Abstract
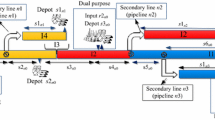
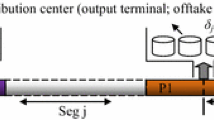
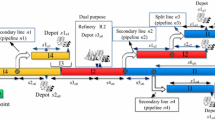
Pipelines carry different types of petroleum products from production areas to long-distance terminals. This paper introduces a novel mixed-integer linear programming based on a continuous time representation for scheduling a multi-product pipeline system connecting a unique refinery to several distribution centers where the mid-terminals are able to both inject product into the pipeline and receive product from it. This model allows the multiple removal terminals to withdraw product from the pipeline at the same time. The problem goal is to minimize the overall operational cost of the pipeline, such as interface and pumping costs. The result shows that the proposed method leads to better pipeline schedules than previous approaches in solution quality.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIMMS, Version 3.9. In:Haarlem BV (ed) Paragon Decision Technology, the Netherlands (2009). http://www.aimms.com
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2004) Optimal scheduling of multiproduct pipeline systems using a non-discrete MILP formulation. Comput Chem Eng 28:2053–2068
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2008) Dynamic scheduling of multiproduct pipelines with multiple delivery due dates. Comput Chem Eng 32:728–753
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2008) Efficient tool for the scheduling of multiproduct pipelines and terminal operations. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:9941–9956
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2009) Optimal scheduling of refined products pipelines with multiple sources. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:6675–6689
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2010) Operational scheduling of refined products pipeline networks with simultaneous batch injections. Comput Chem Eng 34:1687–1704
Cafaro VG, Cafaro DC, Mendéz CA, Cerdá J (2012) Detailed scheduling of single-source pipelines with simultaneous deliveries to multiple offtake stations. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6145–6165
Hane CA, Ratliff HD (1995) Sequencing inputs to multi-commodity pipelines. Ann Oper Res 57:73–101
Herrán A, de la Cruz JM, de Andrés B (2010) Mathematical model for planning transportation of multiple petroleum products in a multi-pipeline system. Comput Chem Eng 34:401–413
Herrán A, de la Cruz JM, de Andrés B (2012) Global search metaheuristics for planning transportation of multiple petroleum products in a multi-pipeline, system. Comput Chem Eng 37:248–261
Lee H, Pinto JM, Grossmann IE, Park S (1996) Mixed-integer linear programming model for refinery short-term scheduling of crude oil unloading with inventory management. Ind Eng Chem Res 35:1630–1641
Magatão L, Arruda LVR, Neves FA (2004) Programming approach for scheduling commodities in a pipeline. Comput Chem Eng 28:171–185
Magatão L, Arruda LVR, Neves FA (2010) A combined CLP-MILP approach for scheduling commodities in a pipeline. J Sched 14:57–87
MirHassani SA, Abbasi M, Moradi S (2013) Operational scheduling of refined product pipeline with dual purpose depots. Appl Math Model 37:5723–5742
Pinto JM, Joly M, Moro IFL (2000) Planning and scheduling models for refinery operations. Comput Chem Eng 24:2259–2276
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2003) Scheduling of a multiproduct pipeline system. Comput Chem Eng 27:1229–1246
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2004) Efficient MILP formulations and valid cuts for multiproduct pipeline scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 28:1511–1528
Relvas S, Matos HM, Barbosa-Po’voa AFD, Fialho J, Pinheiro AS (2006) Pipeline scheduling and inventory management of a multiproduct distribution oil system. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:7841–7855
Relvas S, Matos HM, Barbosa-Po’voa AFD, Fialho J (2007) Reactive scheduling framework for a multiproduct pipeline with inventory management. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:5659–5672
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2008) A novel continuous time representation for the scheduling of pipeline systems with pumping yield rate constraints. Comput Chem Eng 32:1042–1066
Sasikumar M, Prakash PR, Patil SM (1997) PIPES: a heuristic search model for pipeline schedule generation. Knowl Based Syst 10:169–175
Shah N (1996) Mathematical programming techniques for crude oil scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 20:1227–1232
Techo R, Holbrook DL (1974) Computer scheduling the world’s biggest product pipeline. Pipeline and Gas Journal 4:27–34
Trench CJ (2001) How pipelines make the oil market work -their networks, operation and regulation. Allegro Energy Group, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by José Mario Martínez.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostafaei, H., Alipouri, Y. & Shokri, J. A mixed-integer linear programming for scheduling a multi-product pipeline with dual-purpose terminals. Comp. Appl. Math. 34, 979–1007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-014-0162-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-014-0162-7