Abstract
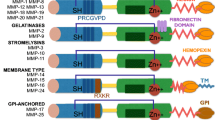
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are a group of zinc dependentenzymes which include the interstitial collagenases, stromelysins,gelatinases and membrane-type metalloproteinases. They are involvedin the remodelling and turnover of the extracellular matrixproteins. They play a role in wound healing and the pathogenesis ofarthritis. In malignancies they play a role in tumor invasion,metastasis and angiogenesis. A number of synthetic matrixmetalloproteinase inhibitors (MMPIs) have been developed forclinical use. In preclinical tumor models they have shown promisingactivity in achievinginhibition of MMPs and reducing tumor growth and metastatic spread.Some have also shown additive or synergistic effects with cytotoxicagents. Phase I and II studies in human subjects have defined themain side effects of these agents as beingmusculoskeletal pains or arthralgias. As they are cytostatic agentsrather than cytotoxic in activity conventional measurements ofradiological response for assessment are not applicable in trials.Biological activity has been demonstrated in certain cancers by theeffects on levels of tumor markers as surrogate markers of tumorresponse and also by a fibrotic stromal reaction seen in tumortissue. Newer agents have been developed withselective inhibition of certain MMPs in an attempt to reduce theside effects. A number of phase III human clinical trialsevaluating MMPs are being carried out at present but onlyone has been formally reported so far. This study suggested thatmarimastat had no survival advantage when compared to chemotherapywith gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Current trialsare assessing efficacy of MMPIs in maintenance of remission afterother modalities of therapy or in combination with cytotoxicagents. MMPs have also been demonstrated to play an important rolein the articular cartilage destruction seen in both rheumatoidarthritis and osteoarthritis. The use of MMPIs in both exvivoand in vivomodels have shown promising resultsand trials are in process to assess their potential role in thecontrol of articular destruction. The true therapeutic role ofMMPIs await the results of these randomized studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duffy M: The role of proteolytic enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 10: 145–155, 1992
Murphy G, Reynolds J, Hembrey R: Metalloproteinases and cancer invasion and metastasis (letter). Int J Cancer 44: 757–760, 1989
Meyer T, Hart IR: Mechanisms of tumour metastasis. Eur J Cancer 34: 214–221, 1998
Liotta L, Tryggvason K, Garbisa S, Hart I, Foltz C, Shafie S: Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature 284: 67–68, 1980
D'Errico A, Garbisa S, Liotta L, Castronovo V, Stetler-Stevenson W, Grigioni W: Augmentation of type IV collagenase, laminin receptor and Ki67 proliferation antigen associated with human colon, gastric and breast carcinoma progression. Mod Pathol 4: 239–246, 1991
Garbisa S, Scagliotti G, Masiero L, Di Francesco C, Caenazzo C, Onisto M, Micela M, Stetler-Stevenson W, Liotta L: Correlation of serum metalloproteinase levels with lung cancer metastasis and response to therapy. Cancer Res 52: 4548–4549, 1991
Engel G, Hesselmeyer K, Auer G, Backdahl M, Eriksson E, Linder S: Correlation between stromelysin 3 mRNA level and outcome of human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 58: 830–835, 1993
Bramhall S, Neoptolemos J, Stamp G, Lemoine N: Imbalance of expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of the matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in human pancreatic carcinoma. J Pathol 182: 347–355, 1997
Murray G, Duncan M, O'Neil P, McKay J, Melvin W, Fothergill J: Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in oesophageal cancer. J Pathol 185: 256–261, 1998
Brown P:Matrix metalloproteinases in gastrointestinal cancer. Gut 43: 161–163, 1998
Kugler A: Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Antican Res 19: 1589–1592, 1999
Khokha R, Zimmer M, Graham S, Lala P, Waterhouse P: Suppression of invasion by inducible expression of TIMP-1 in B 16-F10 melanoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 1017–1022, 1992
DeClerck Y, Perez N, Shimada H, Boone T, Langley K, Taylor S: Inhibition of invasion and metastasis in cells transfected with an inhibitor of metalloprotineases. Cancer Res 52: 701–708, 1992
Murphy A, Unsworth E, Stetler-Stevenson W: TIMP-2 inhibits bFGF-induced human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol 157: 351–358, 1993
Johnson J, Kim H, Chesler L, Bouck N, Polverini P: Inhibition of angiogenesis by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase. J Cell Physiol 160: 194–202, 1994
Werb Z, Vu TH, Rinkenberger JL, Coussens LM: Matrixdegrading proteases and angiogenesis during development and tumor formation. Apmis 107: 11–18, 1999
