Abstract
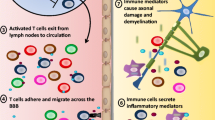
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system white matter. The association of the disease with MHC genes, the inflammatory white matter infiltrates, similarities with animal models, and the observation that MS can be treated with immunomodulatory and immunosuppressive therapies support the hypothesis that autoimmunity plays a major role in the disease pathology. Evidence supports activated CD4+ myelin-reactive T cells as major mediators of the disease. In addition, a renewed interest in the possible contribution of B cells to MS immunopathology has been sparked by nonhuman primate and MS pathological studies. This review focuses on the immunopathology of MS, outlining the hypothetical steps of tolerance breakdown and the molecules that play a role in the migration of autoreactive cells to the CNS. Particular focus is given to autoreactive T cells and cytokines as well as B cells and autoantibodies and their role in CNS pathogenesis in MS.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bobowick AR, Kurtzke JF, Brody JA, Hrubec Z, Gillespie M: Twin study of multiple sclerosis: An epidemiologic inquiry. Neurology 28:978–987, 1978
Kinnunen E, Juntunen J, Ketonen L, Koskimies S, Konttinen YT, Salmi T, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J: Genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. A co-twin study of a nationwide series. Arch Neurol 45:1108–1111, 1988
Mumford CJ, Wood NW, Kellar-Wood H, Thorpe JW, Miller DH, Compston DA: The British Isles survey of multiple sclerosis in twins. Neurology 44:11–15, 1994
Sadovnick AD, Armstrong H, Rice GP, et al.: A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins: Update. Ann Neurol 33:281–285, 1993
Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC: Genetics of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Clin 13:99–118, 1995
Jersild C, Fog T, Hansen GS, Thomsen M, Svejgaard A, Dupont B: Histocompatibility determinants in multiple sclerosis, with special reference to clinical course. Lancet 2:1221–1225, 1973
Hauser SL, Fleischnick E, Weiner HL, Marcus D, Awdeh Z, Yunis EJ, Alper CA: Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 39:275–277, 1989
Francis G, Duquette P, Antel J: Inflammatory demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. In Neurology in Clinical Practice, W Bradley, R Daroff, G Fenichel, C Marsden (eds). Boston, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1996
Wucherpfennig KW, Zhang J, Witek C, Matsui M, Modabber Y, Ota K, Hafler DA: Clonal expansion and persistence of human T cells specific for an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide. J Immunol 152:5581–5592, 1994
Gran B, Hemmer B, Vergelli M, McFarland HF, Martin R: Molecular mimicry and multiple sclerosis: Degenerate T-cell recognition and the induction of autoimmunity. Ann Neurol 45:559–567, 1999
Hemmer B, Fleckenstein BT, Vergelli M, Jung G, McFarland H, Martin R, Wiesmuller KH: Identification of high potency microbial and self ligands for a human autoreactive class II-restricted T cell clone. J Exp Med 185:1651–1659, 1997
Hemmer B, Jacobsen M, Sommer N: Degeneracy in T-cell antigen recognition–Implications for the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. J Neuroimmunol 107:148–153, 2000
Mamula MJ: Epitope spreading: the Role of self peptides and autoantigen processing by B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev 164: 231–239, 1998
Springer TA: Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: The multistep paradigm. Cell 76:301–314, 1994
Raine CS: The Dale E. McFarlin Memorial Lecture: The immunology of the multiple sclerosis lesion. Ann Neurol S61–S72, 1994
Butcher EC: Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: Three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell 67:1033–1036, 1991
Ransohoff RM: Mechanisms of inflammation in MS tissue: Adhesion molecules and chemokines. J Neuroimmunol 98:57–68, 1999
Sobel RA, Mitchell ME, Fondren G: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in cellular immune reactions in the human central nervous system. Am J Pathol 136:1309–1316, 1990
