Abstract
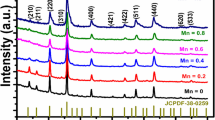
A typical Li+ substituted NiO compound, Li0.29Ni0.71O, was synthesized by molten nitrate method. The effects of Li+ substitution on the structure and magnetic properties of NiO were investigated. X-Ray diffraction(XRD), scanning electron microscope(SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope(HRTEM) analyses confirm the cubic structure of Li0.29Ni0.71O, with a primary particle size of 150 nm. Analysis of the Ni X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) shows the transformation from Ni2+ to Ni3+ induced by Li+ substitution. Two magnetic transitions were observed at 225 and 55 K which were assigned to the ferrimagnetic ordering and spin glass transition, respectively. The different magnetic behavior with respect to that of NiO was attributed to the break of superexchange interaction Ni2+-O-Ni2+ and the formation of different spin clusters after non-magnetic Li+ doping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanno R., Kubo H., Kawamoto Y., Kamiyama T., Izumi F., Takeda Y., Takano M., J. Solid State Chem., 1994, 110, 216
Nagasaka Y., Ohta H., Kawakami K., Ueda A., Ono S., Ikeuchi Y., Nanba T., Hirano A., Kanno R., J. Phys. Chem. Solid, 2003, 64, 1949
Morales J., Perez V. C., Tirado J. L., Mater. Res. Bull., 1990, 25, 623
Li W., Reimers J. N., Dahn J. R., Phys. Rev. B, 1992, 46, 3236
Wang C. W., Ma X. L., Li Z. C., Liang Y. G., Sun J. T., Zhou Y. H., Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8, 289
Huang X. H., Tu J. P., Zhang B., Zhang C. Q., Li Y., Yuan Y. F., Wu H. M., J. Power Sources, 2006, 161, 541
Huang X. H., Tu J. P., Zhang C. Q., Xiang J. Y., Electrochem. Commun., 2007, 9, 1180
Sung W. O., Hyun J. B., Young C. B., Yang K. S., J. Power Sources, 2007, 173, 502
Rahman M. M., Chou S. L., Zhong C., Wang J. Z., Wexler D., Liu H. K., Solid State Ionics, 2010, 180, 1646
Belhomme C., Cassir M., Devynck J., Gregoire G., J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35, 2683
Bajpai A., Banerjee A., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2001, 13, 637
Seehra M. S., Phys. Rev. B, 1988, 38, 11898
Manna S., De S. K., Sol. Stat. Commun., 2009, 149, 297
van Elp J., Eskes H., Kuiper P., Sawatzky G. A., Phys. Rev. B, 1992, 45, 1612
Wu J., Nan C. W., Lin Y. H., Deng Y., Phys. Rev. Letts., 2002, 89, 217601
Antolini E., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2003, 82, 937
Arai H., Tsuda M., Saito K., Hayashi M., Takei H., Sakurai Y., J. Solid State Chem., 2002, 163, 340
Soriano L., Preda I., Gutierrez A., Palacin S., Abbate M., Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 75, 233417
Liu H. S., Li J., Zhang Z. R., Gong Z. L., Yang Y., Electrochem. Acta, 2004, 49, 1151
Kim H. J., Lee J. B., Kim Y. M., Jung M. H., Jaglicic Z., Umek P., Dolinsek J., Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2007, 2, 81
Pena O., Guilloux V. M., Antunes A. B., Peng W., Ma Y. W., Gao Z. S., Moure C., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2009, 321, 1723
Auslous M., Elliot R. J., Magnetic Phase Transitions, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1983, 99
Wang D. P., Chen. H., Du F., Bie X. F., Liu L. N., Wei Y. J., Chen G., Wang C. Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2010, 26(2), 283
Liu N., Yan G. Q., Xu S. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2005, 21(6), 707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Special Funds for Major National Basic Research Project of China(No.2009CB220104), the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.11004073) and the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China(New Teacher)(No.20090061120020) and Partially Supported by the Development Program of Science and Technology of Jilin Province, China(No.201205035).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, F., Bie, Xf., Bian, Xf. et al. Preparation, structure and magnetic properties of lithium substituted NiO by molten salt method. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 29, 210–213 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-2159-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-2159-y