Abstract
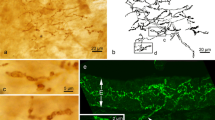
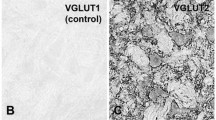
The hard palate of rodents is a mucous membrane covered by a keratinized epithelium that typically contains Merkel cell (MC)-neurite complexes. MCs have engendered considerable research activity because of their involvement in mechanoreception and possibly also Merkel cell carcinomas. MCs derive from the neural crest, differentiate under control of peripheral nerve factors, are enriched in large dense core vesicles, and secrete neuropeptides and other neuroactive molecules. Upon stimulation, MC-neurite complexes produce slowly adapting type I responses. Here we emphasize that the murine hard palate is a highly differentiated sensory region, as shown by intravital staining with a styryl dye and immunocytochemistry with antibodies to vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUTs). The entire palate contained densities of sensory endings and MC-neurite complexes, that nearly paralleled in abundance the vibrissal pads. MCs were differentially distributed in the murine palate; clusters of MCs were most abundant in the antemolar and intermolar rugae, while individual MCs were particularly enriched in the rugae at the mid-portion of the palate and in the postrugal field. VGLUT1, VGLUT2 and VGLUT3 were expressed in MCs throughout, although immunostained MCs were most frequently encountered in intermolar than antemolar rugae. The same transporters were also present in corpuscular endings at the summit of the rugae and in intraepithelial free nerve endings throughout the palate. VGLUTs presumably load glutamate into large dense core vesicles in MCs and into small clear vesicles in corpuscular and free nerve endings. The data suggest that glutamate release, or co-release, is likely to represent an important functional aspect of palatine Merkel cells and neighboring corpuscular and free nerve endings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
AIHARA, Y., MASHIMA, H., ONDA, H., HISANO, S., KASUYA, H., HORI, T., YAMADA, S., TOMURA, H., YAMADA, Y., INOUE, I., KOJIMA, I. & TAKEDA, J. (2000) Molecular cloning of a novel brain-type Na ( + )-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter. Journal of Neurochemistry 74, 2622–2625.
ALVAREZ, F. J., CERVANTES, C., VILLALBA, R., BLASCO, I., MARTINEZ-MURILLO, R., POLAK, J. M. & RODRIGO, J. (1988) Immunocytochemical analysis of calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in Merkel cells and cutaneous free nerve endings of cats. Cell and Tissue Research 254, 429–437.
ANGELSON, J. K., COCHILLA, A. J., KILIC, G., NUSSINOVITCH, I. & BETZ, W. J. (1999) Regulation of dense core release from neuroendocrine cells revealed by imaging single exocytotic events. Nature Neuroscience 2, 440–446.
BAUMANN, K. I., HAMANN, W. & LEUNG, M. S. (1990) Acute effects of neomycin on slowly adapting type I and type II cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the anaesthetized cat and rat. Journal of Physiology 425, 527–544.
BELLOCCHIO, E. E., REIMER, R. J., FREMEAU, R. T. & EDWARDS, R. H. (2000) Uptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles by an inorganic phosphate transporter. Science 289, 957–960.
BERTRAND, G., GROSS, R., PUECH, R., LOUBATIERES-MARIANI, M. M. & BOCKAERT, J. (1993) Glutamate stimulates glucagons secretion via an excitatory amino acid receptor of the AMPA subtype in rat pancreas. European Journal of Pharmacology 237, 45–50.
BETZ, W. J., MAO, F. & SMITH, C. B. (1996) Imaging exocytosis and endocytosis. Current Opinion in Neurobioloy 6, 365–371.
BEZZI, P., GUNDERSEN, V., GALBETE, J. L., SEIFERT, G., STEINHAUSER, C., PILATI, I. & VOLTERRA, A. (2004) Astrocytes contain a vesicular compartment that is competent for regulated exocytosis of glutamate. Nature Neuroscience 7, 613–620.
