Abstract
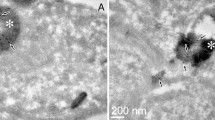
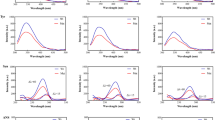
Aggregation of proteins in tissues is associated with several diseases, including Alzheimer's disease. It is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid β peptide (Aβ) in the extracellular spaces of the brain cells, resulting in neuronal death and other pathological changes. α-Crystallin, a small heat-shock protein in lens, and a peptide chaperone having the functional site sequence DFVIFLDVKHFSPEDLTVK of αA-crystallin may inhibit Aβ fibrillogenesis and toxicity. The peptide chaperone (mini-αA-crystallin), having an Aβ interacting domain and a complex solubilizing domain, was shown in previous studies to prevent aggregation of several proteins under denaturing conditions. In this in vitro study, using transmission electron microscopy and thioflavin T binding assay, we show that mini-αA-crystallin arrests the fibril formation of Aβ peptides. Mini-αA-crystallin also suppresses the toxic action of Aβ on rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The wide chaperoning capability of the peptide and its ability to inhibit amyloid fibril formation and suppress toxicity suggest that mini-αA-crystallin may serve as a universal chaperone in controlling diseases of protein aggregation, including Alzheimer's disease. (Mol Cell Biochem 267: 147–155, 2004)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glenner GG: Amyloid beta protein and the basis for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Clin Biol Res 317: 857–868, 1989
Inestrosa NC, Soto C: Molecular biology of the amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. An overview. Biol Res 25: 63–72, 1992
Selkoe DJ: Alzheimer's disease results from the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein. J Alzheimers Dis 3: 75–80, 2001
Iizuka T, Shoji M, Kawarabayashi T, Sato M, Kobayashi T, Tada N, Kasai K, Matsubara E, Watanabe M, Tomidokoro Y, Hirai S: Intracellular generation of amyloid beta-protein from amyloid beta-protein precursor fragment by direct cleavage with beta-and gamma-secretase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 218: 238–242, 1996
Sambamurti K, Greig NH, Lahiri DK: Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease. Neuromolecular Med 1: 1–31, 2002
Ferrer I, Puig B, Blanco R, Marti E: Prion protein deposition and abnormal synaptic protein expression in the cerebellum in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuroscience 97: 715–726, 2000
Riess O, Kruger R: Parkinson's disease — a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder. J Neural Transm Suppl 56: 113–125, 1999
Joachim CL, Mori H, Selkoe DJ: Amyloid beta-protein deposition in tissues other than brain in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 341: 226–230, 1989
Rhoades E, Agarwal J, Gafni A: Aggregation of an amyloidogenic fragment of human islet amyloid polypeptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1476: 230–238, 2000
Harding JJ: Cataract, Alzheimer's disease, and other conformational diseases. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 9: 10–13, 1998
Goldstein LE, Muffat JA, Cherny RA, Moir RD, Ericsson MH,Huang X, Mavros C, Coccia JA, Faget KY, Fitch KA, Masters CL, Tanzi RE, Chylack LT, Jr., Bush AI: Cytosolic beta-amyloid deposition and supranuclear cataracts in lenses from people with Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 361: 1258–1265, 2003
Mattson MP, Barger SW, Cheng B, Lieberburg I, Smith-Swintosky VL, Rydel RE: Beta-amyloid precursor protein metabolites and loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci 16: 409–414, 1993
Behl C, Davis JB, Lesley R, Schubert D: Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell 77: 817–827, 1994
Canevari L, Clark JB, Bates TE: Beta-amyloid fragment 25–35 selectively decreases complex IV activity in isolated mitochondria. FEBS Lett 457: 131–144, 1999
Tabner BJ, Turnbull S, El-Agnaf OM, Allsop D: Formation of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals from A(beta) and alpha-synuclein as a possible mechanism of cell death in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32: 1076–1083, 2002
Gabuzda D, Busciglio J, Yankner BA: Inhibition of beta-amyloid production by activation of protein kinase C. J Neurochem 61: 2326–2329, 1993
