Abstract
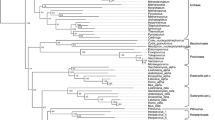
DNA viruses as their host cells require a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase (Pol) to faithfully replicate their genomic information. Large eukaryotic DNA viruses as well as bacterial viruses encode a specific Pol equipped with a proofreading 3′-5′-exonuclease, and other replication proteins. All known viral Pol belong to family A and family B Pol. Common to all viral Pol is the conservation of the 3′-5′-exonuclease domain manifested by the three sequence motifs Exo I, Exo II, and Exo III. The polymerase domain of family A and B Pol is clearly distinguishable. Family A Pol share 9 distinct consensus sequences, only two of them are convincingly homologous to sequence motif B of family B Pol. The putative sequence motifs A, B, and C of the polymerase domain are located near the C-terminus in family A Pol and more central in family B Pol. Thus, family A Pol show a significant greater spacing between the Exo III motif and the Pol motif A that is especially extended in the case of the mitochondrial Pol γ. From each host and virus family whenever possible the consensus sequences of two distantly related polymerase species were aligned for assessment of phylogenetic trees, using both maximum parsimony and distance methods, and evaluated by bootstrap analysis. Three alternative methods yielded trees with identical major groupings. A subdivision of viral family B Pol was achieved resulting in a branch with Pol carrying out a protein-primed mechanism of DNA replication, including adenoviruses, bacteriophages and linear plasmids of plant and fungal origin. Archaebacterial Pol and cellular Pol ∈ were consistently found at the base of this branch. Another major branch comprised alpha- and delta-like viral Pol from mammalian herpesviruses, fish lymphocystis disease virus, insect ascovirus, and chlorella virus. Due to a lower branch integrity Pol of T-even bacteriophages, poxviruses, African swine fever virus, fish herpesvirus, and baculoviruses were not clearly resolved and placed in alternate groupings. A composite and rooted tree of family A and B Pol shows that viral Pol with a protein-priming requirement represent the oldest viral Pol species suggesting that the protein-primed mechanism is one of the earliest modes of viral DNA replication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ito J. and Braithwaite D.K., Nucleic Acids Res 19, 4045-4057, 1991.
Braithwaite D.K. and Ito J., Nucleic Acids Res 21, 787-802, 1993.
Jung G., Leavitt M.C., Hsieh J.-C., and Ito J., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84, 8287-8291, 1987.
Bernad A., Zaballos A., Salas M., and Blanco L., EMBO J 6, 4219-4225, 1987.
Delaru M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., and Argos P., Protein Eng 3, 461-467, 1990.
Zhu W. and Ito J., Nucleic Acids Res 22, 5177-5183, 1994.
Boulet A., Simon M., Faye G., Bauer G.A., and Burgers P.M.J., EMBO J 8, 1849-1854, 1989.
Knopf K.W. and Strick R., in Becker Y. and Darai G. (eds), Frontiers of Virology, Vol 3. Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1994, pp. 87-135.
Cullmann G., Hindges R., Berchtold M.W., and Hübscher U., Gene 134, 191-200, 1993.
Wang T.S.-F., Annu Rev Biochem 60, 513-552, 1991.
Joyce C.M. and Steitz T. A., Annu Rev Biochem 63, 777-822, 1994.
Bernad A., Blanco L., Lázaro J.M., Martin G., and Salas M., Cell, 59, 219-228, 1989.
Blanco L., Bernad A., and Salas M., Gene 112, 139-144, 1992.
Kühn F.J.P. and Knopf C.W., J Biol Chem 271, 29245-29254, 1996.
Simon M., Giot L., and Faye G., EMBO J 10, 2165-2170, 1991.
Freemont P.S., Ollis D.L., Steitz T.A., and Joyce C.M., Proteins 1, 66-73, 1986.
Ruscitti T., Polayes D.A., Karu A.E., and Linn S., J Biol Chem 267, 16806-16811, 1992.
Soengas M.S., Esteban J.A., Lázaro J.M., Bernard A., Blasco M.A., Salas M., and Blanco L., EMBO J 11, 4227-4237, 1992.
Reha-Krantz L.J. and Nonay R.L., J Biol Chem 260, 27100- 27108, 1993.
Stocki S.A., Nonay R.L., and Reha-Krantz L.J., J Mol Biol 254, 15-28, 1995.
Gibbs J.S., Weisshart K., Digard P., De Bruyn-Kops A., Knipe D.M., and Coen D.M., Mol Cell Biol 11, 4786-4795, 1991.
Wang Y., Woodward S., and Hall J.D., J. Virol. 66, 1814-1816, 1992.
McGeoch D.J. and Cook S., J Mol Biol 238, 9-22, 1994.
McGeoch D.J., Cook S., Dolan A., Jamieson F.E., and Telford E.A.R., J Mol Biol 247, 443-458, 1995.
