Abstract
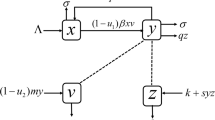
A model for combination therapy of pegylated interferon and lamivudine is presented in this paper. A critical drug efficacy in terms of the parameters of the model comprising of coupled ordinary differential equations is obtained. The dynamics of viral load is greatly impacted by the relation of the efficacies of the individual drugs vis-a-vis the critical efficacy. A control problem is formulated and solved numerically to obtain the optimal therapeutic regimen keeping in mind both biomedical goals and cost constraints.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciupe SM, Ribeiro RM, Nelson PW, Perelson AS (2007) Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Theor Biol 247(1):23–35
Lewin S, Walters T, Locarnini S (2002) Hepatitis B treatment: rational combination chemotherapy based on viral kinetic and animal model studies. Antivir Res 55(3):381–396
Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH, Chisari FV (2003) CD8+ T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 77(1):68–76
Ribeiro RM, Lo A, Perelson AS (2002) Dynamics of hepatitis B virus infection. Microbes Infect 4(8):829–835
Dahari H, Shudo E, Ribeiro RM, Perelson AS (2009) Modeling complex decay profiles of hepatitis B virus during antiviral therapy. Hepatology 49(1):32–38
Murray JM, Purcell RH, Wieland SF (2006) The half-life of hepatitis B virions. Hepatology 44(5):1117–1121
Asselah T, Lada O, Moucari R, Martinot M, Boyer N, Marcellin P (2007) Interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Clin Liver Dis 11(4):839–849
Schalm SW, Heathcote J, Cianciara J, Farrell G, Sherman M, Willems B, Dhillon A, Moorat A, Barber J, Gray DF (2000) Lamivudine and alpha interferon combination treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: a randomised trial. Gut 46(4):562–568
Severini A, Liu XY, Wilson JS, Tyrrell DL (1995) Mechanism of inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus polymerase by (-)-beta-L-\(2^{\prime },3^{\prime }\)-dideoxy-\(3^{\prime }\)-thiacytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39(7):1430–1435
Zoulim F (2004) Mechanism of viral persistence and resistance to nucleoside and nucleotide analogs in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Antivir Res 64(1):1–15
Lewin SR, Ribeiro RM, Walters T, Lau GK, Bowden S, Locarnini S, Perelson AS (2001) Analysis of hepatitis B viral load decline under potent therapy: complex decay profiles observed. Hepatology 34(5):1012–1020
Dahari H, Lo A, Ribeiro RM, Perelson AS (2007) Modeling hepatitis C virus dynamics: liver regeneration and critical drug efficacy. J Theor Biol 247(2):371–381
Neumann AU, Lam NP, Dahari H, Gretch DR, Wiley TE, Layden TJ, Perelson AS (1998) Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy. Science 282:103–107
Lenhart S, Workman JT (2007) Optimal control applied to biological models. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Swan GW (1990) Role of optimal control theory in cancer chemotherapy. Math Biosci 101(2):237–284
Murray JM (1990) Some optimal control problems in cancer chemotherapy with a toxicity limit. Math Biosci 100(1):49–67
Murray JM (1990) Optimal control for a cancer chemotherapy problem with general growth and loss functions. Math Biosci 98(2):273–287
de Pillis LG, Gu W, Fister KR, Head T, Maples K, Murugan A, Neal T, Yoshida K (2007) Chemotherapy for tumors: an analysis of the dynamics and a study of quadratic and linear optimal controls. Math Biosci 209(1):292–315
Fister KR, Panetta JC (2003) Optimal control applied to competing chemotherapeutic cell-kill strategies. SIAM J Appl Math 63(6):1954–1971
Chavez IYS, Morales-Menendez R, Chapa SOM (2009) Glucose optimal control system in diabetes treatment. Appl Math Comput 209(1):19–30
Nanda S, Moore H, Lenhart S (2007) Optimal control of treatment in a mathematical model of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Math Biosci 210(1):143–156
Kirschner D, Lenhart S, Serbin S (1997) Optimal control of the chemotherapy of HIV. J Math Biol 35(7):775–792
Joshi HR (2002) Optimal control of an HIV immunology model. Optim Control Appl Methods 23(4):199–213
Adams BM, Banks HT, Davidian M, Kwon H-D, Tran HT, Wynne SN, Rosenberg ES (2005) HIV dynamics: modeling, data analysis, and optimal treatment protocols. J Comput Appl Math 184(1):10–49
Stengel RF (2008) Mutation and control of the human immunodeficiency virus. Math Biosci 213(2):93–102
Chakrabarty SP, Joshi HR (2009) Optimally controlled treatment strategy using interferon and ribavirin for hepatitis C. J Biol Syst 17(1):97–110
Chakrabarty SP (2009) Optimal efficacy of ribavirin in the treatment of hepatitis C. Optim Control Appl Methods 30(6):594–600
Pachpute G, Chakrabarty SP (2013) Dynamics of hepatitis C under optimal therapy and sampling based analysis. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(8):2202–2212
Martin NK, Pitcher AB, Vickerman P, Vassall A, Hickman M (2011) Optimal control of hepatitis C antiviral treatment programme delivery for prevention amongst a population of injecting drug users. PLoS ONE 6(8):e22309
Manna K, Chakrabarty SP (2015) Chronic hepatitis B infection and HBV DNA-containing capsids: modeling and analysis. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 22(1–3):383–395
Srivastava PK, Chandra P (2010) Modeling the dynamics of HIV and CD4+ T cells during primary infection. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(2):612–618
van den Driessche P, Watmough J (2002) Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math Biosci 180(1–2):29–48
Heffernan JM, Smith RJ, Wahl LM (2005) Perspectives on the basic reproductive ratio. J R Soc Interface 2(4):281–293
Adams BM, Banks HT, Kwon H-D, Tran HT (2004) Dynamic multidrug therapies for HIV: optimal and STI control approaches. Math Biosci Eng 1(2):223–241
Fister KR, Lenhart S, McNally JS (1998) Optimizing chemotherapy in an HIV model. Electron J Differ Equ 32:1–12
Fleming WH, Rishel RW (1975) Deterministic and stochastic optimal control. Springer, Berlin
Garira W, Musekwa SD, Shiri T (2005) Optimal control of combined therapy in a single strain HIV-1 model. Electron J Differ Equ 52:1–22
Chakrabarty SP, Banerjee S (2010) A control theory approach to cancer remission aided by an optimal therapy. J Biol Syst 18(1):75–91
Burden T, Ernstberger J, Fister KR (2004) Optimal control applied to immunotherapy. Discrete Cont Dyn Syst Ser B 4(1):135–146
Kirk DE (2004) Optimal control theory: an introduction. Dover Publications, Mineola
Acknowledgements
The first author gratefully acknowledges the financial support provided by the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati for pursuing his Ph.D. The authors express their gratitude to the reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manna, K., Chakrabarty, S.P. Combination therapy of pegylated interferon and lamivudine and optimal controls for chronic hepatitis B infection. Int. J. Dynam. Control 6, 354–368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0306-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0306-x