Washington R, Burton J, Todd RF, Newman W, Dragovic L, Dore-Duffy P: Expression of immunologically relevant endothelial cell activation antigens on isolated central nervous system microvessels from patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 35:89–97, 1994
Cannella B, Raine CS: The adhesion molecule and cytokine profile of multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol 37:424–435, 1995
Brosnan CF, Cannella B, Battistini L, Raine CS: Cytokine localization in multiple sclerosis lesions: Correlation with adhesion molecule expression and reactive nitrogen species. Neurology 45:S16–S21, 1995
Bo L, Peterson JW, Mork S, Hoffman PA, Gallatin WM, Ransohoff RM, Trapp BD: Distribution of immunoglobulin superfamily members ICAM-1,-2,-3, and the beta 2 integrin LFA-1 in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1060–1072, 1996
Zhang GX, Baker CM, Kolson DL, Rostami AM: Chemokines and chemokine receptors in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 6:3–13, 2000
Leppert D, Waubant E, Galardy R, Bunnett NW, Hauser SL: T cell gelatinases mediate basement membrane transmigration in vitro. J Immunol 154:4379–4389, 1995
Nielsen BS, Timshel S, Kjeldsen L, Sehested M, Pyke C, Borregaard N, Dano K: 92 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-9) is expressed in neutrophils and macrophages but not in malignant epithelial cells in human colon cancer. Int J Cancer 65:57–62, 1996
Cuzner ML, Gveric D, Strand C, Loughlin AJ, Paemen L, Opdenakker G, Newcombe J: The expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator, matrix metalloproteases and endogenous inhibitors in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis: Comparison of stages in lesion evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1194–1204, 1996
Maeda A, Sobel RA: Matrix metalloproteinases in the normal human central nervous system, microglial nodules, and multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:300–309, 1996
Yong VW, Krekoski CA, Forsyth PA, Bell R, Edwards DR: Matrix metalloproteinases and diseases of the CNS. Trends Neurosci 21:75–80, 1998
Kieseier BC, Seifert T, Giovannoni G, Hartung HP: Matrix metalloproteinases in inflammatory demyelination: targets for treatment. Neurology 53:20–25, 1999
Rosenberg GA, Kornfeld M, Estrada E, Kelley RO, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG: TIMP-2 reduces proteolytic opening of blood-brain barrier by type IV collagenase. Brain Res 576:203–207, 1992
Rosenberg GA, Dencoff JE, McGuire PG, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Injury-induced 92–kilodalton gelatinase and urokinase expression in rat brain. Lab Invest 71:417–422, 1994
Anthony DC, Miller KM, Fearn S, Townsend MJ, Opdenakker G, Wells GM, Clements JM, Chandler S, Gearing AJ, Perry VH: Matrix metalloproteinase expression in an experimentallyinduced DTH model of multiple sclerosis in the rat CNS. J Neuroimmunol 87:62–72, 1998
Allegretta M, Nicklas JA, Sriram S, Albertini RJ: T cells responsive to myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Science 247:718–721, 1990
Burns J, Rosenzweig A, Zweiman B, Lisak RP: Isolation of myelin basic protein-reactive T-cell lines from normal human blood. Cell Immunol 81:435–440, 1983
Chou YK, Vainiene M, Whitham R, Bourdette D, Chou CH, Hashim G, Offner H, Vandenbark AA: Response of human T lymphocyte lines to myelin basic protein: Association of dominant epitopes with HLA class II restriction molecules. J Neurosci Res 23:207–216, 1989
Martin R, Jaraquemada D, Flerlage M, Richert J, Whitaker J, Long EO, McFarlin DE, McFarland HF: Fine specificity and HLA restriction of myelin basic protein-specific cytotoxic T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol 145:540–548, 1990
Ota K, Matsui M, Milford EL, Mackin GA, Weiner HL, Hafler DA: T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature 346:183–187, 1990
Pette M, Fujita K, Kitze B, Whitaker JN, Albert E, Kappos L, Wekerle H: Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocyte lines from MS patients and healthy individuals. Neurology 40:1770–1776, 1990
Richert JR, Robinson ED, Deibler GE, Martenson RE, Dragovic LJ, Kies MW: Evidence for multiple human T cell recognition sites on myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol 23:55–66, 1989