Liotta L, Steeg P, Stetley-Stevenson W: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 65: 327–336, 1991
Foulds L: The experimental study of tumor progression. Cancer Res 14: 327–339, 1964
Mignatti P, Tsuboi R, Robbins E, Rifkin D: In vitroangiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: Requirement for bFGF-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol 108: 671–682, 1989
Weidner N, Semple J, Welch W, Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive breast carcinoma. N Eng J Med 324: 1–8, 1991
Evans JD, Ghaneh P, Kawesha A, Neoptolemos JP: Role of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in pancreatic cancer. Digestion 58: 520–528, 1997
Duffy MJ, McCarthy K: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: prognostic markers and targets for therapy. Int J Oncol 12: 1343–1348, 1998
Abbas A, Lichtman A, Pober J: Cellular and Molecular Immunology: (3rd ed.) Philadelphia: WE Saunders, 1997, pp 157–159
Brooks PC: Role of integrins in angiogenesis. Eur J Canc 32A: 2423–2429, 1996
Brooks PC, Silletti S, von Schalscha TL, Friedlander M, Cheresh DA: Disruption of angiogenesis by PEX, a noncatalytic metalloproteinase fragment with integrin binding activity. Cell 92: 391–400, 1998
Deruygina E, Bourdon M, Reisfeld R, Strongin A: Remodeling of collagen matrix by human tumor cells requires activation and cell surface association of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Cancer Res 58: 3743–3750, 1998
Gilles C, Bassuk J, Pulyaeva H, Sage E, Foidart J-M, Thompson E: SPARC/Osteonectin induces matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 58: 5529–5536, 1998
Brown PD, Giavazzi R: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition: a review of anti-tumour activity. Ann Oncol 6: 967–974, 1995
Taraboletti G, Garofalo A, Belotti D, Drudis T, Borsolti P, Scanziani E, Brown P, Giavazzi R: Inhibition of angiogenesis and murine haemangioma growth by batimastat, a synthetic inhibitor of matrix metailoproteinases. J Natl Cancer Inst 87: 293–298, 1995
Sternlicht M, Lochter A, Sympson C, Huey B, Rougler J, Gray J, Pinkel D, Bissell M, Werb Z: The stromal proteinase MMP3/stromelysin-1 promotes mammary carcinogenesis. Cell 98: 137–146, 1999
Chambers AF, Matrisian LM: Changing views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 1260–1270, 1997
Gore M, A'Hern R, Stankiewicz M, Slevin M: Tumour marker levels during marimastat therapy (letter). Lancet 348: 263–264, 1996
Brown PD: Clinical studies with matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Apmis 107: 174–180, 1999
Chirivi RG, Garofalo A, Crimmin MJ, Bawden LJ, Stoppacciaro A, Brown PD, Giavazzi R: Inhibition of the metastatic spread and growth of B 16-BL6 murine melanoma by a synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Int J Cancer 58: 460–464, 1994
Watson SA, Morris TM, Parsons SL, Steele Rl, Brown PD: Therapeutic effect of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, batimastat, in a human colorectal cancer ascites model. Brit J Cancer 74: 1354–1358, 1996
Davies B, Brown P, East N, Crimmin M, Balkwill F: A synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor decreases tumour burden and prolongs survival of mice bearing human ovarian carcinoma xenograft. Cancer Res 56: 715–720, 1993
Macauley V, O'Byrne K, Saunders M, Salisbury A, Long L, Gleeson F, Ganeson T, Harris A, Talbot D: Phase I study of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BE-94) in patients with malignant pleural effusions (Abstract). Br J Cancer 71: 11, 1995
Talbot DC, Brown PD: Experimental and clinical studies on the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Eur J Cancer 32A: 2528–2533, 1996
Wojtowicz-Praga SM, Dickson RB, Hawkins MJ: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Invest New Drugs 15: 61–75, 1997
Galardy RE, Cassabonne ME, Giese C, Gilbert JH, Lapierre F, Lopez H, Schaefer ME, Stack R, Sullivan M, Summers B: Low molecular weight inhibitors in corneal ulceration. Am NY Acad Sci 732: 315–323, 1994
Tressler RJ, Wee J, Summers B et al.: Galardin, a potent metalloproteinase inhibitor, prolongs survival time in a B16-F10 melanoma experimental metastasis model (Abstract). Clin Exp Metastasis 12: 28, 1994
Millar AW, Brown PD, Moore J, Galloway WA, Cornish AG, Lenehan TJ, Lynch KP: Results of single and repeat dose studies of the oral matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor marimastat in healthy male volunteers. Brit J Clin Pharm 45: 21–26, 1998
Tierney GM, Griffin NR, Stuart RC, Kasem M, Lynch KP, Lury JT, Brown PD, Millar AW, Steele RJC, Parsons SL: A pilot study of the safety and effects of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor marimastat in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 35: 563–568, 1999
Nemunaitis J, Poole C, Primrose J, Rosemurgy A, Malfetano J, Brown P, Berrington A, Cornish A, Lynch K, Rasmussen H, Kerr D, Cox D.: Combined analysis of studies of the effects of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor marimastat on serum tumor markers in advanced cancer: selection of a biologically active and tolerable dose for longer-term studies. Clin Can Res 4: 1101–1109, 1998
