Abstract
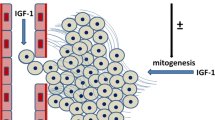
Experimental evidence suggests an important role of the type I IGF receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer development. Breast tumors and breast cancer cell lines express the IGF-IR. IGF-IR levels are higher in cancer cells than in normal breast tissue or in benign mammary tumors. The ligands of the IGF-IR are potent mitogens promoting monolayer and anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Interference with IGF-IR activation, expression, or signaling inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. In addition, recent studies established the involvement of the IGF-IR in the regulation of breast cancer cell motility and adhesion. We have demonstrated that in MCF-7 cells, overexpression of the IGF-IR promotes E-cadherin-dependent cell aggregation, which is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and prolonged survival in three-dimensional culture.
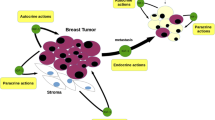
The expression or function of the IGF-IR in breast cancer cells is modulated by different humoral factors, such as estrogen, progesterone, IGF-II, and interleukin-1. The IGF-IR and the estrogen receptor (ER) are usually co-expressed and the two signaling systems are engaged in a complex functional cross-talk controlling cell proliferation.
Despite the convincing experimental evidence, the role of the IGF-IR in breast cancer etiology, especially in metastatic progression, is still not clear. The view emerging from cellular and animal studies is that abnormally high levels of IGF-IRs may contribute to the increase of tumor mass and/or aid tumor recurrence, by promoting proliferation, cell survival, and cell-cell interactions. However, in breast cancer, except for the well established correlation with ER status, the associations of the IGF-IR with other prognostic parameters are still insufficiently documented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubin R, Baserga R: Biology of disease. IGF IR. Its role in cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumorigenicity. Lab Invest 73:311–331, 1995
Dickson RB, Lippman ME: Growth factors in breast cancer. Endocr Rev 16:559–589, 1995
Lee AV, Yee D: Insulin-like growth factors and breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 49:415–421, 1995
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J: Type I IGF receptor in human breast disease. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22:59–67, 1992
Papa V, Gliozzo B, Clark GM, McGuire WL, Moore D, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Vigneri R, Goldfine ID, Pezzino V: Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 53:3736–3740, 1993
Pezzino V, Papa V, Milazzo G, Gliozzzo B, Russo P, Scalia PL: Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in breast cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci 784:189–201, 1996
Kleinman D, Karas M, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D, Philip M, Segev Y, Levy J, Sharoni Y: Modulation of insulin-like growth factor I receptors and membrane-associated IGF binding proteins in endometrial cancer cells by estradiol. Endocrinology 136:2531–2537, 1995
Collecchi P, Giannessi PG, Baldini E, Naccarato AG, Passoni A, Bevilaqua G, Conte PF: Effects of primary chemotherapy on biological parameters of locally advanced breast cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci 784:419–426, 1996
Railo MJ, Smitten K, Pekonen F: The prognostic value of insulin-like growth factor-I in breast cancer patients. Results of a follow-up study on 126 patients. Eur J Cancer 30A:307–311, 1994
Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP, Beuscart R, Demaille A: Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor I receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50:6931–6935, 1990
Foekens JA, Portengen H, Janssen M, Klijn JGM: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and insulin-like growth factor-1-like activity in human primary breast cancer. Cancer 63:2139–2147, 1989
Pekonen F, Partanen S, Makinen T, Rutanen E-M: Receptors for epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I and their relation to steroid receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 48:1343–1347, 1988
Foekens J, Portengen H, van Putten WLJ, Trapman AM, Reubi J-C, Alexieva-Figusch J, Klijn JGM: Prognostic value of receptors for insulin-like growth factor I, somatostatin, and epidermal growth factor in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:7002–7009, 1989
Berns EM, Klijn JGM, van Staveren IL, Portengen H, Foekens JA: Sporadic amplification of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor gene in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 52:1036–1039, 1992
Webster NJG, Resnic JL, Reichart DB, Strauss B, Haas M, Seely BL: Repression of the insulin receptor promoter by the tumor suppressor gene product p53 — a possible mechanism for receptor overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res 56:2781–2788, 1996
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, Henzel W, Le Bon T, Kathuria S, Chen E, Jacobs S, Francke U, Rachamandran J, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y: Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J 5:2503–2512, 1986