BYERS, M. & YEH, Y. (1984) Fine structure of subepithelial "free nerve endings'' and corpuscular trigeminal nerve endings in anterior hard palate of the rat. Somatosensory Research 1, 265–279.
CAHUSAC, P. M. (2003) Are glutamate receptors involved in transmission at the junction between Merkel cell and nerve terminal? In The Merkel cell: Structure-Development-Function-Cancerogenesis(edited by BAUMANN, K. I., HALATA, Z. & MOLL, I.) pp. 155–162. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
CHAN, E., YUNG, W. H. & BAUMANN, K. I. (1996) Cytoplasmic Ca 2 concentrations in intact Merkel cells of an isolated, functioning rat sinus hair preparation. Experimental Brain Research 108, 357–366.
CHOU, M. J., KOSAZUMA, T., TAKIGAWA, T., YAMADA, S., TAKAHARA, S. & SHIOTA, K. (2004).Glutamatergic phenotype of Merkel cells 373 Palatal shelf movement during palatogenesis: Afate map of the fetal mouse palate cultured in vitro. Anatomy & Embryology 208,19–25.
COGGESHALL, R. E. & CARLTON, S. M. (1998) Ultra-structural analysis of NMDA AMPA kainate receptors on unmyelinated and myelinated axons in the periphery. Journal of Comparative Neurology 391,78–86.
DE CAMILLI, P., HAUCKE, V., TAKEI, K. & MUGNAINI, E. (2001) The structure of synapses. In Synapses(edited by COWAN, W. M. AND SUDHOF, C. & STEVENS, C. F.) pp. 81–133. Baltimore and London: Johns Hopkins University Press.
DE GROOT, J., ZHOU, S. & CARLTON, S. M. (2000) Peripheral glutamate release in the hind paw following low and high intensity sciatic stimulation. Neuroreport 11, 497–502.
DIAMOND, J., MILLS, L. R. & MEAROW, K. M. (1988) Evidence that the Merkel cell is not the transducer in the mechanosensory Merkel cell-neurite complex. Progress in Brain Research 74,51–56.
EDWARDS, R. H. (1992) The transport of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles. Current Opinions in Neurobiology 2, 586–594.
ENGLISH, B., WANG, Z. Z., STEYNER, N., STENSAAS, L. J., MARTIN, H. & TUCKETT, R. P. (1992) Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in Merkel cells and their afferent neurons in touch domes from the hairy skin of rats. Anatomical Research 232,112–120.
ERICKSON, J. D., SCHAFER, M. K., BONNER, T. A., EIDEN, L. E. & WEIHE, E. (1996) Distinct pharmacological properties and distribution in neurons and endocrine cells of two isoforms of the human vesicular monoamine transporter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A. 93, 5166–5171.
FAGAN, B. M. & CAHUSAC, P. (2001) Evidence for glutamate receptor mediated transmission at mechanoreceptors in the skin. Neuroreport 12, 341–347.
FINDLATER, G. S., COOKSEY, E. J., ANAND, A., PAINTAL, A. S. & IGGO, A. (1987) The effect of hypoxia on slowly adapting type I (SAI) cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the cat and rat. Somatosensory Research 5,1–17.
FREMEAU, R. T., TROYER, M. D., PAHNER, I., NYGAARD, G. O., TRAN, C. H., REIMER, R. J., BELLOCCHIO, E. E., FORTIN, D., STORM-MATHISEN, J. & EDWARDS, R. H. (2001) The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron 2, 247–260.
FREMEAU, R. T., BURMAN, J., QUERSHI, T., TRAN, C. H., PROCTOR, J., JOHNSON, J., ZHANG, H., SULZER, D., COPENHAGEN, D. R., STORM-MATHISEN, J., REIMER, R. J., CHAUDHRY, F. A. & EDWARDS, R. H. (2002) Identification of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 suggests novel modes of signaling by glutamate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A.. 99, 14488–14493.