Kerlero de Rosbo N, Milo R, Lees MB, Burger D, Bernard CC, Ben-Nun A: Reactivity to myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Peripheral blood lymphocytes respond predominantly to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Clin Invest 92:2602–2608, 1993
Sun J, Link H, Olsson T, Xiao BG, Andersson G, Ekre HP, Linington C, Diener P: T and B cell responses to myelinoligodendrocyte glycoprotein in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 146:1490–1495, 1991
Sun JB, Olsson T, Wang WZ, Xiao BG, Kostulas V, Fredrikson S, Ekre HP, Link H: Autoreactive T and B cells responding to myelin proteolipid protein in multiple sclerosis and controls. Eur J Immunol 21:1461–1468, 1991
Markovic-Plese S, Fukaura H, Zhang J, al-Sabbagh A, Southwood S, Sette A, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA: T cell recognition of immunodominant and cryptic proteolipid protein epitopes in humans. J Immunol 155:982–992, 1995
Zhang J, Markovic-Plese S, Lacet B, Raus J, Weiner HL, Hafler DA: Increased frequency of interleukin 2–responsive T cells specific for myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 179:973–984, 1994
Jenkins MK: The ups and downs of T cell costimulation. Immunity 1:443–446, 1994
Scholz C, Patton KT, Anderson DE, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA: Expansion of autoreactive T cells in multiple sclerosis is independent of exogenous B7 costimulation. J Immunol 160:1532–1538, 1998
Lovett-Racke AE, Trotter JL, Lauber J, Perrin PJ, June CH, Racke MK: Decreased dependence of myelin basic proteinreactive T cells on CD28–mediated costimulation in multiple sclerosis patients. A marker of activated/memory T cells. J Clin Invest 101:725–730, 1998
Burns J, Bartholomew B, Lobo S: Isolation of myelin basic protein-specific T cells predominantly from the memory T-cell compartment in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 45:33–39, 1999
Williams K, Ulvestad E, Antel JP: B7/BB-1 antigen expression on adult human microglia studied in vitro and in situ. Eur J Immunol 24:3031–3037, 1994
Windhagen A, Newcombe J, Dangond F, Strand C, Woodroofe MN, Cuzner ML, Hafler DA: Expression of costimulatory molecules B7–1 (CD80), B7–2 (CD86), and interleukin 12 cytokine in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Exp Med 182:1985–1996, 1995
Genc K, Dona DL, Reder AT: Increased CD80(+) B cells in active multiple sclerosis and reversal by interferon beta-1b therapy. J Clin Invest 99:2664–2671, 1997
Karandikar NJ, Vanderlugt CL, Bluestone JA, Miller SD: Targeting the B7/CD28:CTLA-4 costimulatory system in CNS autoimmune disease. J Neuroimmunol 89:10–18, 1998
Croxford JL, O'Neill JK, Ali RR, Browne K, Byrnes AP, Dallman MJ, Wood MJ, Fedlmann M, Baker D: Local gene therapy with CTLA4–immunoglobulin fusion protein in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 28:3904–3916, 1998
Issazadeh S, Navikas V, Schaub M, Sayegh M, Khoury S: Kinetics of expression of costimulatory molecules and their ligands in murine relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in vivo. J Immunol 161:1104–1112, 1998
Kuchroo VK, Das MP, Brown JA, Ranger AM, Zamvil SS, Sobel RA, Weiner HL, Nabavi N, Glimcher LH: B7–1 and B7–2 costimulatory molecules activate differentially the Th1/Th2 developmental pathways: Application to autoimmune disease therapy. Cell 80:707–718, 1995
Racke MK, Scott DE, Quigley L, Gray GS, Abe R, June CH, Perrin PJ: Distinct roles for B7–1 (CD-80) and B7–2 (CD-86) in the initiation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest 96:2195–2203, 1995
Miller S, Vanderlugt C, Lenschow D, Pope J, Karandikar N, Dal Canto M, Bluestone J: Blockade of CD28/B7–1 interaction prevents epitope spreading and clinical relapses of murine EAE. Immunity 3:739–745, 1996
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A: Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383:787–793, 1996
O'Garra A: Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity 8:275–283, 1998
Leonard JP, Waldburger KE, Schaub RG, Smith T, Hewson AK, Cuzner ML, Goldman SJ: Regulation of the inflammatory response in animal models of multiple sclerosis by interleukin-12. Crit Rev Immunol 17:545–553, 1997
Bright JJ, Musuro BF, Du C, Sriram S: Expression of IL-12 in CNS and lymphoid organs of mice with experimental allergic encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol 82:22–30, 1998