Soos MA, Nave BT, Siddle K: Immunological studies of type I IGF receptors and insulin receptors: characterization of hybrid and atypical receptor subtypes. Adv Exp Med Biol 343:145–157, 1993
Myers M, Sun XJ, White M: The IRS-1 signaling system. TIBS 19:289–293, 1994
He W, Craparo A, Zhu Y, O'Neill TJ, Wang LM, Pierce JH, Gustafson TA: Interaction of insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) with the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors. Evidence for two distinct phosphotyrosine-dependent interaction domains within IRS-2. J Biol Chem 271:11641–11645, 1996
Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Grignani F, McGlade J, Cavaool F, Forni G, Nicoletti I, Grignani F, Pawson T, Pelicci PG: A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell 70:93–104, 1992
Giorgetti S, Pelicci PG, Pelicci G, van Obberghen E: Involvement of Src-homology/collagen (SHC) proteins in signaling through the insulin receptor and the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Eur J Biochem 223:195–202, 1994
Lamothe B, Bucchini D, Jami J, Joshi RL: Interaction of p85 subunit of Pl-3 kinase with insulin and IGF-I receptors analyzed using the two-hybrid system. FEBS Letters 371:51–55, 1995
Morrione A, Valentinis B, Li S, Ooi JYT, Margolis B, Baserga R: Grb10: A new substrate of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res 56:3165–3167, 1996
O'Neill TJ, Rose DW, Pillay TS, Hotta K, Olefsky JM, Gustafson TA: Interaction of a GRB-IR splice variant (a human GRB10 homolog) with the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Evidence for a role in mitogenic signaling. J Biol Chem 271:22506–22513, 1996
Beitner-Johnson D, Blakesley VA, Shen-Orr Z, Jimenez M, Stannard B, Wang LM, Pierce J, LeRoith D: The proto-oncogene product c-Crk associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and 4PS. Modulation by insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and enhanced IGF-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 271:9287–9290, 1996
Argetsinger LS, Hsu GW, Myers MG, Billestrup N, White MF, Carter-Su C: Growth hormone, interferon-gamma, and leukemia inhibitory factor promoted tyrosyl phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem 270:14685–14692, 1995
Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Salcini AE, Romano A, Mele S, Borrello MG, Gegatto O, Di Fiore PP, Pelicci PG: Constitutive phosphorylation of SHC proteins in human tumors. Oncogene 11:899–907, 1995
Habib T, Herrera R, Decker SJ: Activators of protein kinase C stimulate association of SHC and the PEST tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem 269:25243–25246, 1994
Guvakova M, Surmacz E: Overexpressed IGF-I receptors reduce estrogen growth requirements, enhance survival, and promote E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion in human breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 231:149–162, 1997
Doerr M, Jones J: The roles of integrins and extracellular matrix proteins in the IGF-I-stimulated chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 271:2443–2447, 1996
Vuori K, Ruoslahti E: Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with integrins. Science 266:1576–1578, 1994
Giancotti F: Signal transduction by the α6/β4 integrin: charting the path between lammin binding and nuclear events. J Cell Science 109:1165–1172
Quinn KA, Treston AM, Unsworth EJ, Miller MJ, Vos M, Grimley C, Battey J, Mulshine JL, Cuttitta F: Insulin-like growth factor expression in human cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 271:11477–11483, 1996
Surmacz E, Burgaud J-L: Overexpression of IRS-1 in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 induces loss of estrogen requirements for growth and transformation. Clin Cancer Res 1:1429–1436, 1995
Ellis MJC, Singer C, Hornby A, Rasmussen A, Cullen KJ: Insulin-like growth factor mediated stromal-epithelial interactions in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 31:249–261, 1994
Arteaga C: Interference of the IGF-I system as a strategy to inhibit breast cancer growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22:101–106, 1992
Brunner N, Spang-Thomsen M, Cullen K: The T 61 human breast cancer xenograft. An experimental model of estrogen therapy of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 39:87–92, 1996
Ravera F, Miglietta L, Pirani P, Ferrini S, Favoni RE: Suramin-induced growth inhibition and insulin-like growth factor-I binding blockade in human breast carcinoma cell lines: potentially related events. Eur J Cancer 29A:225–230, 1993
Figucroa JA, Yee D: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: potential inhibitors of cancer cell growth. Drugs of the Future 19:477, 1994
Neuenschwander S, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D: Growth inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by stable expression of an insulin-like growth factor I receptor antisense ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 136:4298–4303, 1995
Manni A, Wright C, Buck H: Growth factor involvement in the multihormonal regulation of MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth in soft agar. Breast Cancer Res Treat 20:43–52, 1991
Nolan M, Jankowska L, Prisco M, Xu S, Guvakova M, Surmacz E: Differential roles of IRS-1 and SHC signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer, in press
