604
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026451805604