FREMEAU, R. T., KAM, K., QURESHI, T., JOHNSON, J., COPENHAGEN, D. R., STORM-MATHISEN, J., CHAUDHRY, F. A., NICOLL, R. A. & EDWARDS, R. H. (2004) Vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2 target two functionally distinct synaptic release sites.Science 304, 1815–1819.
FUKUDA, J., ISHIMINE, H. & MASAKI, Y. (2003) Long-term staining of live Merkel cells with FM dyes. Cell and Tissue Research 311 , 325–3
GARCIA-CABALLERO, T., PINTOS, E., GALLEGO, R., PARRADO, C., BLANCO, M., BJORNGHAGEN, V., FORTEZA, J. & BEIRAS, A. (2003) MOC-31/Ep-CAM immunoreactivity in Merkel cells and Merkel cell carcinomas. Histopathology 43, 480–484.
GASNIER, B. (2000) The loading of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles. Biochimie 82, 327–337.
GAUWEILER, B., WEIHE, E., HARTSCHUH, W. & YANAIHARA, N. (1988) Presence and coexistence of chromatogranin Aand multiple neuropeptides in Merkel cells of mammalian oral mucosa. Neuroscience Letters 89, 121–126.
GENEVER, P. G., MAXFIELD, S. J., KENNOVIN, G. D., MALTMAN, J., BOWGEN C. J., RAXWORTHY, M. J. & SKERRY, T. M. (1999) Evidence for a novel glutamate signaling pathway in keratinocyte. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 112, 337–342.
GOTTSCHALDT, K. M., IGGO, A. & YOUNG, D. V. (1973) Functional characteristics of mechanoreceptors in sinus hair follicles of the cat. Journal of Physiology 235, 287–315.
GOTTSCHALDT, K. M. & VAHLE-HINZ, C. (1981) Merkel cell receptors: Structure and transducer function. Science 214, 183–186.
GRAS, C., HERZOG, E., BELLENCHI, G. C., BERNARD, V., RAVASSARD, P., POHL, M., GASNIER, B., GIROS, B. & EL MESTIKAWY, S. (2002) A third vesicular glutamate transporter expressed by cholinergic and serotoninergic neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 22, 5442–5451.
GUHA, U., GOMES, W. A., SAMANTA, J., GUPTA, M., RICE, F. L. & KESSLER, J. A. (2004) Target-derived BMP signaling limits sensory neuron number and the extent of peripheral innervationin vivo. Development 131, 1175–1186.
HALATA, Z. & BAUMANN, K. I. (1999) Sensory nerve endings in the hard palate and papilla incisiva of the rhesus monkey. Anatomy & Embryology 199, 427–437.
HALATA, Z., COOPER, B. Y., BAUMANN, K. I., SCHWEGMANN, C. & FRIEDMANN, R. M. (1999) Sensory nerve endings in the hard palate and papilla incisiva of the goat. Experimental Brain Research 129, 218–229.
HALATA, Z., GRIM, M. & BAUMANN, K. I. (2003) Friedrich Sigmund Merkel and his "Merkel cell'', morphology, development, and physiology; review and new results. Anatomical Record 271, 225–239.
HARTSCHUH, W. & GRUBE, D. (1979) The Merkel cella memberof the APUDcell-system? Fluorescence and electron microscopic contribution to the neurotransmitter function of the Merkel cell granules. Archives of Dermatology Research 265,115–122.
HARTSCHUH, W. & WEIHE, E. (1988) Multiple messenger candidates and marker substances in the mammalian Merkel cell-axon complex, a light and electron microscopic immunohistochemical study. Progress in Brain Research 74, 181–187.
HARTSCHUH, W., WEIHE, E., YANAIHARA, N. & REINECKE, M. (1983) Immunohistochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) of variousmammals: Evidence for a neuromodulator function of the Merkel cell. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 81, 361–364.
HAYASHI, M., MORIMOTO, R., YAMAMOTO, M. A. & MORIYAMA, M Y. (2003a) Expression and localization of vesicular glutamate transporters in pancreatic islets, upper gastrointestinal tract, and testis. Journal of Hysto-chemistry & Cytochemistry 51, 1375–1390.
