Abstract
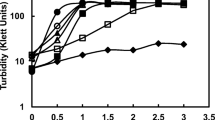
The possibility of regulating endospore formation by changing cultivation conditions was for the first time shown in acidophilic chemolithotrophic bacteria Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans type strain 1269 and the thermotolerant strain K1 formerly described as “S. thermosulfidooxidans subsp. thermotolerans”. Suppression of sporulation occurred when these strains were cultured in Manning's liquid medium with yeast extract. This medium was optimized by gradually reducing the concentrations of ferrous iron salts (the source of energy), phosphorous, nitrogen, and yeast extract and simultaneously increasing the concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and manganese (the elements important for sporogenesis) to attain higher yields of endospores by strains 1269 and K1. As a result, a new medium A was proposed, in which, under aeration, the life cycle of the strains studied culminated in sporulation at a level of 45 and 60%, respectively, of the total cell number. In a series of additional tests, the growth temperature and medium pH were adjusted to obtain the maximum yield of endospores. The optimal ranges found were 40–50°C and pH 1.8–2.2 for strain 1269 and 35–40°C and pH 2.5–2.7 for strain K1. An even higher yield of endospores, amounting to 55 and 75% for strains 1269 and K1, respectively, was obtained when the above growth conditions were combined (growth on medium A at optimal temperatures and pH under static conditions). Our results suggest a new approach to optimizing sporulation by acidophilic chemolithotrophs, which consists in limiting the energy and nutrient sources and using temperature and pH values within the tolerance bounds of these cultures but outside their growth optimum ranges.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Ninth Edition,Holt, J.G. et al., Eds, Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1994. Translated under the title Opredelitel’ bakterii Berdzhi), Moscow: Mir, 1997.
Golovacheva, R.S. and Karavaiko, G.I., Sulfobacillus, a New Genus of Thermophilic Spore-Forming Bacteria, Mikrobiologiya, 1978, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 815-822.
Kovalenko, E.V. and Malakhova, P.T., Spore-Forming Iron-Oxidizing Bacterium Sulfobacillus thermosulfi-dooxidans, Mikrobiologiya, 1983, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 962-966.
Norris, P.R., Clark, D.A., Owen, J.P., and Waterhouse, S., Characteristics of Sulfobacillus acidophilussp. nov. and Other Moderately Thermophilic Mineral-Sulfide-Oxidizing Bacteria, Microbiology, 1996, vol. 142, pp. 775-783.
Dufresne, S., Bousquet, J., Boissinot, M., and Guay, R., Sulfobacillus disulfidooxidanssp. nov.-a New Acidophilic Disulfide-Oxidizing, Gram-Positive, Spore-Forming Bacterium, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1996, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 1056-1064.
Vinter, V., Chaloupka, J., and Stastina, J., Caslavska, J., Possibilities of Cellular Differentiation into Different Hypometabolic Forms, Spores V, Halvorson, H.O. et al., Eds., Washington DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1972, pp. 390-397.
Mulyukin, A.L., Lusta, K.A., Gryaznova, M.N., Kozlova, A.N., Duzha, M.V., Duda, V.I., and El’-Registan, G.I., Formation of Resting Cells by Bacillus cereusand Micrococcus luteus, Mikrobiologiya,1996, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 782-789.
Bogdanova, T.I., Tsaplina, I.A., Sayakin, D.D., Karavaiko, G.I., and Kovalenko, E.V., Morphology and Cytology of the Bacterium Sulfobacillus thermosulfi-dooxidanssubsp. thermotolerans, Mikrobiologiya, 1990, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 844-855.
Manning, H.L., New Medium for Isolating Iron-Oxidizing and Heterotrophic Acidophilic Bacteria from Acid Mine Drainage, Appl. Microbiol.,1975, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 1010-1015.
Loginova, L.G., Khraptsova, G.I., Egorova, L.A., and Bogdanova, T.I., The Acidophilic Obligately Thermophilic Bacteria Bacillus acidocaldariusIsolated form Hot Springs and Soil of the Kunashir Island, Mikrobiologiya, 1978, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 947-952.
Wisotzkey, J.D., Jurtshuk, P., Jr., Fox, G.E., Deinhard, G., and Poralla, K., Comparative Sequence Analysis of 16S rRNA (rDNA) of Bacillus acidocaldarius, Bacillus acidoterrestris, and Bacillus cycloheptanicusand Proposal for Creation of a New Genus Alicyclobacillusgen. nov, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1992, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 263-269.
Karavaiko, G.I., Tourova, T.P., Tsaplina, I.A., and Bogdanova, T.I., Investigation of the Phylogenetic Position of Aerobic, Moderately Thermophilic Bacteria Oxidizing Fe2+, S0, and Sulfide Minerals and Affiliated the Genus Sulfobacillus, Mikrobiologiya, 2000, vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 857-860.
Karavaiko, G.I., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Tsaplina, I.A., Bogdanova, T.I., and Zakharchuk, L.M., Growth and Carbohydrate Metabolism of Sulfobacilli, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 293-299.
Kuznetsov, V.D., Parallelism in Hereditary Variability and the Populational Concept of Species in Prokaryotes, Zh. Obshch. Biol., 1987, vol. XLVIII, no. 4, pp. 466-477.
El’-Registan, G.I., The Role of Membranotropic Autoregulatory Factors in the Processes of Microbial Growth and Differentiation, Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation,Moscow, 1988.
Kerravalla, L.I., Srinivasan, V.R., and Halvorson, H.O., Endogenous Factor in Sporogenesis in Bacteria, J. Bacteriol., 1964, vol. 88, pp. 374-380.
El’-Registan, G.I., Duda, V.I., Kozlova, A.N., Mityushina, L.L., and Poplaukhina, O.G., Changes in the Anabolism and Ultrastructural Organization of Bacillus cereusCells under the Effect of a Specific Autoregulatory Factor, Mikrobiologiya, 1979, vol. 48, pp. 240-244.
Duda, V.I., Pronin, S.V., El';-Registan, G.I., Kaprel'yants, A.S., and Mityushina, L.L., Formation of Resting Refractile Cells by Bacillus cereusunder the Effect of an Autoregulatory Factor, Mikrobiologiya, 1982, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 77-81.
Svetlichnyi, V.A., Romanova, A.K., and El'-Registan, G.I., A Study of the Content of Membrane-Active Autoregulators during Lithoautotrophic Growth of Pseudomonas carboxydoflava, Mikrobiologiya, 1986, vol. 55, pp. 55-59.
Mulyukin, A.L., Lusta, K.A., Gryaznova, M.N., Babusenko, E.S., Kozlova, A.N., Duzha, M.V., Mityushina, L.L., Duda, V.I., and El'-Registan, G.I., Formation of Resting Cells in Microbial Suspensions Undergoing Autolysis, Mikrobiologiya, 1997, vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 42-49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogdanova, T.I., Mulyukin, A.L., Tsaplina, I.A. et al. Effect of the Medium Composition and Cultivation Conditions on Sporulation in Chemolithotrophic Bacteria. Microbiology 71, 158–163 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015137902580
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015137902580