Steward WP: Marimastat (BB2516): current status of development. Cancer Chemotherapy & Pharmacology 43: S56–S60 1999
Rasmussen HS, McCann PP: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition as a novel anticancer strategy: a review with special focus on batimastat and marimastat. Pharmacol Thera 75: 69–75, 1997
Hutchinson JW, Tierney GM, Parsons SL, Davis TR: Dupuytren's disease and frozen shoulder induced by treatment with a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. J Bone Joint Surg – British Volume 80: 907–908, 1998
Rasmussen H, Rugg T, Brookes C, Baillet M, Harris J: First placebo controlled safety review of marimastat: a potential new therapeutic class (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 193a, 1999
British Biotech PLC: Results of marimastat Study 128-pancreatic cancer monotherapy trial (Press release) February 1999, http://www.britishbiotech.com/news/british _biotech_news99.htm
Rosemurgy A, Buckels J, Charnley R, Winston R, Steward W, Staddon A, Curtis L, Rugg T, Rasmussen H: A randomized study comparing marimastat to gemcitabine as first line therapy in patients with non-resectable pancreatic cancer (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 261a, 1999
British Biotech Pie: Results of marimastat Study 145 in gastric cancer (Press release), July 1999, http://www.britishbiotech. com/news/british_biotech_news99.htm
Adams M, Thomas H: A phase I study of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, marimastat, administered concurrently with carboplatin, to patients with relapsed ovarian cancer (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Onc 17: 217a, 1998
Anderson I, Supko J, Eder J, Vasconvelles M, Shapiro G, Skarin A, Shipp M, Janicek M, Lynch C, Lopez M, Bowers M, Rasmussen H: Pilot Pharmacokinetic Study of Marimastat (MAR) in combination with carboplatin (C)/paclitaxel (T) in patients with metastatic or locally advanced inoperable nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 187a, 1999
Jones P, Elliot M, Dobbs N, Kakkar D, Ganesan T, Harris A: Phase I/II study of combination antiangiogenesis therapy with marimastat, captopril and fragmin (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 447a, 1999
Grochow LB: Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors (MMPI's) (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9 (Suppl 2): 11, 1998
Clemens GR, Detzer K, Bomhard E, von Keutz E: Pre-clinical drug safety profile for the antimetastatic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitory agent BAY 12-9566 (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9 (Suppl 2): 74, 1998
Hibner B, Bull C, Flynn C, Eberwein D, Garrison T, Casazza A, Carter C, Gibson N: Activity of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor BAY 12-9566 against murine subcutaneous metastatic in vivomodels (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 75, 1998
Flynn C, Bull C, Matherne C, Eberwein D, Gibson N, Hibner B: Anti-invasive and anti-metastatic activity of the novelMMP Inhibitor BAY 12-9566 in subcutaneous and orthotopic models using the human colon carcinoma, HCT 116 (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9 (Suppl 2): 75, 1998
Hirte H, Goel R, Bennett K, Elias I, Shah A, Seymour L: Phase I study of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) BAY 12-9566 in patients with advanced cancer (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 75, 1998
Goel R, Hirte H, Shah A, Major P, Waterfield S, Holohan S, Bennett K, Elias I, Seymour L: Phase I study of the metalloproteinase inhibitor Bayer 12-9566 (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 17: 217a, 1998
Erlichman C, Adjei A, Alberts S, Sloan J, Goldberg R, Pitot H, Rubin J: Phase I study of BAY 12-9566 – a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 17: 217a, 1998
Tolcher A, Rowinsky E, Rizzo J, Britten C, Siu L, Humphrey R, Smetzer L, Sorenson M, Von Hoff D, Eckhardt S: A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the oral matric metallopro399 teinase inhibitor BAY 12-9566 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 160a, 1999
Seymour L, Hirte H, Goel R, Moore M, Elias I, Kumor K, Humphrey R: Planned and completed NCIC CTG trials with bay 12-9566, a novel metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 76, 1998
Shalinsky D, Brekken J, Zou H, Bloom L, McDermott C, Appelt K: AG3340, a novel MMP inhibitor, has a superior therapeutic index to carboplatin in nude mice bearing chemoresistant human MV522 lung cancer tumors (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 73, 1998
Hande K, Wilding G, Ripple G, Fry J, Arzoomanian R, Dixon M, Yuen G, Collier M: A phase I study of AG3340, a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, in patients having advanced cancer (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 74, 1998
