Abstract
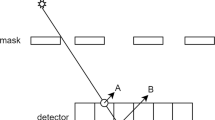
It is well known that inter-crystal scattering and penetration (ICS–P) are major spatial resolution limiting parameters in dedicated SPECT scanners with pixelated crystal. In this study, the effect of ICS–P on crystal identification in different crystal configurations was evaluated using GATE Monte Carlo simulation. A 99mTc pencil-beam toward central crystal element was utilized. Beam incident angle was assumed to vary from 0° to 45° in 5° steps. The effects of various crystal configurations such as pixel-size, pixel-gap, and crystal material were studied. The influence of photon energy on the crystal identification (CI) was also investigated. Position detection accuracy (PDA) was defined as a factor indicating performance of the crystal. Furthermore, a set of 99mTc point-source simulations was performed in order to calculate peak-to-valley (PVR) ratio for each configuration. The results show that the CsI(Na) manifests higher PDA than NaI(Tl) and YAP(Ce). In addition, as the incident angle increases, the crystal becomes less accurate in positioning of the events. Beyond a crystal-dependent critical angle, the PDA monotonically reduces. The PDA reaches 0.44 for the CsI(Na) at 45° beam angle. The PDAs obtained by the point-source evaluation also behave the same as for the pencil-beam irradiations. In addition, the PVRs derived from flood images linearly correlate their corresponding PDAs. In conclusion, quantitative assessment of ICS–P is mandatory for scanner design and modeling the system matrix during iterative reconstruction algorithms for the purpose of resolution modeling in ultra-high-resolution SPECT.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.R. Meikle, P. Kench, M. Kassiou et al., Small animal SPECT and its place in matrix of molecular imaging technologies. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 45–61 (2005). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/50/22/R01
F.J. Beekman, B. Vastenhouw, Design and simulation of a high-resolution stationary SPECT system for small animals. Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 4579–4592 (2005). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/49/19/009
M.T. Madsen, Recent advances in SPECT imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 48, 661–673 (2007). doi:10.2967/jnumed.106.032680
H. Zaidi, Recent developments and future trends in nuclear medicine instrumentation. Z. Med. Phys. 16, 5–17 (2006). doi:10.1078/0939-3889-00288
Y. Shao, S.R. Cherry, S. Siegel et al., A study of inter-crystal scatter in small scintillator arrays designed for high resolution PET imaging. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 43, 1938–1944 (1996). doi:10.1109/23.507250
M. Rasouli, M.R. Ay, A. Takavar et al., The influence of inter-crystal scattering on detection efficiency of dedicated breast gamma camera: a Monte Carlo study, in 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, vol 22 (2009), pp. 2451–2454. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-89208-3_588
F. Adibpour, M.R. Ay, S. Sarkar et al., Quantification of inter-crystal scattering and parallax effect in pixelated high-resolution small-animal gamma camera: a Monte Carlo study, in 5th Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biological Engineering, vol 35 (2011), pp. 708–711. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-21729-6_172
N. Zeraatkar, M.R. Ay, P. Ghafarian et al., Monte Carlo-based evaluation of inter-crystal scatter and penetration in the PET subsystem of three GE Discover PET/CT scanners. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 669, 508–514 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2011.07.049
N. Ghazanfari, S. Sarkar, G. Loudos et al., Quantitative assessment of crystal material and size on the performance of rotating dual-head small-animal PET scanner using Monte Carlo modeling. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 15, 33–39 (2012)
H. Zaidi, Relevance of accurate Monte Carlo modeling in nuclear medical imaging. Med. Phys. 26, 574–608 (2000). doi:10.1118/1.598559
S. Jan, G. Santin, D. Strul et al., GATE: a simulation toolkit for PET and SPECT. Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 4543–4561 (2004). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/49/19/007
V. Moji, N. Zeraatkar, M.H. Farahani et al., Performance evaluation of a newly developed high-resolution, dual-head animal SPECT system based on the NEMA NU1-2007 standard. J. Appl. Clin. Med. 15, 267–287 (2014). doi:10.1120/jacmp.v15i6.4936
S. Sajedi, N. Zeraatkar, V. Moji et al., Design and development of a high resolution animal SPECT scanner dedicated for rat and mouse imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 741, 169–176 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2014.01.001
N. Zeraatkar, S. Sajedi, M.H. Farahani et al., Resolution-recovery-embedded image reconstruction for a high resolution animal SPECT system. Phys. Med. 30, 774–781 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2014.05.013
M.J. Berger, J.H. Hubble, S.M. Seltzer et al. XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database. http://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Xcom/Text/XCOM.html
G.F. Knoll, Radiation detection and measurement, 4th edn. (Wiley, New York, 2010), pp. 223–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Research Center for Molecular and Cellular Imaging (RCMCI), Tehran University of Medical Sciences (No. 29885).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahani, H., Raisali, G., Kamali-Asl, A. et al. How crystal configuration affects the position detection accuracy in pixelated molecular SPECT imaging systems?. NUCL SCI TECH 28, 47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0206-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0206-y