Leonard JP, Waldburger KE, Goldman SJ: Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antibodies against interleukin 12. J Exp Med 181:381–386, 1995
Segal BM, Dwyer BK, Shevach EM: An interleukin (IL)-10/ IL-12 immunoregulatory circuit controls susceptibility to autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 187:537–546, 1998
Begolka WS, Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Miller SD: Differential expression of inflammatory cytokines parallels progression of central nervous system pathology in two clinically distinct models of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 161:4437–4446, 1998
Khoury SJ, Hancock WW, Weiner HL: Oral tolerance to myelin basic protein and natural recovery from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are associated with downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and differential upregulation of transforming growth factor beta, interleukin 4, and prostaglandin E expression in the brain. J Exp Med 176:1355–1364, 1992
Owens T, Renno T, Taupin V, Krakowski M: Inflammatory cytokines in the brain: Does the CNS shape immune responses? Immunol Today 15:566–571, 1994
Antel JP, Owens T: Immune regulation and CNS autoimmune disease. J Neuroimmunol 100:181–189, 1999
Genain CP, Cannella B, Hauser SL, Raine CS: Identification of autoantibodies associated with myelin damage in multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 5:170–175, 1999
Krakowski ML, Owens T: The central nervous system environment controls effector CD4+ T cell cytokine profile in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 27:2840–2847, 1997
Popko B, Corbin JG, Baerwald KD, Dupree J, Garcia AM: The effects of interferon-gamma on the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 14:19–35, 1997
Hemmer B, Vergelli M, Calabresi P, Huang T, McFarland HF, Martin R: Cytokine phenotype of human autoreactive T cell clones specific for the immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide (83–99). J Neurosci Res 45:852–862, 1996
Hermans G, Stinissen P, Hauben L, Van den Berg-Loonen E, Raus J, Zhang J: Cytokine profile of myelin basic protein-reactive T cells in multiple sclerosis and healthy individuals. Ann Neurol 42:18–27, 1997
Pette M, Pette DF, Muraro PA, Farnon E, Martin R, McFarland HF: Interferon-beta interferes with the proliferation but not with the cytokine secretion of myelin basic protein-specific, T-helper type 1 lymphocytes. Neurology 49:385–392, 1997
Windhagen A, Anderson DE, Carrizosa A, Balashov K, Weiner HL, Hafler DA: Cytokine secretion of myelin basic protein reactive T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 91:1–9, 1998
Correale J, Gilmore W, McMillan M, Li S, McCarthy K, Le T, Weiner LP: Patterns of cytokine secretion by autoreactive proteolipid protein-specific T cell clones during the course of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 154:2959–2968, 1995
Comabella M, Balashov K, Issazadeh S, Smith D, Weiner HL, Khoury SJ: Elevated interleukin-12 in progressive multiple sclerosis correlates with disease activity and is normalized by pulse cyclophosphamide therapy. J Clin Invest 102:671–678, 1998
Siveke JT, Hamann A: T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells respond differentially to chemokines. J Immunol 160:550–554, 1998
Balashov KE, Rottman JB, Weiner HL, Hancock WW: CCR5(+) and CXCR3(+) T cells are increased in multiple sclerosis and their ligands MIP-1alpha and IP-10 are expressed in demyelinating brain lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6873–6878, 1999
Sorensen TL, Tani M, Jensen J, Pierce V, Lucchinetti C, Folcik VA, Qin S, Rottman J, Sellebjerg F, Strieter RM, Frederiksen JL, Ransohoff RM: Expression of specific chemokines and chemokine receptors in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients. J Clin Invest 103:807–815, 1999
Blain M, Nalbantoglu J, Antel J: Interferon-gamma mRNA expression in immediately ex-vivo CSF T cells. J Neuroimmunol 54:149, 1994
Hofman FM, Hinton DR, Johnson K, Merrill JE: Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med 170:607–612, 1989