Wilding G, Small E, Ripple G, Keller M, Yuen G, Collier M: Phase I study of AG3340, a matrix metalloprotease inhibitor, in combination with mitoxantrone/prednisone in patients having advanced prostate cancer (Abstract). Ann Oncol 9: 74, 1998
D'Olimpio J, Hande K, Collier M, Michelson G, Paradiso L, Clendeninn N: Phase I study of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor AG3340 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin for the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 160, 1999
Collier M, Shepherd F, Ahmann F, Keller M, Michelson G, Paridiso L, Clendeninn N: A novel approach to studying the efficacy of AG3340, a selective inhibitor of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 482a, 1999
Dupont E, Savard PE, Jourdain C, Juneau C, Thibodeau A, Ross N, Marenus K, Maes DH, Pelletier G, Sauder DN: Antiangiogenic properties of a novel shark cartilage extract: potential role in the treatment of psoriasis. J Cutaneous Med Surg 2: 146–152, 1998
Latreille J, Riviere M, Batist G, Falardeau P, Dupont E: AE-941 (Neovastat), an inhibitor of angiogenesis: Phase I/II lung cancer clinical trial results. Ann Oncol 9, 1998
Riveriere M, Latreille J, Farlardeau, Batist G, Dupont E: AE-941 (Neovastat), an inhibitor of angiogenesis: Phase I/II cancer clinical trial results (Abstract). Cancer Invest 17, 1999
Levitt NC, Eskens F, Propper DJ, Harris AL, Denis L, Ganesan TS, Mather RA, McKinley L, Planting A, Talbot DC, Van Beurden V, Van der Burg M.: A phase one pharmacokinetic study of CGS27023A, a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (Abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 17: 213a, 1998
Igarashi N, Otani Y, Yokoyama T, Kimata M, Kubota T, Kitajima M: Combination therapy of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor and cytotoxic agent reduces peritoneal dissemination of gastric carcinoma model in vivo(Abstract). Proc Am Assoc Can Res 39: 308, 1998
Bottomley KM, Johnson WH, Walter DS: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in arthritis. J Enzyme Inhib 13: 79–101, 1998
Moldovan F, Pelletier J-P, Hambor J, Cloutier J-M, Martel-Pelletier J: Collagenase-3 (matrix metalloprotease 13) is preferentially localized in the deep later of human arthritic cartilage in situ: in vitromimicking effect by transforming growth factor beta. Arthritis Rheum 40: 1653–1661, 1997
Walakovits L, Moore V, Bhardwaj N, Gallick G, Lark M: Detection of stromelysin and collagenase in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and posttraumatic knee injury. Arthritis Rheum 35: 35–42, 1992
Zafarullah M, Pelletier J-P, Cloutier J-M, Martel-Pelletier J: Elevated metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase mRNA in human osteoarthritic synovia. J Rheumatol 20: 693–697, 1993
Hembry R, Bagga M, Reynolds J, Hamblen D: Immunolocalisation studies on six matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2, in synovia from patients with osteo-and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 54: 25–32, 1995
Bottomley K, Borkakoti N, Bradshaw D, Brown P, Broadhurst M, Budd J, Elliot L, Eyers P, Hallan T, Handa B, Hill C, James M.: Inhibition of bovine nasal cartilage degradation by selective matix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Biochem J 323: 483–488, 1997
Lewis E, Bishop J, Bottomley D, Bradshaw D, Brewster M, Broadhurst M, Brown P, Budd J, Elliott L, Greenham A, Johnson W, Nixon J.: Re-32-3555, an orally active collagenase inhibitor, prevents cartilage breakdown in vitroand in vivo. Brit J Pharm 121: 540–546, 1997
Brewster M, Lewis E, Wilson K, Greenham A, Bottomley K: Ro 32-3555, an orally active collagenase selective inhibitor, prevents structural damage in the STR/ORT mouse model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41: 1639–1644, 1998
Wood N, Aitken M, Harris S, Kitchener S, McClelland G, Sharp S: The tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the cartilage protective agent (R032-3555) in healthy male volunteers (Abstract). Brit J Clin Pharm 42: 676P–677P, 1996
Lollini L, Haller J, Eugui E, Womble S, Martin R, Campbell J, Hendricks T, Broka C, Moskowitz R, Van Wart H, Caulfield J: Disease modification by RS-130830, a collagenase-3 selective inhibitor in experimental osteoarthritis (OA) (Abstract). Arthritis Rheum 40: 341, 1997
Macchiarini P, Fontanini G, Hardin M, Squartini F, Angeletti C: Relation of neovascularisation to metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lancet 340: 145–146, 1992
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yip, D., Ahmad, A., Karapetis, C.S. et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors: Applications in Oncology. Invest New Drugs 17, 387–399 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006386406584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006386406584