Abstract
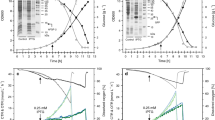
Production of recombinant proteins often interferes with the physiology of the host organism by causing stress responses. In recombinant Escherichia coli, the cellular content of ColE1-derived plasmids and, consequently, the synthesis of the constitutively synthesized plasmid-encoded proteins generally increases after a temperature upshift. Simultaneous induction of inducible recombinant proteins that are synthesized at high levels and tend to form inclusion bodies, however, attenuates the plasmid amplification. This phenomenon was observed using temperature- as well as IPTG-inducible expression systems. Thus, high-level recombinant gene expression in connection with inclusion body formation does not only interfere with host cell but also with plasmid-related functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey JE (1993) Host-vector interactions in Escherichia coli. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 48: 29-52.
Bentley WE,Mirjalili N,Andersen DC,Davis RH,Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the 'metabolic burden' associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 35: 668-681.
Carter P,Bedouelle H,Winter G (1985) Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucl. Acids Res. 13: 4431-4443.
Clewell DB (1972) Nature of ColE1-plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of chloramphenicol. J. Bacteriol. 110: 667-676.
Dong H,Nilsson L,Kurland CG (1995) Gratuitous overexpression of genes in Escherichia coli leads to growth inhibition and ribosome destruction. J. Bacteriol. 177: 1497-1504.
Estapé D,van den Heuvel J,Rinas U (1998) Susceptibility towards intramolecular disulphide-bond formation affects conformational stability and folding of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem. J. 335: 343-349.
Farewell A,Neidhardt FC (1998) Effect of temperature on in vivo protein synthetic capacity in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 180: 4704-4710.
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol. Adv. 13: 247-261.
Goff SA,Goldberg AL (1985) Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell 41: 587-595.
Harcum SW,Bentley WE (1999) Heat-shock and stringent responses have overlapping protease activity in Escherichia coli. Implications for heterologous protein yield. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 80: 23-37.
Hecker M,Schroeter A,Mach F (1983) Replication of pBR322 DNA in stringent and relaxed strains of Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 190: 355-357.
Hellmuth K,Korz DJ,Sanders EA,Deckwer W-D (1994) Effect of growth rate on stability and gene expression of recombinant plasmids during continuous and high cell density cultivation of Escherichia coli TG1. J. Biotechnol. 32: 289-298.
Hoffmann F,Rinas U (2000) Kinetics of heat-shock response and inclusion body formation during temperature-induced production of basic fibroblast growth factor in high-cell-density cultures of recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Prog. 16: 1000-1007.
Hoffmann F,Rinas U (2001) On-line estimation of the metabolic burden resulting from synthesis of plasmid-encoded and heatshock proteins by monitoring respiratory energy generation. Biotechnol. Bioeng., accepted.
Hoffmann F,Posten C,Rinas U (2001) Kinetic model of in vivo folding and inclusion body formation in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 72: 315-322.
Kaprálek F,Tichý PJ,Fábry M,Sedlácek J (1998) Effects of temperature and novobiocin on the expression of calf prochymosin gene and on plasmid copy number in recombinant Escherichia coli. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 43: 63-67.
Pilon AL,Yost P,Chase TE,Lohnas GL,Bentley WE (1996) High-level expression and efficient recovery of ubiquitin fusion proteins from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Prog. 12: 331-337.
Sambrook J,Fritsch EF,Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Schein CH (1989) Production of soluble recombinant proteins in bacteria. Bio/Technology 7: 1141-1149.
Seeger A,Schneppe B,McCarthy JEG,Deckwer WD,Rinas U (1995) Comparison of temperature-and isopropyl-β-D-thiogalacto-pyranoside-induced synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor in high-cell-density cultures of recombinant Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 17: 947-953.
Seo JH,Bailey JE (1986) Continuous cultivation of recombinant Escherichia coli: existence of an optimum dilution rate for maximum plasmid and gene product concentration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28: 1590-1594.
Studier FW,Moffat BA (1986) Use of the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 189: 113-130.
Teich A,Lin HY,Andersson L,Meyer S,Neubauer P (1998) Amplification of ColE1 related plasmids in recombinant cultures of Escherichia coli after IPTG induction. J. Biotechnol. 64: 197-210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, F., Rinas, U. Plasmid amplification in Escherichia coli after temperature upshift is impaired by induction of recombinant protein synthesis. Biotechnology Letters 23, 1819–1825 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012718200638
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012718200638