Abstract
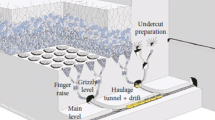
Nowadays along with population growth, industry development, consumption of mineral resources and the fact that the reserves on hand are running out, the depth of surface and underground mines for further exploitation are increasing. During recent years, in underground mining, the block caving method for low-grade and large-scale deposits has shown a growing rate of application. The dimensions of blocks are one of the most important parameters which should be taken into account since it has been proved to have a great deal of effect on technical issues such as commencement of caving and mine design. In this study, some assumptions were considered and having used these assumptions for estimation of optimized length and width of block, a relationship was explored. And finally, it was transformed into an inequality. Solving this inequality provides us with the optimized length and width of the block. The explored relationship was analysed using MATLAB and the resulting graphs thereof were drawn. Simulation was carried out using the Phase2 software and the results were compared with the different modes of the block. In the blocks that were 55, 60 and 65 m in length, the total displacement (the total displacement as a result of applying force in order to cave), yielded elements (percent) and Yielded Joints reached a satisfactory condition which enables perfect caving to occur. In addition, in the 70 m block, these values reached their maximum. It was concluded in this paper that the optimal block size is between 55 and 65 m.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laubscher DH (2003) Cave mining handbook, mining sciences. 34(8)
Butcher RJ (1999) Design rules for avoiding draw horizon damage in deep level block caves. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 99:151–155
Woo K, Eberhardt E (2009) Characterization and empirical analysis of block caving induced surface subsidence and macro deformations. In: Proceedings of the 3rd CANUS rock mechanics symposium. Toronto, Canada
Someehneshin J (2013) Calculation of optimum length and width of the block in block caving method. MSc Thesis, Azad University, Iran
Butcher A, Cunningham R, Edwards K, Lye A, Simmons J, Stegman C, Wyllie A (2009), Northparkes Mines. AMMOP
Oraee K (2004) Underground Metalliferous Mining. Tehran Polytechnic Press, Tehran
Brady BHG, Brown ET (2005) Rock mechanics for underground mining. Springer, Dordrecht
Marinos V, Marimos P, Hoek E (2005) The geological strength index: applications and limitations. Bull Eng Geol Eviron 64:55–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Someehneshin, J., Oraee-Mirzamani, B. & Oraee, K. Analytical Model Determining the Optimal Block Size in the Block Caving Mining Method. Indian Geotech J 45, 156–168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-014-0119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-014-0119-1