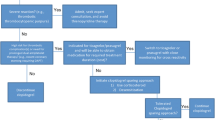
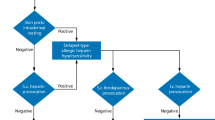
Abstract
Anticoagulation and antiplatelet drugs are among the most commonly used medical drugs. In addition to the long-established heparins, hirudins, coumarins and antiplatelet drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid, numerous novel and predominantly synthetic pharmacologic agents have come onto the market in recent years. These new agents act at various sites in coagulation and have significantly broadened treatment options. Whilst immunological hypersensitivity reactions are on the whole rare, they have a considerable impact on patient management when they do occur. The present overview discusses the currently known hypersensitivity reactions to anticoagulant and antiplatelet agents, with particular attention to the newer substance classes including P2Y12 inhibitors, glycoprotein IIb/IIIb receptor antagonists, direct factor Xa inhibitors and direct thrombin inhibitors.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- ADR:
-
Adverse drug reaction
- AERD:
-
Aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease
- AGEP:
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- ASA:
-
Acetylsalicylic acid
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- COOH:
-
Carboxyl group
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- DILI:
-
Drug induced liver injury
- DRESS:
-
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic systems
- EMA:
-
European Medicines Agency
- Fab:
-
Fragment antigen binding
- FDA:
-
US Food and Drug Administration
- GP:
-
Glycoprotein
- HACA:
-
Human antichimeric antibodies
- HAMA:
-
Human anti-murine antibodies
- HIT:
-
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- HMWH:
-
High molecular weight heparin (unfractionated heparin)
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- LMWH:
-
Low molecular weight heparin
- LT:
-
Leukotriene
- NSAID:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- PDE:
-
Phosphodiesterase
- PG:
-
Prostaglandin
- P2Y12:
-
Adenosine receptor
- SCAR:
-
Severe cutaneous adverse reaction
- TEN:
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- TIA:
-
Transient ischemic attack
- T-R:
-
Thromboxane receptor
- TxA2:
-
Thromboxane A2
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Scherer K, Tsakiris DA, Bircher AJ. Hypersensitivity reactions to anticoagulant drugs. Curr Pharm Des 2008;14:2863–73
Bircher AJ, Harr T, Hohenstein L, Tsakiris D. Hypersensitivity reactions to anticoagulant drugs: diagnosis and management options. Allergy 2006;61:1432–40
Kowalski ML, Makowska JS, Blanca M, Bavbek S, Bochenek G, Bousquet J et al. Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - classification, diagnosis and management: review of the EAACI/ENDA and GA2LEN/HANNA. Allergy 2011;66:818–29
McCann A. Antiplatelet therapy after coronary occlusion. Australian Prescriber 2007;30:92–96
Cheema AN, Mohammad A, Hong T, Jakubovic HR, Parmar GS, Sharieff W et al. Characterization of clopidogrel hypersensitivity reactions and management with oral steroids without clopidogrel discontinuation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58:1145–54
Gurbel PA, Jeong YH, Tantry US. Cutaneous clopidogrel hypersensitivity. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58:1455–6
Makkar K, Wilensky RL, Burke Julien M, Herrmann HC, Spinler SA. Rash with both clopidogrel and ticlopidine in two patients following percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents. Ann Pharmacother 2006;40:1204–7
Campbell KL, Cohn JR, Fischman DL, Walinsky P, Mallya R, Jaffrani W, Savage MP. Management of clopidogrel hypersensitivity without drug interruption. Am J Cardiol 2011;107:812–6
Lokhandwala J, Best PJM, Henry Y, Berger PB. Allergic reactions to clopidogrel and cross-reactivity to other agents. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2011;11:52–7
Comert A, Akgun S, Civelek A, Kavala M, Sarigül S, Yildirim T, Arsan S. Clopidogrel-induced hypersensitivity syndrome associated with febrile pancytopenia. Int J Dermatol 2005;44:882–4
