Abstract
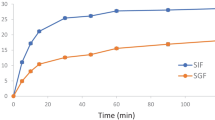
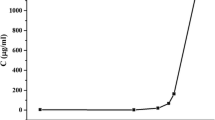
In the present investigation, an attempt was made to improve the dissolution properties of water insoluble herbal active ingredient, Embelin (EBN) by utilizing liquisolid technique, which might offer improved bioavailability. The compacts were prepared using Capryol 90 as non-volatile solvent, Neusilin as carrier and Aerosil 200 as coating material. Mathematical model and 32 factorial design with liquid load factor (X1) and drug concentration (X2) as the independent variables, was utilized to prepare the liquisolid powder systems. The prepared systems were subjected for studying micromeritic properties and possible drug-excipient interactions by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD). Dissolution studies revealed improvement in the drug release properties. Physicochemical characterization of liquisolid compacts by FTIR, DSC and PXRD techniques suggested reduction in drug crystallinity elaborating for the dissolution enhancement. The study reveals that liquisolid technique is a promising alternative for enhancing dissolution characteristics of EBN.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansel HC, Allen LV, Popovich NG (1999) Pharmaceutical dosage forms and drug delivery systems, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 60–63
Chitra M, Shyamala Devi CS, Sukumar E (2003) Antibacterial activity of embelin. Fitoterapia 74(4):401–403
Elkordy AA, Tiong N (2009) Effects of liquisolid formulations on dissolution of naproxen. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 73:373–384
Elkordy AA, Essa EA, Dhuppad S, Jammigumpula P (2012) Liquisolid technique to enhance and to sustain griseofulvin dissolution: effect of choice of non-volatile liquid vehicles. Int J Pharm 434:122–132
Elkordy AA, Tan XN, Essa EA (2013) Spironolactone release from liquisolid formulations prepared with Capryol™ 90, Solutol HS-15 and Kollicoat SR 30 D as non-volatile liquid vehicles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 83:203–223
Gosangari S, Dyakonov T (2013) Enhanced dissolution performance of curcumin with the use of supersaturable formulations. Pharm Dev Technol 18(2):475–480
Gubbi SR, Jarag R (2010) Formulation and characterization of atorvastatin calcium liquisolid compacts. Asian J Pharm Sci 5(2):50–60
Gupta R, Sharma AK, Sharma MC, Gupta RS (2012) Antioxidant activity and protection of pancreatic β-cells by embelin in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Diabetes 4(3):248–256
Hussein A, Afouna M, El-Menshave S (2012) Enhancement of the in vitro dissolution and in vivo oral bioavailability of silymarin from liquid-filled hard gelatin capsules of semisolid dispersion using Gelucire 44/14 as a carrier. Pharmazie 67(3):209–214
Joy B, Lakshmi S (2010) Antiproliferative properties of embelia ribes. Open Proc Chem J 3:17–22
Padh H, Patel BV (2001) Herbal drugs. Curr Sci 81:15–16
Pathan RA, Bhandari U (2012) Preparation and characterization of embelin-phospholipid complex as effective drug delivery tool. J Incl Phenom Macro Chem 69:139–147
Radhakrishnan N, Alam M (1975) Antifertility effects of embelin in albino rats. Indian J Exp Biol 13(1):70–71
Sayyad FJ, Tulsankar SL, Kolap UB (2013) Design and development of liquisolid compact of candesartancilexetil to enhance dissolution. J Pharm Res 10:1–8
Sikarwar MS, Sharma S, Jain AK, Parial SD (2008) Preparation, characterization and evaluation of marsupsin–phospholipidcomplex. AAPS PharmSciTech 9:129–137
Spireas S (2002) Liquisolid systems and methods of preparing same US Patent 6423339B1
Tripathi SN (1979) Screening of hypoglycemic action in certain indigenous drugs. J Res Ind Med 14:159–169
Vaskula S, Vemula S, Bontha V, Garepally P (2012) Liquisolid compacts: an approach to enhance the dissolution rate of Nimesulide. J App Pharm Sci 2(5):115–121
Yousef J, Baharak Jafari N, Ali N (2007) Liquisolid technique for dissolution rate enhancement of high dose water insoluble drug (carbamazepine). Int J Pharm 341:26–34
Acknowledgments
This article dose not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. All authors (K. Parmar, J. Patel, and N. Sheth) declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors are thankful to Mr. Swapnil Goyal (Asst. Prof. BR Nahta College of Pharmacy, Mandsaur) for providing the gift sample of EBN. The support of Gattefose, Mumbai is gratefully acknowledged to provide the gift sample of Capryol 90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parmar, K., Patel, J. & Sheth, N. Fabrication and characterization of liquisolid compacts of Embelin for dissolution enhancement. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 44, 391–398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0134-3