Abstract
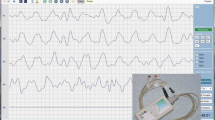
The aim of this study was to record gastric myoelectric activity using multichannel electrogastrography (EGG) and to determine if there are differences due to age, gender, body mass, and study location. In 61 normal subjects from four centers, fasting multichannel EGG was recorded for 1 h, followed by two 1-h postprandial recordings after a test meal. Variables assessed included dominant frequency (DF) and its power, percentage time in 2- to 4-cpm frequency, and percentage slow-wave coupling (%SWC). There were no significant differences in EGG parameters with respect to gender or age. Subjects with a BMI >25 had a decrease in the absolute DF power but a similar increase in the postprandial DF power. Subjects with a BMI >25 had a postprandial decrease in the %SWC compared to those with a BMI <25. There was a decrease in postprandial %SWC in European/Asian centers compared to American centers. In conclusion, multichannel EGG provides assessment of electrical slow-wave coupling in addition to determining dominant frequency, power, and percentage normal rhythm. This multicenter study of normal subjects shows similar multichannel EGG values among different genders and ages. Body mass and ethnicity may impact on some of the EGG values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilleri M, Hasler W, Parkman HP, Quigley EMM, Soffer E: Measurement of gastroduodenal motility in the GI laboratory. Gastroenterology 115:147-762, 1998
Parkman HP, Hasler WL, Barnett JL, Eaker EY: Electrogastrography: a document prepared by the gastric section of the American Motility Society Clinical GI Motility Testing Task Force. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:89-102, 2003
Verhagen MAMT, van Schelven LJ, Samsom M, Smout AJPM: Pitfalls in the analysis of electrogastrographic recordings. Gastroenterology 117:453-460, 1999
Couterier D, Roze C, Paolaggi J, Debray C: Electrical activity of the normal human stomach. Comparative study of recordings obtained from the serosal and mucosal sides. Am J Dig Dis 17:969-976, 1972
Hamilton JW, Bellahsene BE, Reicherlderfer M, Webster JH, Bass P: Human electrogastrograms—Comparison of surface and mucosal recordings. Dig Dis Sci 31:33-39, 1986
Familoni BO, Bowes KL, Kingma YJ, Cote KR: Can transcutaneous recordings detect gastric electrical abnormalities? Gut 32:141-146, 1991
Chen J, Schirmer BD, McCallum RW: Serosal and cutaneous recordings of gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with gastroparesis. Am J Physiol 266:G90-G98, 1994
Parkman HP, Harris AD, Miller MA, Fisher RS: Influence of age, gender, and menstrual cycle on the normal electrogastrogram. Am J Gastroenterol 91:127-133, 1996
Chen J, McCallum RW: Gastric slow wave abnormalities in patients with gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterology 87:477-482, 1992
Jebbink HJA, van Berge-Henegouwen GP, Bruijs PPM, Akkermans LMA, Smout AJPM: Gastric myoelectrical activity and gastrointestinal motility in patients with functional dyspepsia. Eur J Clin Invest 25:429-437, 1995
Pfaffenbach B, Adamek RJ, Kuhn K, Wegener M: Electrogastrography in healthy subjects—Evaluation of normal values, influence of age and gender. Dig Dis Sci 40:1445-1450, 1995
Lin Z, Eaker EY, Sarosiek I, McCallum RW: Gastric myoelectrical activity and gastric emptying in patients with functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2384-2389, 1999
Chen JDZ, Zhou X, Lin XM, Ouyang S, Liang J: Detection of gastric slow wave propagation from the cutaneous electrogastrogram. Am J Physiol 40:G424-G430, 1999
Lin X, Chen JDZ: Abnormal gastric slow waves in patients with functional dyspepsia assessed by multichannel electrogastrography. Am J Physiol 280:G1370-G1375, 2001
Chen J, Stewart WR, McCallum RW: Adaptive spectral analysis of episodic rhythmic variations in gastric myoelectric potentials. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40:128-135, 1993
Wang ZS, Elsenbruch S, Orr WC, Chen JDZ. Detection of gastric slow wave uncoupling from multi-channel electrogastrogram: validations and applications. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:457-465, 2003
Koch KL, Stern RM: Electrogastrographic data acquisition and analysis: The Penn State experience. In Electrogastrography—Principles and Applications. JZ Chen, RW McCallum (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1994, pp 45-74
Liang J, Chen JDZ: What can be measured from surface electrogastrography: Computer simulations. Dig Dis Sci 42:1331-1343, 1997
McNearney T, Lin X, Shrestha J, Lisse J, Chen JDZ: Characterization of gastric myoelectrical rhythms in patients with systemic sclerosis using multichannel surface electrogastrography. Dig Dis Sci 47:690-698, 2002
Mintchev MP, Otto SJ, Bowes KL: Electrogastrography can recognize gastric electrical uncoupling in dogs. Gastroenterology 112:2006-2011, 1997
Jones TF, Lin Z, Sarosiek I, Moncure M, McCallum RW: Assessment of gastric emptying and myoelectrical activity in the morbidly obese patients. Abstract presented at the 2001 meeting of the International EGG Society
Riezzo G, Chiloiro M, Guerra V: Electrogastrography in healthy children—Evaluation of normal values, influence of age, gender, and obesity: Dig Dis Sci 43:1646-1651, 1998
Chen J, Vandewalle J, Sansen W, van Cutsen E, Vantrappen G, Janssens J: Observation of the propagation direction of human electrogastric activity from cutaneous recordings. Med Biol Eng Comput 27:538-542, 1989
Tosetti C, Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V, et al.: Gastric emptying of solids in morbid obestiy. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 20:200-205, 1996
Verdich C, Madsen JL, Toubro S, et al.: Effect of major weight reduction on gastric emptying. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:899-905, 2000
Abell TL, Malagelada JR: Electrogastrography. Current assessment and future perspectives. Dig Dis Sci. 33:982-992, 1988
Stern RM, Hu S, Uijtdehaage SH, Muth ER, Xu LH, Koch KL: Asian hypersusceptibility to motion sickness. Hun Hered 46:7-14, 1996
Simonian HP, Panganamamula K, Chen JZ, Fisher RS, Parkman HP: Multichannel electrogastrography (EGG) in symptomatic patients: A single center study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:338, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonian, H.P., Panganamamula, K., Parkman, H.P. et al. Multichannel Electrogastrography (EGG) in Normal Subjects: A Multicenter Study. Dig Dis Sci 49, 594–601 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000026304.83214.50
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000026304.83214.50