HAYASHI, M., OTSUKA, M., MORIMOTO, R., HIROTA, S., YATSUSHIRO, S., TAKEDA, J., YAMAMOTO, A. & MORIYAMA, Y. (2001) Differentiation-associated Na +-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter (DNPI) is a vesicular glutamate transporter in endocrine glutamatergic systems. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 43400–43406.
HAYASHI, M., YAMADA, H., UEHARA, S., MORIMOTO, R., MUROYAMA, A., YATSUSHIRO, S., TAKEDA, J., YAMAMOTO, A. & MORIYAMA, Y. (2003b) Secretory granule-mediated cosecretion of L-glutamate and glucagons triggers glutamatergic signal transmission in islets of Langerhans. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278, 1966–1974.
HE, L., TUCKETT, R. T. & ENGLISH, K. B. (2003) 5-HT2 and 3 receptor antagonists suppress the response of rat type 1 slowly adapting mechanoreceptor: An in vitro study. Brain Research 969, 230–236.
HERZOG, E., BELLENCHI, G. C., GRAS, C., BERNARD, W., RAVASSARD, P., BEDET, C., GASNIER, B., GIROS, B. & EL MESTIKAWY, S. (2001) The existence of a second vesicular glutamate transporter specifies cell populations of glutamatergic neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 21,RC181 (1–6).
HERZOG, E., GILLCHRIST, J., GRAS, C., MUZERELLE, A., RAVASSARD, P., GIROS, B., GASPAR, P. & EL MISTIKAWY, S. (2004) localization of VGLUT3, the vesicular glutamate transporter type 3, in the rat brain. Neuroscience 123, 983–1002.
HINOI, E., TAKARADA, T., UESHIMA, T., TSUCHIHASHI, Y. & YONEDA, Y. (2004a) Glutamate signaling in peripheral tissues. European Journal of Biochemistry 271,1–13.
HINOI, E., TAKARADA, T. & YONEDA, Y. (2004b) Glutamate signaling system in bone. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 91, 215–220.
HITCHCOCK, I. S., GENEVER, P. G. & CAHUSAC, P. M. (2004) Essential components for a glutamatergic synapse between Merkel cell and nerve terminal in rats. Neuroscience Letters 362, 196–199.
ICHIKAWA, H., MATSUO, S., SILOS-SANTIAGO, I., JAQUIN, M. F. & SUGIMOTO T. (2001) Developmental dependency of Merkel endings on trks in the palate. Molecular Brain Research 88, 171–175.
IGGO, A. & FINDLATER, G. S. (1984) A review of Merkel cell mechanisms. In Sensory Receptor Mechanisms(edited by HAMANN, W., IGGO, A.) pp. 117–131. Singapore: World Scientific Publ. Co.
IGGO, A. & MUIR, A. R. (1969) The structure and function of a slowly adapting touch corpuscle in hairy skin. Journal of Physiology 200, 763–796.
IKEDA, I., YAMASHITA, Y., ONO, T. & OGAWA, H. (1994) Selective phototoxic destruction of rat Merkel cells abolishes responses of slowly adapting type 1 mechanoreceptor units. Journal of Physiology 479, 247–256.
KANEKO, T., FUJIYAMA, F. & HIOCHI, H. (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of candidates for vesicular glutamate transporters in the rat brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology 444,39–62.
KINKELIN, I., BROCKER, E. B., KOLTZENBURG, M. & CARLTON, S. M. (2000) localization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in peripheral axons of human skin. Neuroscience Letters 283, 149–152.
KRUGER, L., LIGHT, A. R. & SCHWEIZER, F. E. (2003) Axonal terminals of sensory neurons and their morphological diversity. Journal of Neurocytology 132, 205–216.