Selmaj K, Raine CS, Cannella B, Brosnan CF: Identification of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Clin Invest 87:949–954, 1991
Kabat EA, Glusman M, Knaub V: Quantitative estimation of the albumin and gamma globulin in normal and pathologic cerebrospinal fluid by immunochemical methods. Am J Med 4:653–662, 1948
Tourtellotte WW: The cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, PJ Vinken, GW Bruyn, HL Klawans, and JC Koetsier (eds). Amsterdam/New York, Elsevier Science, 1985, 79–130
Sharief MK, Thompson EJ: Intrathecal immunoglobulin M synthesis in multiple sclerosis. Relationship with clinical and cerebrospinal fluid parameters. Brain 114:181–195, 1991
Sharief MK, Hentges R: Importance of intrathecal synthesis of IgD in multiple sclerosis. A combined clinical, immunologic, and magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 48:1076–1079, 1991
Walsh MJ, Tourtellotte WW, Roman J, Dreyer W: Immunoglobulin G, A, and M-clonal restriction in multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid and serum–Analysis by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 35:313–327, 1985
Esiri MM: Multiple sclerosis: A quantitative and qualitative study of immunoglobulin-containing cells in the central nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 6:9–21, 1980
Prineas JW, Wright RG: Macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells in the perivascular compartment in chronic multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest 38:409–421, 1978
Lowenthal A, Van Sande M, Karcher D: The differential diagnosis of neurological diseases by fractionating electrophoretically the CSF G-globulins. J Neurochem 235:229–233, 1960
Thompson EJ, Kaufmann P, Shortman RC, Rudge P, McDonald WI: Oligoclonal immunoglobulins and plasma cells in spinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Br Med J 1:16–17, 1979
Andersson M, Alvarez-Cermeno J, Bernardi G, et al.: Cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: a consensus report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:897–902, 1994
Kostulas VK: Oligoclonal IgG bands in cerebrospinal fluid. Methodological and clinical aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 103:1–112, 1985
Vandvik B: Oligoclonal IgG and free light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Scand J Immunol 6:913–922, 1977
Nagelkerken LM, van Zoonen-van Exel M, van Walbeek HK, Aalberse RC, Out TA: Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis by means of anti-idiotypic antisera. J Immunol 128:1102–1106, 1982
Kabat EA, Freedman DA, Murray JP, Knaub V: A study of the crystalline albumin, gamma globulin and the total protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of one hundred cases of multiple sclerosis and other diseases. Am J Med Sci 219:55–64, 1950
Whitaker JN, Beneveniste EN: Cerebrospinal fluid. In Handbook of Multiple Sclerosis, SD Cook (ed). New York, Marcel Dekker, 1996, pp 295–316
Adams JM, Imagawa DT: Measles antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 111:562–566, 1962
Sandberg-Wollheim M, Vandvik B, Nadj C, Norrby E: The intrathecal immune response in the early stage of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 81:45–53, 1987
Bray PF, Luka J, Culp KW, Schlight JP: Antibodies against Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen (EBNA) in multiple sclerosis CSF, and two pentapeptide sequence identities between EBNA and myelin basic protein. Neurology 42:1798–1804, 1992
Vartdal F, Vandvik B, Norrby E: Viral and bacterial antibody responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 8:248–255, 1980
Vartdal F, Vandvik B: Multiple sclerosis. Electrofocused “bands” of oligoclonal CSF IgG do not carry antibody activity against measles, varicella-zoster or rotaviruses. J Neurol Sci 54:99–107, 1982
Vandvik B, Norrby E, Nordal HJ, Degre M: Oligoclonal measles virus-specific IgG antibodies isolated from cerebrospinal fluids, brain extracts, and sera from patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 5:979–992, 1976
Vandvik B, Vartdal F, Norrby E: Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: Intrathecal synthesis of oligoclonal virus-specific IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies. J Neurol 228:25–38, 1982