Doogue MP, Begg EJ, Bridgman P. Clopidogrel hypersensitivity syndrome with rash, fever and neutropenia. Mayo Clin Proc 2005;80:1368–70
Phillips EJ, Knowles SR, Shear NH. Serum sickness-like reaction associated with clopidogrel. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2003;56:583
Meissner M, Bier C, Wolter M, Kaufmann R, Gille J. Suberythrodermic pustular psoriasis induced by clopidogrel. Br J Dermatol 2006;155:630
Ellerbroek JC, Cleveland MG. Clopidogrel-associated acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Cutis 2011;87:181–5
Shetty RK, Madken M, Naha K, Vivek G. Leucocytoclastic vasculitis as a late complication of clopidogrel therapy. BMJ Case reports 2013; doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007861
Erpolat S, Nazli Y, Colak N, Yenidunya S. Leucocytoclastic vasculitis associated with clopidogrel. Cut Ocular Toxicology 2012;31:171–3
Fernandez-Ruiz M, Carbonell-Porras A, Garcia-Reyne A, Lopez-Medrano F. Management of a hypersensitivitity reaction to thienopyridines: prasugrel-induced fever and hepatitis resolved after switching to clopidogrel. Rev Esp Cardiol 2012;65:767–76
Yosipovitch G, Rechavia E, Reinmesser M, David M, Tikva P. Adverse cutaneous reactions to ticlopidine in patients with coronary stents. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999;41:473–6
Kurokawa M, Nishijima S. Lichen planus-type drug eruption resulting from ticlopidine. Int J Dermatol 2005;44:436–7
Schmutz JL, Barbaud A, Trechot PF. Premier cas de toxidermie pigmentée fixe à la cétirizine (Zyrtec, Virlix) et à la ticlopidine (Ticlid) avec épidermotest positif. Ann Dermatol Venereol 2002;129:458
Ceylan G, Kirimli Æ, Akarsu M, Ündar B, Güneri S. Early ticlopidine-induced hepatic dysfunction, dermatitis and irreversible aplastic anaemia after coronary artery stenting. Am J Hematol 1998;59:260
Strippoli D, Russo G, Simonetti V, Motolese A. Lyell syndrome due to ticlopidine. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 2011;146:497–500
Pintor E, Sanmartin M, Azcona L, Hernandez R, Fernandey-Cruz A, Macaya C. Vasculitis leucocitoclastica en relacion con ticlopidina. Rev Esp Cariol 2001;54:114–6
Curtis BR, Divgi A, Garritty M, Aster RH. Delayed thrombocytopenia after treatment with abciximab: a distinct clinical entity associated with the immune response to the drug. J Thromb Haemost 2004;2:985–92
Tcheng JE, Kereiakes DJ, Lincoff AM, George BS, Kleiman NS, Sane DC et al. Abciximab readministration: results of the ReoPro Readministration Registry. Circulation 2001;104:870–5
Hawkins C, Gatenby P, McGill D. Severe hypotension complicating primary angioplasty: allergy to abciximab. Allergy 2003;58:688–9
Guzzo JA, Nichols TC. Possible anaphylactic reaction to abciximab. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent 1999;48:71–3
Iakovou Y, Mangina A, Milissari E, Cokkinos DV. Acute profound thrombocytopenia associated with anaphylactic reaction after abciximab therapy during percutaneous coronary angioplasty. Cardiology 2001; 95:215–6
Pharand C, Palisaitis DA, Hamel D. Potential anaphylactic shock with abciximab readministration. Pharmacotherapy 2002;22:380–3
Scherer K, Spoerl D, Bircher AJ. Adverse drug reactions to biologics. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2010;8(6):411–26
Moneret-Vautrin DA, Morisset M, Vignaud JM, Kanny G. T-cell mediated allergy to abciximab. Allergy 2002;57:269–70
Kang SY, Kim JY, Kim MY, Lee SY, Kim MH, Kim TW et al. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome induced by cliostazol and carbamazepine. J Dermatol 2012;39:723–4
Concepción Martín I, Fernández de Palencia Espinosa MA, Garrido Corro B, De La Rubia Nieto A. [Toxic epidermal necrolysis with fatal ending due to the concurrent use of carbamazepine, cilostazol and omeprazol: a case report]. Farm Hosp 2011;35:217–8
Weinmann P, Moretti JL, Leynadier F. Anaphylaxis-like reaction induced by dipyridamole during myocardial scintigraphy. Am J Med 1994;97:488
Salava A, Alanko K, Hyry H. Dipyridamole-induced ecxematous drug eruption with positive patch test reaction. Contact Dermatitis 2012;67:101–18
