Abstract
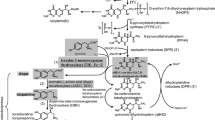
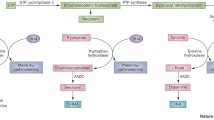
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) deficiency is generally considered as a cause of the autosomal recessive form of dopa-responsive dystonia, also known as Segawa disease. Clinical hallmarks comprise parkinsonian and other extrapyramidal symptoms. Biochemically the defect leads to the defective synthesis of catecholamines, in particular dopamine. The diagnosis relies on a characteristic pattern of biogenic amine metabolites exclusively in the CSF and can be confirmed by establishing a mutation in the TH gene. Here we present a patient meeting all diagnostic criteria, including a new homozygous mutation (926T>C) with confirmed parental heterozygosity, extrapyramidal symptoms, but atypical other symptoms with periodic neurological episodes observed every 4 days and unresponsive to dopa treatment. The CSF biochemical abnormalities were severe. Uncharacteristically, a strongly abnormal urinary catecholamine metabolite pattern was also consistently observed. The atypical presentation of this patient shows that the clinical and metabolic phenotype of TH deficiency is more variable than formerly thought, and that the condition should no longer be considered as a treatable disorder per se.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abeling NG, van Gennip AH, Overmars H, Voute PA (1984) Simultaneous determination of cathecholamines and metanephrines in urine by HPLC with flurometric detection. Clin Chim Acta 137: 211–226.
Abeling NGGM, VanGennip AH, Barth PG, Van Cruchten A, Westra M, Wuburg FA (1998) Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: a new case with a mild clinical presentation and unexpected laboratory findings. J Inherit Metab Dis 21: 3256–3258.
Bräutigam C, Wevers RA, Jansen RJT, et al (1998) Biochemical hallmarks of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Clin Chem 44: 1874–1904.
Braäutigam C, Steenbergen-Spanjers GCH, Hoffmann GF, et al (1999) Biochemical and molecular genetic characteristics of the severe form of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Clin Chem 45: 2073–2078.
Hyland K, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: diagnostic methodology. Clin Chem 38: 2405–2410.
Hyland K, Surtees RA, Rodeck C, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of a new inborn error of neurotransmitter amine synthesis. Neurology 42: 1980–1988.
Knappskog PM, Flatmark T, Mallet J, Lüdecke B, Bartholomé K (1995) Recessively inherited L-DOPA-responsive dystonia caused by a point mutation (Q381K) in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Hum Mol Genet 4: 1209–1212.
Lüdecke B, Dworniczak B, Bartholomé K (1995) A point mutation in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene associated with Segawa's syndrome. Hum Genet 95: 123–125.
Lüdecke B, Knappskog PM, Clayton PT, et al (1996) Recessively inherited L-DOPA-responsive parkinsonism in infancy caused by a point mutation (L205P) in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Hum Mol Genet 5: 1023–1028.
Sjösström R, Ekstedt J, Anggard E (1975) Concentration gradients of monoamine metabolites in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38: 666–668.
Stroomer AEM, Overmars H, Abeling NGGM, Van Gennip AH (1990) Simultaneous determination of acidic 3,4-dihydroxy-phenylalanine metabolites and 5-hydroxy-indole-3-acetic acid in urine by HPLC. Clin Chem 36: 1834–1837.
van den Heuvel LPWJ, Luiten B, Smeitink JAM, et al (1998) A common point mutation in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene in autosomal recessive L-dopa responsive dystonia (DRD) in the Dutch population. Hum Genet 102: 644–646.
Wevers RA, De Rijk-Van Andel JF, Bräutigam C, et al (1999) A review of biochemical and molecular genetic aspects of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency including a novel mutation (291delC). J Inherit Metab Dis 22: 364–373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Lonlay, P., Nassogne, M.C., van Gennip, A.H. et al. Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency unresponsive to L-dopa treatment with unusual clinical and biochemical presentation. J Inherit Metab Dis 23, 819–825 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026760602577
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026760602577