Abstract
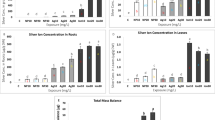
Impact of chemically synthesized silver nano-particles (AgNPs) was evaluated on nitrate, potassium, sodium and chloride content, and physiological and chemical characteristics of Lycopersicon esculentum Mill (tomato) plants. Silver nano-particles were synthesized by chemical reduction of metal salt precursor silver nitrate. The average size of the nano-particles was 50 nm and the shape was spherical. The results showed a significant decrease in nitrate and potassium content of treated tomato plants. An 24-fold increase in sodium content of treated tomato plants was observed as well as reduction in chloride content at the highest concentration. A significant increase in ascorbic acid and total phenol content was observed in treated tomato plants, which simulated the stress condition induced by AgNPs. On the other hand soluble sugar, photosynthetic pigments content, root and shoot length, and number of leaves decreased significantly in treated plants. Silver nano-particles induced oxidative stress as inferred from the magnitude of the changes found in the physiological and biochemical parameters tested. Silver nano-particles can intensify the antagonistic relationship of potassium/sodium, and nitrate/chloride in relation to each other. Also increase in non-enzymatic components is a strategy to modulate AgNPs toxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asharani, P. V., Wu, Y. L., Gong, Z., & Valiyaveettil, S. (2008). Toxicity of silver nano-particles in zebra fish models. Nanotechnology, 19, 255102–255110.
Ashley, M. K., Grant, M., & Grabov, A. (2006). Plant responses to potassium deficiencies: A role for potassium transport proteins. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 425–436.
Bazzaz, F. A., Carlson, R. W., & Rife, G. L. (1975). Inhibition of corn and sunflower photosynthesis lead. Physiologia Plantarum, 34, 326–329.
Benn, T. M., & Westerhoff, P. (2008). Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 4133–4139.
Carmen, I. U., Chithra, P., Huang, Q., Takhistov, P., Liu, S., & Kokini, J. L. (2003). Nanotechnology: A new frontier in food science. Food Technology, 57, 24–29.
Cataldo, D. A., Haroon, S. L., & Yougs, V. L. (1975). Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 6, 71–80.
Chaffei, C., Gouia, H., & Gorbel, M. H. (2003). Nitrogen metabolism of tomato under cadmium stress conditions. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 26, 1617–1634.
Choi, O., & Hu, Z. Q. (2008). Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 4583–4588.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for the determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Eshel, A., & Waisel, Y. (1979). Distribution of sodium and chloride in leaves of Suaedamonoica. Physiologia Plantarum, 46, 151–154.
Gill, P. K., Sharma, A. D., Singh, P., & Bhullar, S. S. (2001). Effect of various abiotic stresses on the growth soluble sugars and water relations of sorghum seedlings grown in light and darkness. Bulgarian Journal of Plant Physiology, 27, 72–84.
Gouia, H., Gorbel, M. H., & Meyer, C. (2000). Effects of cadmium on activity of nitrate reductase and on other enzymes of the nitrate assimilation pathway in bean. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 38, 629–638.
Gubbins, E. J., Batty, L. C., & Lead, J. R. (2011). Phytotoxicity of silver nano-particles to Lemna minor L. Environmental Pollution, 159, 1551–1559.
Hamada, A. M., & El-Enany, A. E. (1994). Effect of NaCl salinity on growth, pigment and mineral element contents, and gas exchange of broad bean and pea plants. Biologia Plantarum, 36, 75–81.
Hemalatha, S., Anburaj, A., & Francis, K. (1997). Effect of heavy metals on certain biochemical constituents and nitrate reductase activity in Orzya sativa L. seedlings. Journal of Environmental Biology, 18, 313–319.
Huang, G. Y., Wang, Y. S., Sun, C. C., Dong, J. D., & Sun, Z. X. (2010). The effect of multiple heavy metals on ascorbate, glutathione and related enzymes in two mangrove plant seedling (Kandeliacandel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies, 39, 11–25.