Jao T, Tsai TH, Jeng JS. Aggrenox (Asasantin retard)-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2008;67:264–5
Pinero-Saavedra M, Prados Castano M, Ortega Camarero M, Leguisamo Milla S. DRESS syndrome induced by acenocoumarol with tolerance to warfarin and dabigatran: a case report. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2013;24:576–8
Hohenstein E, Tsakiris D, Bircher AJ. Delayed-type hypersensitivity to the ultra-low-molecular-weight heparin fondaparinux. Contact Dermatitis 2004;51(3):149–51
Harr T, Scherer K, Tsakiris DA, Bircher AJ. Immediate type hypersensitivity to low molecular weight heparins and tolerance of unfractioned heparin and fondaparinux. Allergy 2006;61:787–8
Kishimoto TH, Viswanathan K, Ganguly T, Elankumaran S, Smith S, Pelzer K et al. Contaminated heparin associated with adverse clinical events and activation of the contact system. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2457–67
Lovecchio F. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Clinical Toxicology 2014;52:579–83
Godoy Monzon D, Iserson KV, Cid A, Vazquez JA. Oral thromboprophylaxis in pelvic trauma: a standardized protocol. J Emergency Med 2012;43:612–7
Yates J, Choudhry M, Keys G. A case report describing a suspected rivaroxaban hypersensitivity reaction in a surgical patient. J Clin Pharm Ther 2013;38:159–61
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, ed. FDA draft briefing document for the Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee (CRDAC). 2011. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/CardiovascularandrenalDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/ucm270796.pdf
To K, Reynolds C, Spinler SA. Rash associated with dabigatran etexilate. Pharmacotherapy 2013;33: e23–7
Caldeira D, Barra M, Santos AT, Abreu D de, Pinto FJ, Ferreira JJ, Costa J. Risk of drug-induced liver injury with the new oral anticoagulants: systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2014;100:550–6
Davies EM, Packard KA, Knezevich JT, Campbell JA. New and emerging anticoagulant therapy for atrial fibrillation and acute coronary syndrome. Pharmacotherapy 2011;31:975–1016
Bilen O, Teruya J. Complications of anticoagulation. Dis Mon 2012;58:440–7
Thorne K, Jayathissa S, Dee S, Briggs N, Taylor J, Reid S et al. Adherence and outcomes of patients prescribed dabigatran (Pradaxa) in routine clinical practice. Intern Med J 2014;44:261–5
Whitehead H, Boyd JM, Blais DM, Hummel J. Drug-induced exanthem following dabigatran. Ann Pharmacother 2011;45:e53
Tsoupris A, Tzimas T, Gkabrelas K, Akritidis N. Iron complex, dabigatran and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome: a case-report. J Clin Pharm Ther 2013;38:177–8
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, ed. 2010. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/CardiovascularRenal/DrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM247244.pdf
Keisu M, Andersson TB. Drug-induced liver injury in humans: the case of ximelagatran. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2010;196:407–18
Greinacher A, Lubenow N, Eichler P. Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions associated with lepirudin in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Circulation 2003;108:2062–5
Warkentin TE, Koster A. Bivalirudin: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2005;6:1349–71
Schrör K. Antiaggregatorische Therapie. In: Pötsch B, Madlener K, eds. Hämostaseologie, 2. Aufl. Heidelberg - Berlin: Springer; 2010. p 795–800
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cite this as Scherer Hofmeier K, Bircher AJ. Hypersensitivity reactions to modern antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs. Allergo J Int 2015; 24:58–66 DOI: 10.1007/s40629-015-0043-7
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofmeier, K.S., Bircher, A.J. Hypersensitivity reactions to modern antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs. Allergo J Int 24, 58–66 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-015-0048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-015-0048-2