Surmacz E, Sell C, Swantek J, Kato H, Roberts CT, LeRoith D, Baserga R: Dissociation of mitogenesis and transforming activity by C-terminal truncation of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Exp Cell Res 218:370–380, 1995
Bracke ME, Vyncke BM, Bruyneel EA, Vermeulen SJ, De Bruyne GK, Van Larebeke NA, Vleminck K, Van Roy FM, Mareel MM: Insulin-like growth factor I activates the invasion suppressor function of E-cadherin in MCF 7 human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 68:282–289, 1993
Rocha RL, Hilsenbeck SG, Jackson JG, Van Der Berg CL, Weng C-W, Lee AV, Yee D: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and insulin receptor substrate 1 in breast cancer: correlation with clinical parameters and disease-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 3:103–109, 1997
Stein D, Wu J, Fuqua SAW, Roonprapunt C, Yajnik V, D'Eustachio P, Moskow JJ, Buchberg AM, Osborne CK, Margolis B: The SH2 domain protein GRB-7 is co-amplified, overexpressed, and in a tight complex with HER2 in breast cancer. EMBO J 13:1331–1340, 1994
Daly RJ, Binder MD, Sutherland RL: Overexpression of GRB2 gene in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 9:2723–2727, 1994
Edelmann LA, Santos-Moore A, Clark JW, Frackelton AR Jr: Modulation of SHC tyrosine phosphorylation in breast cancer cell lines. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 35:A2666, 1994
Kleinman D, Karas M, Danilenko M, Arbell A, Roberts CT, LeRoith D, Levy J, Sharoni Y: Stimulation of endometrial cancer cell growth by tamoxifen is associated with increased insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I induced tyrosine phosphorylation and reduction in IGF binding proteins. Endocrinology 137:1089–1095, 1996
Van der Burg B, Rutteman GR, Blankenstein MA, de Latt SW, Zoelen EJJ: Mitogenic stimulation of human breast cancer cells in growth factor-defined medium: synergistic action of insulin and estrogen. J Cell Physiol 134:101–108, 1988
Stewart A, Johnson MD, May FEB, Westley BR: Role of insulin-like growth factors and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor in the estrogen-stimulated proliferation of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 265:21172–21178, 1990
Jordan CV: Molecular mechanisms of antiestrogen action in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 31:41–52, 1994
Freiss G, Rochefort H, Vignon F: Mechanism of 4-hydroxytamoxifen anti-growth factor activity in breast cancer cells: alterations of growth factor receptor binding sites and tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173:919–926, 1990
Kawamura I, Lacey E, Mizota T, Tsujimoto S, Nishigaki F, Manda T, Shimomura K: The effect of droloxifene on the insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated growth of breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res 14:427–432, 1994
De Cupis A, Noonan D, Pirani P, Ferrera A, Clerico L, Favoni RE: Comparison between novel steroid-like and conventional nonsteroidal antiestrogens in inhibiting oestradiol-and IGF-I-induced proliferation of human breast cancer-derived cells. Br J Pharm 116:2391–2400, 1995
Freiss G, Vignon F: Antiestrogens increase protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 8:1389–1396, 1994
McCotter D, van den Berg HW, Boylan M, McKibben B: Changes in insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and binding protein secretion associated with tamoxifen resistance and estrogen independence in human breast cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Letters 99:239–245, 1996
Migliaccio A, Di Domenico M, Castoria G, deFalco A, Bontempo P, Nola E, Auricchio F: Tyrosine kinase/p21ras/MAP-kinase pathway activation by estradiol-receptor complex in MCF-7 cells. EMBO J 15:1292–1300, 1996
Katzenellenbogen BS, Norman MJ: Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: interrelationships among insulin/insulin-like growth factor I, serum, and estrogen. Endocrinology 126:891–898, 1990
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhho Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P: Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494, 1995
Goldfine ID, Papa V, Vigneri R, Siiteri P, Rosenthal S: Progetsin regulation of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors in cultured human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22:69–79, 1992
Werner H, Karnieli E, Rauscher FJ, LeRoith D: Wild-type and mutant p53 differentially regulate transcription of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8318–8323, 1996
Costantino A, Vinci C, Mineo R, Frasca F, Pandini G, Milazzo G, Vigneri R, Belfiore A: Interleukin-1 blocks insulin and insulin-like growth factor-stimulated growth in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by inhibiting receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Endocrinology 137:4100–4107, 1996
Guvakova M, Surmacz E: Tamoxifen interferes with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 57:2606–2610, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surmacz, E., Guvakova, M.A., Nolan, M.K. et al. Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor function in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47, 255–267 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005907101686
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005907101686