Abstract
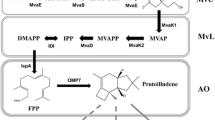
Mevalonate is biosynthesized from acetyl-CoA and metabolized to isoprenoid compounds in a wide variety of organisms although certain types of prokaryotes employ another route for isoprenoid biosynthesis (the non-mevalonate pathway). To establish a fermentative process for mevalonate production, enzymes for mevalonate synthesis from Enterococcus faecalis were expressed in Escherichia coli, a non-mevalonate pathway bacterium. Mevalonate was accumulated, indicating a redirection of acetate metabolism by the expressed enzyme. The recombinant E. coli produced 47 g mevalonate l−1 in 50 h of fed-batch cultivation in a 2 l jar fermenter; this is the highest titer ever reported demonstrating the superiority of E. coli in its ability of acetyl-CoA supply and its inability is degrade mevalonate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi J, Lee SY, Han K (1998) Cloning of the Alcaligenes latus poly-hydroxyalkanonate biosynthesis genes and use of these genes for enhanced production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 4897-4903.
Han MH, Yoon SS, Lee SY (2001) Proteome analysis of metabolically engineered Escherichia coli producing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). J. Bacteriol. 183, 301-308.
Hedl M, Sutherlin A, Wilding EI, Mazzulla M, McDevitt D, Lane P, Burgner II JW, Lehnbeuter KR, Stauffacher CV, Gwynn MN, Rodwell VW (2002) Enterococcus faecalis acetoacetyl-coenzyme A thiolase/3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, a dual-function protein of isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 184: 2116-2122.
Hong SH, Park SJ, Moon SY, Park JP, Lee SY (2003) In silico prediction and validation of the importance of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83: 854-863.
Kuzuyama T, Dairi T, Yamashita H, Shoji Y, Seto H (2004) Hetero-logous mevalonate production in Streptomyces lividans TK23. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 68: 931-934.
Martin VJJ, Pitera DJ, Withers ST, Newman JD, Keasling JD (2003) Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 796-802.
Nishi T (1988) Studies on the maximization of foreign gene expression in Escherichia coli. PhD thesis, Tokyo University, Tokyo.
Otsuka K, Itoh M, Yoshizawa K (1973) On the determination of mevalonic acid by thin-layer and gas chromatography. Agric. Biol. Chem. 37: 1013-1017.
Rohmer M, Seemann M, Horbach S, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (1996) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvate as precursors of isoprenic units in an alternative non-mevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118: 2564-2566.
Sambrook J, Fritsh EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sutherlin A, Hedl M, Sanchez-Neri B, Burgner II JW, Stauffacher CV Rodwell VW (2002) Enterococcus faecalis 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase, an enzyme of isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 184: 4065-4070.
Tamura G (1956) Hiochic acid, a new growth factor for Lactoba-cillus homohiochi and Lactobacillus heterohioch. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2: 431-434.
Wang F, Lee SY (1997) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by fed-batch culture of filamentation-suppressed recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 4765-4769.
Wolf ED, Hoffman HC, Aldrich EP, Skeggs RH, Wright DL, Folkers K (1956) â-Hydroxy-â-methyl-ä-valerolactone (divalonic acid), a new biological factor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78: 4498-4499.
Yamashita H, Shimada T, Sugiyama H EP392,346 (Oct. 17, 1990), (1991). Chem. Abstr. 114, 205566h.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabata, K., Hashimoto, SI. Production of mevalonate by a metabolically-engineered Escherichia coli . Biotechnology Letters 26, 1487–1491 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000044449.08268.7d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000044449.08268.7d