Luxton RW, Zeman A, Holzel H, Harvey P, Wilson J, Kocen R, Morgan-Hughes J, Miller DH, Compston A, Thompson EJ: Affinity of antigen-specific IgG distinguishes multiple sclerosis from encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 132:11–19, 1995
Panitch HS, Hooper CJ, Johnson KP: CSF antibody to myelin basic protein. Measurement in patients with multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Arch Neurol 37:206–209, 1980
Warren KG, Catz I: A correlation between cerebrospinal fluid myelin basic protein and anti-myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol 21:183–189, 1987
Warren KG, Catz I: Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein within multiple sclerosis central nervous system tissue. J Neurol Sci 115:169–176, 1993
Warren KG, Catz I: An extensive search for autoantibodies to myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid of non-multiplesclerosis patients: Implications for the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Eur Neurol 42:95–104, 1999
Warren KG, Catz I: Relative frequency of autoantibodies to myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Sci 121:66–73, 1994
Warren KG, Catz I, Johnson E, Mielke B: Anti-myelin basic protein and anti-proteolipid protein specific forms of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 35:280–289, 1994
Moller JR, Johnson D, Brady RO, Tourtellotte WW, Quarles RH: Antibodies to myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 22:55–61, 1989
Banki K, Colombo E, Sia F, Halladay D, Mattson DH, Tatum AH, Massa PT, Phillips PE, Perl A: Oligodendrocyte-specific expression and autoantigenicity of transaldolase in multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 180:1649–1663, 1994
Bronstein JM, Lallone RL, Seitz RS, Ellison GW, Myers LW: A humoral response to oligodendrocyte-specific protein in MS: A potential molecular mimic. Neurology 53:154–161, 1999
Mehta PD, Frisch S, Thormar H, Tourtellotte WW, Wisniewski HM: Bound antibody in multiple sclerosis brains. J Neurol Sci 49:91–98, 1981
Mehta PD, Miller JA, Tourtellotte WW: Oligoclonal IgG bands in plaques from multiple sclerosis brains. Neurology 32:372–376, 1982
Mattson DH, Roos RP, Arnason BG: Isoelectric focusing of IgG eluted from multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis brains. Nature 287:335–337, 1980
Xiao BG, Linington C, Link H: Antibodies to myelinoligodendrocyte glycoprotein in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with multiple sclerosis and controls. J Neuroimmunol 31:91–96, 1991
Genain CP, Nguyen MH, Letvin NL, Pearl R, Davis RL, Adelman M, Lees MB, Linington C, Hauser SL: Antibody facilitation of multiple sclerosis-like lesions in a nonhuman primate. J Clin Invest 96:2966–2974, 1995
Salier JP, Goust JM, Pandey JP, Fudenberg HH: Preferential synthesis of the G1m(1) allotype of IgG1 in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients. Science 213:1400–1402, 1981
Mathiesen T, von Holst H, Fredrikson S, Wirsen G, Hederstedt B, Norrby E, Sundqvist VA, Wahren B: Total, anti-viral, and anti-myelin IgG subclass reactivity in inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system. J Neurol 236:238–242, 1989
Qin Y, Duquette P, Zhang Y, Talbot P, Poole R, Antel J: Clonal expansion and somatic hypermutation of V(H) genes of B cells from cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 102:1045–1050, 1998
Smith-Jensen T, Burgoon MP, Anthony J, Kraus H, Gilden DH, Owens GP: Comparison of immunoglobulin G heavy-chain sequences in MS and SSPE brains reveals an antigen-driven response. Neurology 54:1227–1232, 2000
Colombo M, Dono M, Gazzola P, Roncella S, Valetto A, Chiorazzi N, Mancardi GL, Ferrarini M: Accumulation of clonally related B lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Immunol 164:2782–2789, 2000
Baranzini SE, Jeong MC, Butunoi C, Murray RS, Bernard CC, Oksenberg JR: B cell repertoire diversity and clonal expansion in multiple sclerosis brain lesions. J Immunol 163:5133–5144, 1999
Dasgupta MK, Catz I, Warren KG, McPherson TA, Dossetor JB, Carnegie PR: Myelin basic protein: A component of circulating immune complexes in multiple sclerosis. Can J Neurol Sci 10:239–243, 1983