KURZEN, H., KAUL, S., EGNER, U., DEICHMAN, M. & HARTSCHUH, W. (2003) Expression of MUC 1 and Ep-CAM in Merkel cell carcinomas: Implications for immunotherapy. Archives of Dermatology Research 295, 146–154.
LEUNG, M. S. & WONG, C. C. (2000) Expressions of putative neurotransmitters and neuronal growth related genes in Merkel cell-neurite complexes of the rat. Life Sciences 66, 1481–1490.
LI, J. L., XIONG, K. H., DONG, Y. L., FUJIYAMA, F., KANEKO, T. & MIZUNO, N. (2003) Vesicular glutamate transporters VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 in the trigeminal ganglion neurons of the rat with special reference to coexpression. Journal of Comparative Neurology 463, 212–220.
MERKEL, F. (1875) Tastzellen und Tastkoerperchen bei den Hausthieren und beim Menschen. Archiv f ¨ ur Mikroskopische Anatomie 11, 636–652.
MEYERS, J. R., MACDONALD, R. B., DUGGAN, A., LENZI, D., STANDAERT, D. G., CORWIN, J. & COREY, D. P. (2003) Lighting up the senses: FM1–43 loading of sensory cells through nonselective ion channels. Journal of Neuroscience 23, 4054–4065.
MILLS, L. R. & DIAMOND, J. (1995) Merkel cells are not the mechanosensory transducers in the touch dome of the rat. Journal of Neurocytology 24,117–134.
MILLS, L. R., NURSE, C. A. & DIAMOND J. (1989) The neural dependency of Merkel cell development in the rat: The touch domesand foot pads contrasted. Developmental Biology 136,61–74.
MOLL, I. & MOLL, R. (2003) Merkel cell carcinomaa short review. In: The Merkel Cell: Structure-Development-Function-Cancerogenesis.(edited by BAUMANN, K. I., HALATA, Z., MOLL, I. ) pp. 179–184. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
MORIMOTO, R., HAYASHI, M., YATSUSHIRO, S., OTSUKA, M., YAMAMOTO, A. & MORIYAMA, Y. (2003) Co-expression of vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUT1 and VGLUT2) and their association with synaptic-like microvesicles in rat pinealocytes. Journal of Neurochemistry 84, 382–391.
MORIYAMA, Y., HAYASHI, M., YAMADA, H., YATSUSHIRO, S., ISHIO, S. & YAMAMOTO, A. (2000) Synaptic-like microvesicles, synaptic vesicle counterparts in endocrine cells, are involved in a novel regulatory mechanism for the synthesis and secretion of hormones. Journal of Experimental Biology 203,117–125.
MORIYAMA, Y. & YAMAMOTO, A. (1995a) Microvesicles isolated from bovine pineal gland specifically.Glutamatergic phenotype of Merkel cells 375 accumulate L-glutamate. Federation of European Biochemical Societies Letters 367, 233–236.
MORIYAMA, Y. & YAMAMOTO , A. (1995b) Vesicular L-glutamate transporter in microvesicles from bovine pineal gland: Driving force, mechanism of chloride anion-activation, and substrate specificity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 22314–22320.
MUNGER, B. (1965) The intraepidermal innervation of the snout skin of the opossum. The Journal of Cell Biology 26, 79–97.
MUNGER, B. (1975) Cytology of mechanoreceptors in oral mucosa and facial skin of the rhesus monkey. In The Nervous System(edited by BRADY, R. O.) pp. 71–79. New York: Raven Press.
MURRAY, J. C. & SCHUTTE, B. C. (2004) Cleft palate: Players, pathways, and pursuits. Journal of Clinical Investigation 113, 1676–1678.
NUNZI, M. G., PISAREK, A. & MUGNAINI, E. (2004) Expression of vesicular glutamate transporters establishes the glutamatergic phenotype of the Merkel cell-neurite complex in the mouse palatine mucosa. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts30. (published electronically)
NUNZI, M. G., RUSSO, M. & MUGNAINI, E. (2003) Vesicular glutamate transporters VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 define two subsets of unipolar brush cells in organotypic cultures of mouse vestibulocerebellum. Neuroscience 122, 359–371.
