Abstract
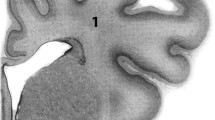
White matter injury is the most frequently observed brain lesion in preterm infants. The etiology remains unclear, however, both cerebral hypoperfusion and intrauterine infections have been suggested as risk factors. We compared the neuropathological outcome, including the effect on oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and microglia, following either systemic asphyxia or endotoxemia in fetal sheep at midgestation. Fetal sheep were subjected to either 25 minutes of umbilical cord occlusion or systemic endotoxemia by administration of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS O111:B4, 100 ng/kg, IV). Periventricular white matter lesions were observed in 2 of 6 asphyxiated fetuses, whereas the remaining animals showed diffuse injury throughout the subcortical white matter and neuronal necrosis in subcortical regions, including the striatum and hippocampus. LPS-treatment resulted in focal inflammatory infiltrates and cystic lesions in periventricular white matter in 2 of 5 animals, but with no neuron specific injury. Both experimental paradigms resulted in microglia activation in the white matter, damaged astrocytes, and loss of oligodendrocytes. These results show that the white matter at midgestation is sensitive to injury following both systemic asphyxia and endotoxemia. Asphyxia induced lesions in both white and subcortical grey matter in association with microglia activation, and endotoxemia resulted in selective white matter damage and inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Fujimoto, S., Yamaguchi, N., Togari, H., Wada, Y., and Yokochi, K. 1994. Cerebral palsy of cystic periventricular leukomalacia in low-birth-weight infants. Acta Paediatr. 83:397–401.
Volpe, J. J. 1998. Brain injury in the premature infant: Overview of clinical aspects, neuropathology, and pathogenesis. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 5:135–151.
Banker, B. Q. and Larroche, J.-C. 1962. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy: A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch. Neurol. 7:386–410.
Takashima, S. and Tanaka, K. 1978. Development of cerebrovascular architecture and its relationship to periventricular leukomalacia. Arch. Neurol. 35:11–16.
De Reuck, J. L. 1984. Cerebral angioarchitecture and perinatal brain lesions in premature and full-term infants. Acta Neurol. Scand. 70:391–395.
Back, S. A., Luo, N. L., Borenstein, N. S., Levine, J. M., Volpe, J. J., and Kinney, H. C. 2001. Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal white matter injury. J. Neurosci. 21:1302–1312.
Dammann, O. and Leviton, A. 1998. Infection remote from the brain, neonatal white matter damage, and cerebral palsy in the preterm infant. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 5:190–201.
Leviton, A. 1993. Preterm birth and cerebral palsy: Is tumor necrosis factor the missing link? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 35:553–558.
Deguchi, K., Oguchi, K., and Takashima, S. 1997. Characteristic neuropathology of leukomalacia in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Neurol. 16:296–300.
Nelson, K. B., Dambrosia, J. M., Grether, J. K., and Phillips, T. M. 1998. Neonatal cytokines and coagulation factors in children with cerebral palsy. Ann. Neurol. 44:665–675.
Reddy, K., Mallard, C., Guan, J., Marks, K., Bennet, L., Gunning, M., Gunn, A., Gluckman, P., and Williams, C. 1998. Maturational change in the cortical response to hypoperfusion injury in the fetal sheep. Pediatr. Res. 43:674–682.
Gilles, F. H., Averill, D. R., Jr., and Kerr, C. S. 1977. Neonatal endotoxin encephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2:49–56.
Young, R. S., Yagel, S. K., and Towfighi, J. 1983. Systemic and neuropathologic effects of E. coli endotoxin in neonatal dogs. Pediatr. Res. 17:349–353.
Yoon, B. H., Kim, C. J., Romero, R., Jun, J. K., Park, K. H., Choi, S. T., and Chi, J. G. 1997. Experimentally induced intrauterine infection causes fetal brain white matter lesions in rabbits. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 177:797–802.
Debillon, T., Gras-Leguen, C., Verielle, V., Winer, N., Caillon, J., Roze, J. C., and Gressens, P. 2000. Intrauterine infection induces programmed cell death in rabbit periventricular white matter. Pediatr. Res. 47:736–742.
Mallard, E. C., Gunn, A. J., Williams, C. E., Johnston, B. M., and Gluckman, P. D. 1992. Transient umbilical cord occlusion causes hippocampal damage in the fetal sheep. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 167:1423–1430.
Mallard, E. C., Williams, C. E., Gunn, A. J., Gunning, M. I., and Gluckman, P. D. 1993. Frequent episodes of brief ischemia sensitize the fetal sheep brain to neuronal loss and induce striatal injury. Pediatr. Res. 33:61–65.
Gilland, E., Bona, E., and Hagberg, H. 1998. Temporal changes of regional glucose use, blood flow, and microtubule-associated protein 2 immunostaining after hypoxia-ischemia in the immature rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18:222–228.
Braun, P. E., Sandillon, F., Edwards, A., Matthieu, J. M., and Privat, A. 1988. Immunocytochemical localization by electron microscopy of 2′3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase in developing oligodendrocytes of normal and mutant brain. J. Neurosci. 8:3057–3066.
Paneth, N., Rudelli, R., Monte, W., Rodriguez, E., Pinto, J., Kairam, R., and Kazam, E. 1990. White matter necrosis in very low birth weight infants: Neuropathologic and ultrasonographic findings in infants surviving six days or longer. J. Pediatr. 116:975–984.
Duggan, P. J., Maalouf, E. F., Watts, T. L., Sullivan, M. H., Counsell, S. J., Allsop, J., Al-Nakib, L., Rutherford, M. A., Battin, M., Roberts, I., and Edwards, A. D. 2001. Intrauterine T-cell activation and increased proinflammatory cytokine concentrations in preterm infants with cerebral lesions. Lancet 358:1699–1700.
