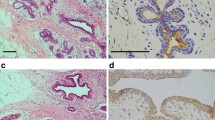
Abstract
A series of 80 female patients undergoing surgeryfor primary breast ductal infiltrating carcinoma not otherwisespecified (NOS) was immunohistochemically studied in order toverify any relationships between Proliferating Cell Nulear Antigen(PCNA) immunostaining, Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) immunoreactivity,and several clinicopathological predictors.Positive PCNA scores (> 20% of strongly immunopositivemalignant nuclei) were observed in neoplastic cells' nucleiin 13 tumors (16.25%) and were intimately associatedwith axillary nodal involvement (p=0.0131), relativelyhigh tumor grades (p=0.0016), increased tumorsize (p=0.0312), and low or negativelevels of estrogen receptors (p=0.0323). HSP70positive immunoexpression in malignant cells' cytoplasm (percentage ofHSP70 immunoreactive cells > 10%) was detected in33 samples (41.25%). It correlated significantly with presenceof axillary lymph nodal metastases (p=0.0033)and rather poor tumor differentiation (p=0.0014),whereas an association of borderline statistical significance emergedbetween HSP70 immunoreactivity and high progesterone receptor status(p=0.0637).PCNA positive immunostaining demonstrates the tumors' proliferative fractionand might be used as an indicator ofincreased malignant potential in breast cancer since itwas associated with four adverse prognosticators. HSP70 immunodetectionis a probable marker of the biological stressexperienced by breast cancer cells, since it wasrelated to relatively high tumor grades. Since bothproteins may potentially predict disease outcome, their prognosticsignificance must be validated by direct relation tosurvival. A multivariate statistical analysis including the variableswith which both proteins were associated will revealany possible independent prognostic value of PCNA andHSP70 immunostaining in local, ductal invasive breast cancerNOS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz GF, Schwarting R, Rabindranauth P, Finkel GC: Clinical applications of serum and tissue markers in malignant disease: breast cancer as the paradigm. Clin Chem 39 (11Pt2): 2404–2412, 1993
Marshall E: Search for a killer. Locus shifts from fats to hormones. Science 259: 618–623, 1993
O'Higgins N: Aspects of breast cancers. Chirurgie 118(5): 324–327, 1992
Hall PA, Levison DA, Woods AL: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections as index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol 162(4): 285–294, 1990
Benz CC, Keniry MA, Lord JM: Biochemical correlates of the antitumor and antimitochondrial properties of gossypol enantiomers. Mol Pharmacol 37(6): 840–847, 1990
Mivechi NF, Rossi JJ: Use of polymerase chain reaction to detect the expression of the MR 70,000 heat shock genes in control or heat shock leukemic cells as correlated to their heat response. Cancer Res 50(10): 2877–2884, 1990
Robbins SL: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 5th Ed. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994, pp 291–303
Porter-Jordan K, Lippman ME: Overview of the biologic markers of breast cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 8(1): 73–100, 1994
Ciocca DR, Fuqua SA, Lock-Lim S: Response of human breast cancer cells to heat shock and chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res 52: 3648–3654, 1992
Miller WR, Ellis IO, Sainsbury JRC, Dixon JM: ABC of breast diseases: Prognostic factors. BMJ 309: 1573–1576, 1994
Pelosi G, Bresaola E, Menacherry MJ, Manfrin E, Iannuci A: Methodological aspects of the immunostaining of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in cytospin preparations of MCF-7 cell line. Diagn Cytopathol 10(1): 82–85, 1994
Haerslev T, Jacobsen GK: Microwave processing for immunohistochemical demonstration of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue. APMIS 102(5): 395–400, 1994
Lazaris ACh, Davaris P, Nakopoulou L, Theodoropoulos GE, Koullias G, Golematis BCh: Correlation between immunohistochemical expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and flow cytometry parameters in colorectal neoplasia. Dis Colon Rectum 37(11): 1083–1089, 1994
Oda Y, Hashimoto H, Takeshita S, Tsuneyoshi M: The prognostic value of immunohistochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen in synovial sarcoma. Cancer 72(2): 478–484, 1993
Frierson HF Jr: Immunohistochemical analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in infiltrating ductal carcinomas: comparison with clinical and pathologic variables. Mod Pathol 6(3): 290–294, 1993
Betta PG, Battero G, Pavesi M, Pastormelo M, Bellinger D, Tallarida F: Cell proliferation in breast carcinoma assessed by a PCNA grading system and its relation to other prognostic variables. Surg Oncol 2(1): 59–63, 1993