NURSE, C. A. & DIAMOND, J. (1984) A fluorescence microscopic study of the development of rat touch domes and their Merkel cells. Neuroscience 11, 509–520.
NURSE, C. A. & FARRAWAY, L. (1989) Characterization of Merkel cells and mechanosensory axons of the rat by styryl pyridinium dyes. Cell & Tissue Research 255, 125–128.
NURSE, C. A., MEAROW, K. M., HOLMES, M., VISHEAU, B. & DIAMOND, J. (1983) Merkel cell distribution in the epidermis as determined by quinacrine fluorescence. Cell & Tissue Research 228,511–524.
OGAWA, H. (1996) The Merkel cell as a possible mechanoreceptor cell. Progress in Neurobiology 49, 317–334.
OTIS, T. S. (2001) Vesicular glutamate transporters in cognito. Neuron 29,11–14.
PACITTI, E. G. & FINDLATER, G. S. (1998) Calcium channel blockers and Merkel cells. Progress in Brain Research 74, 37–42.
RAMIERI, G., ANSELMETTI, G. C., BARACCHI, F., PANZICA, G. C., VIGLIETTI-PANZICA, C. & MODICA, R. (1990) The innervation of human teeth and gingival epithelium as revealed by means of an antiserum for protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5). American Journal of Anatomy 189, 146–154.
SCHAFER, M. K., VAROQUI, H., DEFAMIE, N., WEIHE, E. & ERICKSON, J. D. (2002) Molecular cloning and functional identification of mouse vesicular glutamate transporter 3 and its expression in subsets of novel excitatory neurons. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, 50734–50748.
SEKERKOVA, G., ZHENG, L., LOOMIS, P. A., CHANGYALEKET, B., WHITLON, D. S., MUGNAINI, E. & BARTLES, G. R. (2004) Espins are multifunctional cytoskeletal regulatory proteins in the microvilli of chemosensory and mechanosensory cells. Journal of Neuroscience 24, 5445–54456.
SENOK, S. S. & BAUMANN, K. I. (1997) Functional evidence for calcium-induced calcium release in isolated rat vibrissal Merkel cell mechanoreceptors. Journal of Physiology 500,29–37.
SENOK, S. S., GENEVER, P. G., CAHUSAC, P. M. & BAUMANN, K. I. (2003) Glutamate receptor-like immunoreactivity in vibrissal Merkel cells: In: The Merkel cell: Structure-Developmen-Function-Cancerogenesis.(edited by BAUMANN, K. I., HALATA, Z., MOLL, I.) pp. 163–168. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
SOMOGYI, J., BAUDE, A., OMORI, Y., SHIMIZU, H., EL MESTIKAWY, S., FUKAYA, M., SHIGEMOTO, R., WATANABE, M. & SOMOGYI, P. (2004) GABAergic basket cells expressing cholecystokinin contain vesicular glutamate transporter type 3 in their synaptic terminals in hippocampus and isocortex of the rat. European Journal of Neuroscience 19, 552–569.
SUGIYAMA, S. (1981) Cytochemistry of Merkel cell-neurite complex in mouse sinus hair follicles. In: Hair Research—Status and Future Aspects(edited by ORFANOS, C. E., MONTAGNA, W., & STUTTGEN, G.), pp 45–51, Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
SZEDER, V., GRIM, M., HALATA, Z. & SIEBER-BLUM, M. (2003) Neuronal crest origin of mammalian Merkel cells. Developmental Biology 253, 258–263.
TACHIBANA, T. (1995) The Merkel cell: Recent findings and unresolved problems. Archives of Histology & Cytology 58, 379–396.
TACHIBANA, T., ENDOH, M., KUMAKAMI, R. & NAWA, T. (2003) Immunohistochemical expression of mGLUR5, P2Y2 receptor, PLC-â 1, and IP3R-I and-II in Merkel cells in rat sinus hair follicles. Histochemistry & Cell Biology 120,1–19.
