Abstract
Wind-tunnel experiments of drifting snow were carried out andsplash functions were formulated to describe probability distributions of vertical restitution coefficient, horizontal restitution coefficient and ejection number when a natural snow particle collided at a natural snow surface. The following results were obtained:
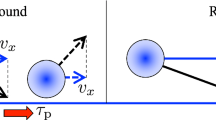
(1) The vertical restitution coefficient was usually larger than unity and decreased sharply with impact angle. At smaller impact angles around 5 degrees the vertical restitution coefficient exceeded a magnitude of ten.
(2) The horizontal restitution coefficient, ranging from -1 to 1.5, decreased with impact velocity, but was not clearly dependent on impact angle.
(3) The ejection number amounted to five per impact and increasedwith impact velocity.
(4) Three splash functions to express the probability distributions of the vertical restitution coefficient, horizontal restitution coefficient and ejection number were formulated, which will be used in future computer simulations of the snow drifting process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. S. and Haff, P. K.: 1988, 'Simulation of Eolian Saltation', Science 241, 820-823.
Anderson, R. S. and Haff, P. K.: 1991, 'Wind Modification and Bed Response during Saltation of Sand in Air', Acta Mechanica Suppl. 1, 21-51.
Araoka, K. and Maeno, N.: 1978, 'Measurements of Restitution Coefficients of Ice', Low Temperature Science Series A 36, 55-65 (in Japanese with English summary).
Bagnold, R. A.: 1941, The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes, Methuen, London, 265 pp.
Chepil, W. S.: 1945a, 'Dynamics of Wind Erosion: I. Nature of Movement of Soil by Wind', Soil Sci. 60, 305-320.
Chepil, W. S.: 1945b, 'Dynamics of Wind Erosion: II. Initiation of Soil Movement', Soil Sci. 60, 397-411.
Chepil, W. S.: 1945c, 'Dynamics of Wind Erosion: III. The Transport Capacity of the Wind', Soil Sci. 60, 475-480.
Dilley, J. P.: 1993, 'Energy Loss in Collisions of Icy Spheres: Loss Mechanism and Size-Mass Dependence', Icarus 105, 225-234.
Dilley, J. P. and Grawford, D.: 1996, 'Mass Dependence of Energy Loss in Collisions of Ice Sphere: An Experimental Study', J. Geophys. Res. 90, 9267-9270.
Hatzes, A. P., Bridges, F. G., and Lin, D. N. C.: 1988, 'Collisional Properties of Ice Spheres at Low Impact Velocities', Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 231, 1091-1115.
Higa, M., Arakawa, M., and Maeno, N.: 1996, 'Measurements of Restitution Coefficients of Ice at Low Temperatures', Planet. Space Sci. 44, 917-925.
Higa, M., Arakawa, M., and Maeno, N.: 1998, 'Size Dependence of Restitution Coefficients of Ice in Relation to Collision Strength', Icarus 133, 310-320.
Kind, R. J.: 1981, 'Snow Drifting', in D. M. Gray and D. H. Male (eds.), Handbook of Snow, Principles, Processes, Management and Use, Pergamon Press, Toronto, pp. 338-359.
Kobayashi, D.: 1972, 'Studies of Snow Transport in Low-Level Drifting Snow', Contributions from the Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido University, Series A 24, 1-58.
Kosugi, K., Nishimura, K., and Maeno, N.: 1995, 'Studies on the Dynamics of Saltation in Drifting Snow', The Report of the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention 54, 111-154.
Maeno, N., Naruse, R., Nishimura, K., Takei, I., Ebinuma, T., Kobayashi, S., Nishimura, H., Kaneda, Y., and Ishida, T.: 1985, 'Wind-Tunnel Experiments on Blowing Snow', Ann. Glaciol. 6, 63-67.
McEwan, I. K. and Willetts, B. B.: 1991, 'Numerical Model of the Saltation Cloud', Acta Mechanica Suppl. 1, 53-66.
Schmidt, D. S., Schmidt, R. A., and Dent, J. D.: 1998, 'Electrostatic Force on Saltating Sand', J. Geophys. Res. 103(D8), 8997-9001.
Sugiura, K.: 1999, Experimental Study of the Snow-Drift Saltation and Splash Process, Ph.D. Thesis, Hokkaido University, 160 pp.
Sugiura, K., Nishimura, K., and Maeno, N.: 1997, 'Velocity and Angle Distributions of Drifting Snow Particles near the Loose Snow Surface', Proceedings of the NIPR Symposium on Polar Meteorology and Glaciology 11, 108-116.
Supulver, K. D., Bridges, F. G., and Lin, D. N. C.: 1995, 'The Coefficient of Restitution of Ice Particles in Glancing Collisions: Experimental Results for Unfrosted Surfaces', Icarus 113, 188-199.
Ungar, J. E. and Haff, P. K.: 1987, 'Steady State Saltation in Air', Sedimentology 34, 289-299.
Werner, B. T.: 1990, 'A Steady-State Model of Wind-Blown Sand Transport', J. Geol. 98, 1-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiura, K., Maeno, N. Wind-Tunnel Measurements Of Restitution Coefficients And Ejection Number Of Snow Particles In Drifting Snow: Determination Of Splash Functions. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 95, 123–143 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002681026929
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002681026929