Citron M, Diehl TS, Capell A, Haass C, Teplow DB, Selkoe DJ: Inhibition of amyloid beta-protein production in neural cells by the serine protease inhibitor AEBSF. Neuron 17: 171–179, 1996
Buxbaum JD, Gandy SE, Cicchetti P, Ehrlich ME, Czernik AJ, Fracasso RP, Ramabhadran TV, Unterbeck AJ, Greengard P: Processing of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein: Modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6003–6006, 1990
Hock C, Konietzko U, Streffer JR, Tracy J, Signorell A, Muller-Tillmanns B, Lemke U, Henke K, Moritz E, Garcia E, Wollmer MA,Umbricht D, de Quervain DJ, Hofmann M, Maddalena A, Papassotiropoulos A, Nitsch RM: Antibodies against beta-amyloid slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 38: 547–554, 2003
Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Liao Z, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Mutter L, Soriano F, Shopp G, Vasquez N, Vandevert C, Walker S, Wogulis M, Yednock T, Games D, Seubert P: Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400: 173–177, 1999
Wood SJ, MacKenzie L, Maleeff B, Hurle MR, Wetzel R: Selective inhibition of Abeta fibril formation. J Biol Chem 271: 4086–4092, 1996
Tomiyama T, Shoji A, Kataoka K, Suwa Y, Asano S, Kaneko H, Endo N: Inhibition of amyloid beta protein aggregation and neurotoxicity by rifampicin. Its possible function as a hydroxyl radical scavenger. J Biol Chem 271: 6839–6844, 1996
Monji A, Tashiro K, Yoshida I, Kaname H, Hayashi Y, Matsuda K, Tashiro N: Laminin inhibits both Abeta40 and Abeta42 fibril formation but does not affect Abeta40 or Abeta42-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 266: 85–88, 1999
Pappolla M, Bozner P, Soto C, Shao H, Robakis NK, Zagorski M, Frangione B, Ghiso J: Inhibition of Alzheimer beta-fibrillogenesis by melatonin. J Biol Chem 273: 7185–7188, 1998
Hilbich C, Kisters-Woike B, Reed J, Masters CL, Beyreuther K: Substitutions of hydrophobic amino acids reduce the amyloidogenicity of Alzheimer's disease beta A4 peptides. J Mol Biol 228: 460–473, 1992
Tjernberg LO, Naslund J, Lindqvist F, Johansson J, Karlstrom AR, Thyberg J, Terenius L, Nordstedt C: Arrest of beta-amyloid fibril formation by a pentapeptide ligand. J Biol Chem 271: 8545–8548, 1996
Soto C, Kindy MS, Baumann M, Frangione B: Inhibition of Alzheimer's amyloidosis by peptides that prevent beta-sheet conformation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 226: 672–680, 1996
Hughes SR, Goyal S, Sun JE, Gonzalez-DeWhitt P, Fortes MA, Riedel NG, Sahasrabudhe SR: Two-hybrid system as a model to study the interaction of beta-amyloid peptide monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 2065–2070, 1996
Pallitto MM, Ghanta J, Heinzelman P, Kiessling LL, Murphy RM: Recognition sequence design for peptidyl modulators of beta-amyloid aggregation and toxicity. Biochemistry 38: 3570–3578, 1999
Watanabe K, Nakamura K, Akikusa S, Okada T, Kodaka M, Konakahara T, Okuno H: Inhibitors of fibril formation and cytotoxicity of beta-amyloid peptide composed of KLVFF recognition element and flexible hydrophilic disrupting element. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290: 121–124, 2002
Findeis MA, Musso GM, Arico-Muendel CC, Benjamin HW, Hundal AM, Lee JJ, Chin J, Kelley M, Wakefield J, Hayward NJ, Molineaux SM: Modified-peptide inhibitors of amyloid beta-peptide polymerization. Biochemistry 38: 6791–6800, 1999
Soto C, Sigurdsson EM, Morelli L, Kumar RA, Castano EM, Frangione B: Beta-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: Implications for Alzheimer's therapy. Nat Med 4: 822–826, 1998
Adessi C, Frossard MJ, Boissard C, Fraga S, Bieler S, Ruckle T, Vilbois F, Robinson SM, Mutter M, Banks WA, Soto C: Pharmacological profiles of peptide drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem 278: 13905–13911, 2003
Soto C: Plaque busters: Strategies to inhibit amyloid formation in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Today 5: 343–350, 1999
Sharma KK, Kumar RS, Kumar GS, Quinn PT: Synthesis and characterization of a peptide identified as a functional element in alphaA-crystallin. J Biol Chem 275: 3767–3771, 2000
Sharma KK, Kumar GS, Murphy AS, Kester K: Identification of 1,1?-bi(4-anilino)naphthalene-5,5?-disulfonic acid binding sequences in alpha-crystallin. J Biol Chem 273: 15474–15478, 1998