Jiang, H., Li, M., Chang, F., Li, W., & Yin, L. (2012). Physiological analysis of silver nano-particles and AgNO3 toxicity to Spirodela polyrrhiza. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31, 1880–1996.
Karami Mehrian, S., Heidari, R., & Rahmani, F. (2015). Effect of silver nano-particles on free amino acids content and antioxidant defense system of tomato plants. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 20, 257–263.
Karimi, R., Solhi, S., Solhi, M., & Safe, A. (2013). Effects of Cd, Pb and Ni on growth and macronutrients in Hordeumvulgare L and Brassica napus L. International Journal of Agronomy and Plant Production, 4, 76–81.
Kibria, M. G. (2008). Dynamics of cadmium and lead in some soils of Chittagong and their influx in some edible crops. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chittagong, Bangladesh.
Kim, S., Choi, J. E., Choi, J., Chung, K. H., Park, K., Yi, J., et al. (2009). Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nano-particles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicology in Vitro, 23, 1076–1084.
Krishnaraj, C., Jagan, E. G., Ramachandran, R., Abirami, S. M., Mohan, N., & Kalaichelvan, P. T. (2012). Effect of biologically synthesized silver nano-particles on Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) Wettst. Plant growth metabolism. Process Biochemistry, 47, 651–658.
Lichtenthaler, H. K., & Wellburn, A. R. (1985). Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf in different solvents. Biochemical Society Transactions, 11, 591–592.
Masclaux, C., Quilleré, I., Gallais, A., & Hirel, B. (2001). The challenge of remobilization in plant nitrogen economy: A survey of physio-agronomic and molecular approaches. Annals of Applied Biology, 138, 69–81.
Mazumdar, H. (2014). The impact of silver nano-particles on plant biomass and chlorophyll content. International Journal of Engineering and Science, 4, 12–20.
Miao, A. J., Schwehr, K. A., Xu, C., Zhang, S. J., Luo, Z. P., Quigg, A., et al. (2009). The algal toxicity of silver engineered nano-particles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3034–3041.
Michalak, A. (2006). Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 15, 523–530.
Mishra, A., & Choudhuri, M. A. (1999). Monitoring or phytotoxicity of lead and mercury from germination and early seedling growth induces two rice cultivars. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 114, 339–346.
Mittler, R. (2002). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends in Plant Science, 7, 405–410.
Navarro, E., Piccapietra, F., Wagner, B., Marconi, F., Kaegi, R., Odzak, N., et al. (2008). Toxicity of silver nano-particles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 8959–8964.
Omaye, S. T., Turnbull, J. D., & Sauberlich, H. E. (1979). Selected methods for the determination of ascorbic acid in animal cells, tissues and fluids. In D. B. McCormick & L. D. Wright (Eds.), Methods in enzymology (Vol. 62, pp. 3–11). New York: Academic Press.
Parekh, D., Purani, K. R., & Vastava, H. S. (1990). Inhibition of chlorophyll biosynthesis by cadmium in greening maize leaf segments. Biochemie Physiologie der Pflanzen, 186, 239–242.
Pradhan, S., Patra, P., Mitra, S., Dey, K. K., Jain, S., Sarkar, S., et al. (2014). Manganese nanoparticles, impact on non-nodulated plant as a potent enhancer in nitrogen metabolism and toxicity study both in vivo and in vitro. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62, 8777–8785.
Radniecki, T. S., Stankus, D. P., Neigh, A., Nason, J. A., & Semprini, L. (2011). Influence of liberated silver from silver nano-particles on nitrification inhibition of Nitrosomonas europaea. Chemosphere, 85, 43–49.
Ruffini-Castiglione, M., & Cremonini, R. (2009). Nano-particles and higher plants. Caryologia, 62, 161–165.