Chamnanvanakij, S., Margraf, L. R., Burns, D., and Perlman, J. M. 2002. Apoptosis and white matter injury in preterm infants. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 5:184–189.
Volpe, J. J. 2001. Neurobiology of periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Pediatr. Res. 50:553–562.
Rees, S., Stringer, M., Just, Y., Hooper, S. B., and Harding, R. 1997. The vulnerability of the fetal sheep brain to hypoxemia at mid-gestation. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 103:103–118.
Matsuda, T., Okuyama, K., Cho, K., Hoshi, N., Matsumoto, Y., Kobayashi, Y., and Fujimoto, S. 1999. Induction of antenatal periventricular leukomalacia by hemorrhagic hypotension in the chronically instrumented fetal sheep. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 181:725–730.
Mallard, E. C., Waldvogel, H. J., Williams, C. E., Faull, R. L., and Gluckman, P. D. 1995. Repeated asphyxia causes loss of striatal projection neurons in the fetal sheep brain. Neuroscience 65:827–836.
De Haan, H. H., Gunn, A. J., Williams, C. E., and Gluckman, P. D. 1997. Brief repeated umbilical cord occlusions cause sustained cytotoxic cerebral edema and focal infarcts in near-term fetal lambs. Pediatr. Res. 41:96–104.
Mayhan, W. G. 1998. Effect of lipopolysaccharide on the permeability and reactivity of the cerebral microcirculation: Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Brain Res. 792:353–357.
Chao, C. C., Hu, S., and Peterson, P. K. 1995. Glia, cytokines, and neurotoxicity. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 9:189–205.
Hagberg, H., Gilland, E., Bona, E., Hanson, L. A., Hahin-Zoric, M., Blennow, M., Holst, M., McRae, A., and Soder, O. 1996. Enhanced expression of interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 messenger RNA and bioactive protein after hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats. Pediatr. Res. 40:603–609.
Kim, W. G., Mohney, R. P., Wilson, B., Jeohn, G. H., Liu, B., and Hong, J. S. 2000. Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: Role of microglia. J. Neurosci. 20:6309–6316.
Anthony, D. C., Bolton, S. J., Feam, S., and Perry, V. H. 1997. Age-related effects of interleukin-1 beta on polymorphonuclear neutrophil-dependent increases in blood-brain barrier permeability in rats. Brain 120:435–444.
Inage, Y. W., Itoh, M., and Takashima, S. 2000. Correlation between cerebrovascular maturity and periventricular leukomalacia. Pediatr. Neurol. 22:204–208.
Hardy, R. J. and Friedrich, V. L., Jr. 1996. Progressive remodeling of the oligodendrocyte process arbor during myelinogenesis. Dev. Neurosci. 18:243–254.
Fern, R. and Moller, T. 2000. Rapid ischemic cell death in immature oligodendrocytes: A fatal glutamate release feedback loop. J. Neurosci. 20:34–42.
Selmaj, K. W. and Raine, C. S. 1988. Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann. Neurol. 23:339–346.
Yonezawa, M., Back, S. A., Gan, X., Rosenberg, P. A., and Volpe, J. J. 1996. Cystine deprivation induces oligodendroglial death: Rescue by free radical scavengers and by a diffusible glial factor. J. Neurochem. 67:566–573.
Follett, P. L., Rosenberg, P. A., Volpe, J. J., and Jensen, F. E. 2000. NBQX attenuates excitotoxic injury in developing white matter. J. Neurosci. 20:9235–9241.
Bennet, L., Rossenrode, S., Gunning, M. I., Gluckman, P. D., and Gunn, A. J. 1999. The cardiovascular and cerebrovascular responses of the immature fetal sheep to acute umbilical cord occlusion. J. Physiol. 517:247–257.
Young, R. S., Hernandez, M. J., and Yagel, S. K. 1982. Selective reduction of blood flow to white matter during hypotension in newborn dogs: A possible mechanism of periventricular leukomalacia. Ann. Neurol. 12:445–448.
Ando, M., Takashima, S., and Mito, T. 1988. Endotoxin, cerebral blood flow, amino acids and brain damage in young rabbits. Brain Dev. 10:365–370.
Quan, N., Whiteside, M., and Herkenham, M. 1998. Time course and localization patterns of interleukin-1 beta messenger RNA expression in brain and pituitary after peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide. Neuroscience 83:281–293.
van Dam, A. M., Poole, S., Schultzberg, M., Zavala, F., and Tilders, F. J. 1998. Effects of peripheral administration of LPS on the expression of immunoreactive interleukin-1 alpha, beta, and receptor antagonist in rat brain. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 840:128–138.
Lacroix, S., Feinstein, D., and Rivest, S. 1998. The bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide has the ability to target the brain in upregulating its membrane CD14 receptor within specific cellular populations. Brain Pathol. 8:625–640.
Nadeau, S. and Rivest, S. 2000. Role of microglial-derived tumor necrosis factor in mediating CD14 transcription and nuclear factor kappa B activity in the brain during endotoxemia. J. Neurosci. 20:3456–3468.
Eklind, S., Mallard, C., Leverin, A. L., Gilland, E., Blomgren, K., Mattsby-Baltzer, I., and Hagberg, H. 2001. Bacterial endotoxin sensitizes the immature brain to hypoxic-ischaemic injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13:1101–1106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallard, C., Welin, AK., Peebles, D. et al. White Matter Injury Following Systemic Endotoxemia or Asphyxia in the Fetal Sheep. Neurochem Res 28, 215–223 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022368915400
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022368915400