Kumar RS, Sharma KK: Chaperone-like activity of a synthetic peptide toward oxidized gamma-crystallin. J Pept Res 56: 157–164, 2000
Sreelakshmi Y, Sharma KK: Interaction of alpha-lactalbumin with mini-alphaA-crystallin. J Protein Chem 20: 123–130, 2001
LeVine H, 3rd: Quantification of beta-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T. Methods Enzymol 309: 274–284, 1999
Shearman MS: Toxicity of protein aggregates in PC12 cells: 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Methods Enzymol 309: 716–723, 1999
Pereira C, Santos MS, Oliveira C: Involvement of oxidative stress on the impairment of energy metabolism induced by A beta peptides on PC12 cells: Protection by antioxidants. Neurobiol Dis 6: 209–219, 1999
Takadera T, Sakura N, Mohri T, Hashimoto T: Toxic effect of a beta-amyloid peptide (beta 22–35) on the hippocampal neuron and its prevention. Neurosci Lett 161: 41–44, 1993
Teplow DB: Structural and kinetic features of amyloid beta-protein fibrillogenesis. Amyloid 5: 121–142, 1998
Esch FS, Keim PS, Beattie EC, Blacher RW, Culwell AR, Oltersdorf T, McClure D, Ward PJ: Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science 248: 1122–1124, 1990
Tjernberg LO, Callaway DJ, Tjernberg A, Hahne S, Lilliehook C, Terenius L, Thyberg J, Nordstedt C: A molecular model of Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation. J Biol Chem 274: 12619–126125, 1999
Tjernberg LO, Lilliehook C, Callaway DJ, Naslund J, Hahne S, Thyberg J, Terenius L, Nordstedt C: Controlling amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation with protease-stable ligands. J Biol Chem 272: 12601–12605, 1997
Ghanta J, Shen CL, Kiessling LL, Murphy RM: Astrategy for designing inhibitors of beta-amyloid toxicity. J Biol Chem 271: 29525–29528, 1996
Santhoshkumar P, Sharma KK: Phe71 is essential for chaperone-like function in alpha A-crystallin. J Biol Chem 276: 47094–47099, 2001
Azriel R, Gazit E: Analysis of the minimal amyloid-forming fragment of the islet amyloid polypeptide. An experimental support for the key role of the phenylalanine residue in amyloid formation. J Biol Chem 276: 34156–34161, 2001
Perez N, Sugar J, Charya S, Johnson G, Merril C, Bierer L, Perl D, Haroutunian V, Wallace W: Increased synthesis and accumulation of heat shock 70 proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 11: 249–254, 1991
Renkawek K, Voorter CE, Bosman GJ, van Workum FP, de Jong WW: Expression of alpha B-crystallin in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 87: 155–160, 1994
Kudva YC, Hiddinga HJ, Butler PC, Mueske CS, Eberhardt NL: Small heat shock proteins inhibit in vitro Abeta(1–42) amyloidogenesis. FEBS Lett 416: 117–121, 1997
Fonte V, Kapulkin V, Taft A, Fluet A, Friedman D, Link CD: Interaction of intracellular beta amyloid peptide with chaperone proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 9439–9444, 2002
Stege GJ, Renkawek K, Overkamp PS, Verschuure P, van Rijk AF, Reijnen-Aalbers A, Boelens WC, Bosman GJ, de Jong WW: The molecular chaperone alphaB-crystallin enhances amyloid beta neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262: 152–156, 1999
Liang JJ: Interaction between beta-amyloid and lens alphaB-crystallin. FEBS Lett 484: 98–101, 2000
Hatters DM, Lindner RA, Carver JA, Howlett GJ: The molecular chaperone, alpha-crystallin, inhibits amyloid formation by apolipoprotein C-II. J Biol Chem 276: 33755–33761, 2001
Yankner BA, Caceres A, Duffy LK: Nerve growth factor potentiates the neurotoxicity of beta amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 9020–9023, 1990
Pike CJ, Walencewicz AJ, Glabe CG, Cotman CW: In vitro aging of beta-amyloid protein causes peptide aggregation and neurotoxicity. Brain Res 563: 311–314, 1991
Walsh DM, Hartley DM, Kusumoto Y, Fezoui Y, Condron MM, Lomakin A, Benedek GB, Selkoe DJ, Teplow DB: Amyloid beta-protein fibrillogenesis. Structure and biological activity of protofibrillar intermediates. J Biol Chem 274: 25945–25952, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santhoshkumar, P., Sharma, K.K. Inhibition of amyloid fibrillogenesis and toxicity by a peptide chaperone. Mol Cell Biochem 267, 147–155 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000049373.15558.b8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000049373.15558.b8