Reindl M, Linington C, Brehm U, Egg R, Dilitz E, Deisenhammer F, Poewe W, Berger T: Antibodies against the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein and the myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases: A comparative study. Brain 122:2047–2056, 1999
Terryberry JW, Thor G, Peter JB: Autoantibodies in neurodegenerative diseases: Antigen-specific frequencies and intrathecal analysis. Neurobiol Aging 19:205–216, 1998
Brokstad KA, Page M, Nyland H, Haaheim LR: Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein are not present in the serum and CSF of MS patients. Acta Neurol Scand 89:407–411, 1994
Olsson T, Baig S, Hojeberg B, Link H: Antimyelin basic protein and antimyelin antibody-producing cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 27:132–136, 1990
Colombo E, Banki K, Tatum AH, Daucher J, Ferrante P, Murray RS, Phillips PE, Perl A: Comparative analysis of antibody and cell-mediated autoimmunity to transaldolase and myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 99:1238–1250, 1997
Lindert RB, Haase CG, Brehm U, Linington C, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R: Multiple sclerosis: B-and T-cell responses to the extracellular domain of the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Brain 122:2089–2100, 1999
Schmidt S: Candidate autoantigens in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 5:147–160, 1999
Barned S, Goodman AD, Mattson DH: Frequency of anti-nuclear antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 45:384–385, 1995
Colaco CB, Scadding GK, Lockhart S: Anti-cardiolipin antibodies in neurological disorders: cross-reaction with anti-single stranded DNA activity. Clin Exp Immunol 68:313–319, 1987
Roussel V, Yi F, Jauberteau MO, Couderq C, Lacombe C, Michelet V, Gil R, Couratier P, Vallat JM, Preud'homme JL: Prevalence and clinical significance of anti-phospholipid antibodies in multiple sclerosis: A study of 89 patients. J Autoimmun 14:259–265, 2000
Spadaro M, Amendolea MA, Mazzucconi MG, Fantozzi R, Di Lello R, Zangari P, Masala G: Autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis: Study of a wide spectrum of autoantibodies. Mult Scler 5:121–125, 1999
Myers KJ, Sprent J, Dougherty JP, Ron Y: Synergy between encephalitogenic T cells and myelin basic protein-specific antibodies in the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 41:1–8, 1992
Wolf SD, Dittel BN, Hardardottir F, Janeway CA Jr: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induction in genetically B cell-deficient mice. J Exp Med 184:2271–2278, 1996
Hjelmstrom P, Juedes AE, Fjell J, Ruddle NH: B-cell-deficient mice develop experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with demyelination after myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein sensitization. J Immunol 161:4480–4483, 1998
Willenborg DO, Prowse SJ: Immunoglobulin-deficient rats fail to develop experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 5:99–109, 1983
Piddlesden SJ, Lassmann H, Zimprich F, Morgan BP, Linington C: The demyelinating potential of antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is related to their ability to fix complement. Am J Pathol 143:555–564, 1993
Baig S, Olsson T, Yu-Ping J, Hojeberg B, Cruz M, Link H: Multiple sclerosis: Cells secreting antibodies against myelinassociated glycoprotein are present in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Immunol 33:73–79, 1991
Crucian B, Dunne P, Friedman H, Ragsdale R, Pross S, Widen R: Alterations in levels of CD28–/CD8+ suppressor cell precursor and CD45RO+/CD4+ memory T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2:249–252, 1995
Mix E, Olsson T, Correale J, Baig S, Kostulas V, Olsson O, Link H: B cells expressing CD5 are increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 79:21–27, 1990
Correale J, Mix E, Olsson T, Kostulas V, Fredrikson S, Hojeberg B, Link H: CD5+ B cells and CD4–8– T cells in neuroimmunological diseases. J Neuroimmunol 32:123–132, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'connor, K.C., Bar-Or, A. & Hafler, D.A. The Neuroimmunology of Multiple Sclerosis: Possible Roles of T and B Lymphocytes in Immunopathogenesis. J Clin Immunol 21, 81–92 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011064007686
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011064007686