Cummings MC, Jurnival CM, Parsons PG, Townsend E: PCNA immuno-staining in breast cancer. Aust N Z J Surg 63(8): 630–636, 1993
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Syrjanen K: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolabeling as a prognostic factor in axillary lymph node negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res 13(2): 533–538, 1993
Siitonen SM, Isola JJ, Rantala IS, Helin HJ: Intratumor variation in cell proliferation in breast carcinoma as determined by antiproliferating cell nuclear antigen monoclonal antibody and automated image analysis. Am J Clin Pathol 99(3): 226–231, 1993
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Papinaho S, Syrjanen K: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PC10) immunolabeling and other proliferation indices as prognostic factors in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 119(5): 288–294, 1993
Schimmelpenning H, Eriksson ET, Franzen B, Zetterberg A, Auer GU: Prognostic value of the combined assessment of proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunostaining and nuclear DNA content in invasive mammary carcinomas. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 423(4): 273–279, 1993
Royds JA, Stephenson TJ, Rees RC, Shorthouse AJ, Silcocks PB: Nm23 protein expression in ductal in situ and invasive human breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(9): 727–731, 1993
Tuccari G, Kizzo A, Muscara M, Giuffre G, Barresi G: PCNA/cyclin expression in breast carcinomas: its relationships with Ki-67, ER, PgR immunostainings and clinicopathologic aspects. Pathologica 85: 47–55, 1993
Botti G, Chiappetta G, D'Aiuto G et al.: PCNA/cyclin and P-glycoprotein as prognostic factors in locally advanced breast cancer. An immunohistochemical retrospective study. Tumori 79(3): 214–218, 1993
Ikeda N, Hirano T, Okuzawa K: Quantitative cytochemical analysis of T1 breast cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 20(6): 821–823, 1993
Gasparini G, Meli S, Pozza F, Cazzavillan S, Bevilacqua P: PC-10 antigen to proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is not related to prognosis in human breast carcinoma. Growth Regul 2(4): 145–150, 1992
Horigushi J, Iino Y, Takei H, Morishita Y, Nakajima T: Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Jpn J Clin Oncol 24(2): 79–84, 1994
Jaatela M, Wissing D: Heat shock proteins product cells from monocyte cytotoxicity: possible mechanism of self protection. J Exp Med 177(1): 231–236, 1993
Jaatela M: Overexpression of major heat shock protein HSP70 inhibits tumor necrosis factor induced activation of phospholipase A2. J Immunol 151(8): 4286–4294, 1993
Srivatsava PK, Udono H, Blachere NE, Li Z: Heat shock proteins transfer peptides during antigen processing and CTL priming. Immunogenetics 39(2): 93–98, 1994
Ciocca DR, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Fuqua SAW, Welch WJ, McGuire WL: Heat shock protein hsp70 in patients with axillary lymph node-negative breast cancer: Prognostic implications. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(7): 570–574, 1993
Koskinen PJ, Sistonen L, Evan G: Nuclear colocalization of cellular and viral myc proteins with HSP70 in myc overexpressing cells. J Virol 65: 842–851, 1991
Lehmann TA, Bennett WP, Metcalf RA: P53 mutations, ras mutations and p53-heat shock protein complexes in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 51: 4090–4096, 1991
Davidoff AM, Iglehart DI, Marks JR: Immune response to p53 is dependent upon p53/HSP70 complexes in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89: 3439–3442, 1992
Van Buskirk AM, De Nagel DC, Guagliardi LE: Cellular and subcellular distribution of PBP 72/74, a peptide-binding protein that plays a role in antigen processing. J Immunol 146(2): 500–506, 1991
Yougel RA, Elliot TJ: Stress proteins, infection and immune surveillance. Cell 59: 5–8, 1989
Kost SL, Smith DF, Sullivan WP: Binding of heat shock proteins to the avian progesterone receptor. Mol Cell Biol 9: 3829–3838, 1989
Edwards DP, Estes PA, Fadok VA: Heat shock alters the composition of heteromeric steroid receptor complexes and enhances receptor activity in vivo. Biochemistry 31(9): 2482–2491, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazaris, A.C., Chatzigianni, E.B., Panoussopoulos, D. et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and heat shock protein 70 immuno-localization in invasive ductal breast cancer not otherwise specified. Breast Cancer Res Treat 43, 43–51 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005706110275
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005706110275