TACHIBANA, T., ENDOH, M. & NAWA, T. (2001) Immunohistochemical expression of G protein á-subunit isoforms in rat and monkey Merkel cell-neurite complexes. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 116: 205–213.
TACHIBANA, T., FUJIWARA, N., SATO, H. & NAWA, T. (1990) A comparative electron microscopic analysis of mechanoreceptors in the hard palate of the mouse (Mus musculus; Rodentia) and the musk shrew (Suncus murinus; Insectivora). Archives of Oral Biology 35, 949–956.
TACHIBANA, T. & NAWA, T. (2002) Recent progress in studies on Merkel cell biology. Anatomical Science International 77,26–33.
TACHIBANA, T., YAMAMOYO, H., TAKAHASHI, N., KAMEGAI, T., SHIBANAI, S., ISEKI, H. & NAWA, T. (1997) Polymorphism of Merkel cells in the rodent palatine mucosa; immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Archives of Histology & Cytology 60, 379–389.
TAKAMORI, S., MALHERBE, P., BROGER & CJAHN, R. (2002) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of human vesicular glutamate transporter 3. European Molecular Biology Organization 3, 798–803.
TAKAMORI, S., RHEE, J. S., ROSENMUND, C. & JAHN, R. (2000) Identification of a vesicular glutamate transporter that defines a glutamatergic phenotype in neurons. Nature 407, 189–194.
TAZAKI, M. & SUZUKI, T. (1998) Calcium inflow of hamster Merkel cells in response to hypoosmotic stimulation indicates a stretch activated ion channel. Neuroscience Letters 243,69–72.
TONG, Q., QUEDRAOGO, R. & KIRCHGESSNER, A. L. (2002) Localization and function of group III metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat pancreatic islets. American Journal of Physiology 282: 1324–1333.
USAMI, S. I., TAKUMI, T., MATSUBARA, A., FUJITA, S. & OTTERSEN, O. P. (2001) Neurotransmission in the vestibular endorgans: Glutamatergic transmission in the afferent synapses of hair cells. Biological Science Space 15, 367–370.
VAN GELE, M., BOYLE, G., COOK, A. L., BOONEFAES, T., ROTTIERS, P., VAN ROY, N., DE PAEPE, A., PARSONS, P. G., LEONARD, J. H. & SPELEMAN, F. (2004) Gene expression profiling reveals two distinct subtypes of Merkel cell carcinoma. In: The Merkel cell: Structure-Development-Function-Cancerogenesis. (edited by BAUMANN, K. I., HALATA, Z. & MOLL, I.) pp 195–202. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
VAROQUI, H., SCH ¨ AFER, M. K.-H., ZHU, H., WEIHE, E. & ERICKSON, J. D. (2002) Identification of the differentiation-associated Na + /Pit as a novel vesicular glutamate transporter expressed in a distinct set of glutamatergic synapses. Journal of Neuroscience 22, 142–155.
WEIHE, E., HARTSCHUH, W., SCH ¨ AFER, M. K.-H., ROMEO, H. & EIDEN, L. E. (1998) Cutaneous Merkel cells of the rat contain both dynorphin A and vesicular monoamine transporter type 1 (VMAT1) immunoreactivity. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 76: 334–339.
YAMADA, H., YATSUSHIRO, S., ISHIO, S., HAYASHI, M., NISHI, T., YAMAMOTO, A., FUTAI, M., YAMAGUCHI, A. & MORIYAMA, Y. (1998) Metabotropic glutamate receptors negatively regulate melatonin synthesis in rat pinealocytes. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 2056–2062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunzi, MG., Pisarek, A. & Mugnaini, E. Merkel cells, corpuscular nerve endings and free nerve endings in the mouse palatine mucosa express three subtypes of vesicular glutamate transporters. J Neurocytol 33, 359–376 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000044196.45602.92
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000044196.45602.92