Salama, H. M. H. (2012). Effects of silver nano-particles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (Zea mays L.). International Research Journal of Biotechnology, 3, 190–197.
Sarita, S., Manisha, G., & Prakash, C. (1996). Bioaccumulation and biochemical effects of mercury in the plant Bacopamonnieri L. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 11, 105–112.
Sela, M., Tel-Or, E., Fritz, E., & Huttermann, A. (1988). Localization and toxic effects of cadmium, copper, and uranium in Azolla. Plant Physiology, 88, 30–36.
Seltenrich, N. (2013). Nanosilver, weighing the risks and benefits. Environmental Health Perspectives, 121, 220–225.
Sgherri, C., Cosi, E., & Navari-Izzo, F. (2003). Phenols and antioxidative status of Raphanussativus grown in copper excess. Physiologia Plantarum, 118, 21–28.
Sileikaite, A., Prosycevas, I., Pulso, J., Juraitis, A., & Guobiene, A. (2006). Analysis of silver nano-particles produced by chemical reduction of silver salt solution. Materials Science, 12, 287–291.
Singleton, V. L., & Rossi, J. A. (1965). Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture, 16, 144–158.
Smirnoff, N., & Wheeler, G. L. (2000). Ascorbic acid in plants, biosynthesis and function. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 19, 267–290.
Stampoulis, D., Sinha, S. K., & White, J. C. (2009). Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nano-particles to plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 9473–9479.
Tiwari, D. K., Dasgupta-Schubert, N., Villaseñor-Cendejas, L. M., Villegas, J., Carreto-Montoya, L., & Borjas-García, S. E. (2014). Interfacing carbon nanotubes (CNT) with plants, Enhancement of growth, water and ionic nutrient uptake in maize (Zea mays) and implications for nanoagriculture. Applied Nanoscience, 4, 577–591.
Trivedi, S., & Erdei, L. (1992). Effects of cadmium and lead on the accumulation of Ca2+ and K+ and on the influx and translocation of K+ in wheat of low and high K+ status. Physiologia Plantarum, 84, 94–100.
Van, A., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effect of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant, Cell and Environment, 13, 195–206.
Wakeel, A. (2013). Potassium–sodium interactions in soil and plant under saline-sodic conditions. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 176, 344–354.
Wang, Y., & Wu, W. H. (2010). Plant sensing and signaling in response to K+ deficiency. Molecular Plant, 3, 280–287.
White, P. J., & Broadley, M. R. (2001). Chloride in soils and its uptake and movement within the plant: A review. Annals of Botany (London), 88, 967–988.
Winkle-Shirley, B. (2002). Biosynthesis of flavonoids and effects of stress. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 5, 218–223.
Yasur, J., & Rani, P. (2013). Environmental effects of nanosilver, impact on castor seed germination, seedling growth, and plant physiology. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1798-3.
Yin, L., Cheng, Y., Espinasse, B., Colman, P. B., Auffan, M., Wiesner, M., et al. (2011). More than the ions, the effects of silver nano-particles on Loliummultiflorum. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 2360–2362.
Zhang, Y. (2013). Ascorbic acid in plants. Springer briefs in plant science. New York: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-4127-4_2.
Zhao, L., Peralta-Videa, J. R., Rico, C. M., Hernandez-Viezcas, J. A., Sun, Y., Niu, G., et al. (2014). CeO2 and ZnO nano-particles change the nutritional qualities of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62, 2752–2759.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Professors, R. De Lima, R. Heidari and K.H. Farhadi, Drs. F. Rahmani, M. Forough, R. Molaei and Mrs. S.H. Shiatey for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karami Mehrian, S., Karimi, N. Biological testing of the chemically synthesized silver nano-particles for nitrate, chloride, potassium and sodium contents, and some physiological and biochemical characteristics of tomato plants. Ind J Plant Physiol. 22, 48–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-016-0250-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-016-0250-3