Doolittle R.F., Anderson K.L., and Feng D., In The Hierarchy of Life (Fernholm B., Bremer K., and Jornvall H., eds.), Elsevier Science Publisher, Amsterdam, 73-85, 1989.
Felsenstein, J., PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.572c, University of Washington, 1995.
Higgins D.G., Bleasby A.J., and Fuchs R., Comput Appl Biosci 8, 189-191, 1992.
Thompson J.D., Higgins D.G., and Gibson T.J., Nucleic Acids Res 22, 4673-4680, 1994.
Saitou N. and Nei M., Mol Biol Evol 4, 406-425, 1987.
Schwartz R.M. and Dayhoff M.O., In Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure (Dayhoff M.O., ed.) National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington D.C. Vol. 5,Supplement 3, 353-358, 1978.
Felsenstein J., Annu Rev Genet 22, 521-565, 1988.
Delius H. and Hofmann, B., Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 186, 13-31, 1994.
Argos P., Tucker A.D., and Philipson L., Virology 149, 208- 216, 1986.
Wong S.W., Wahl A.F., Yuan P.-M., Arai N., Pearson B.E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M.W., and Wang T.S.-F., EMBO J 7, 37-47, 1988.
Hwang C.B., Ruffner K.L., and Coen D.M., J Virol 66, 1774- 1776, 1992.
Freemont P.S., Friedman J.M., Beese L.S., Sanderson M.R., and Steitz T.A., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85, 8924-8928, 1988.
Derbyshire V., Freemont P.S., Sanderson M.R., Beese L.S., Friedman J.M., Joyce, C.M., and Steitz T.A., Science 240, 199- 201, 1988
Derbyshire V., Grindley N.D.F., and Joyce C.M., EMBO J 10, 17-24, 1991.
Blanco L., Bernad A., Blasco M.A., and Salas M., Gene (Amst), 100, 27-38, 1991.
Gibbs J.S., Chiou H., Bastow K., Cheng Y.C., and Coen D.M., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85, 6672-6676, 1988.
Copeland W.C. and Wang T.S.-F., J Biol Chem 268, 11028- 11040, 1993.
Copeland W.C. and Wang T.S.-F., J Biol Chem 268, 11041- 11049, 1993.
Eom S.H., Wang J., and Steitz, T.A., Nature 382, 278-281, 1996.
Hall J.D., Orth K.L., and Claus-Walker D., J Virol 70, 4816- 4818, 1996.
Polesky A.H., Dahlberg M.E., Benkovic S.J., Grindley N.D.F., and Joyce C.M., J Biol Chem 267, 8417-8428, 1992.
Blasco, M.A., Bernad A., Blanco L., and Salas M., J Biol Chem 266, 7904-7909, 1991.
Dorsky D.I. and Crumpacke C.S., J Virol 64, 1394-1397, 1990.
Marcy A.I., Hwang C.B.C., Ruffner K.L., and Coen D.M., J Virol 64, 5883-5890, 1990.
Dong Q., Copeland, W.C., and Wang T.S.-F., J Biol Chem 268, 24163-24174, 1993.
Blasco M.A., Lazaro J.M., Bernad A., Blanco L., and Salas M., J Biol Chem 267, 19427-19434, 1992.
Blasco M.A., Lazaro J.M., Blanco L., and Salas M., J Biol Chem 268, 16763-16770, 1993.
Lawyer F.C., Stoffel S., Saik R.K., Myambo K., Drummond R., and Gelfand D.H., J Biol Chem 264, 6427-6437, 1989.
Pellock B.J., Lu A., Meagher R.B., Weise M.J., and Miller L.K., Virology 216, 146-157, 1996.
Davison A.J., Virology 186, 9-14, 1992.
Bernard J. and Mercier A., Arch Virol 132, 437-442, 1993.
Woese C.R. and Fox G.E., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74, 5088- 5090, 1977.
Woese C.R., Microbiol Rev 51, 221-271, 1987.
Tidona, C.A. and Darai, G., Virology 230, 207-216, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knopf, C.W. Evolution of Viral DNA-Dependent DNA Polymerases. Virus Genes 16, 47–58 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007997609122
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007997609122
- DNA viruses
- Herpesviridae
- Adenoviridae
- Ascoviridae
- Baculoviridae
- Phycodnaviridae
- cytoplasmic DNA viruses
- Iridoviridae
- Poxviridae
- African swine fever virus
- fish lymphocystis disease virus
- vaccinia virus
- bacterial viruses
- bacteriophages
- Myoviridae
- Siphoviridae
- Mycoviridae
- Podoviridae
- Tectiviridae
- family A DNA polymerases
- family B DNA polymerases
- DNA polymerase α
- DNA polymerase β
- DNA polymerase δ
- DNA polymerase ∈
- DNA polymerase γ
- mitochondrial DNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- protein-primed mechanism of DNA replication
- proofreading activity
- exonuclease domain
- polymerase domain
- molecular phylogeny