Abstract
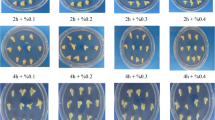
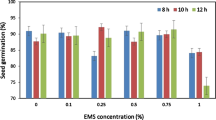
Ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis is a powerful hunting tool to seek novel players for improving agromonic traits. Together with rapid evolution of the next-generation sequencing techniques, the EMS mutagenesis has been revaluated for its utilization to breed crops in practical agriculture and to study functions of key players in valuable agronomic traits. In this study, we systematically investigated conditions for EMS mutagenesis in Dongjin (Oryza sativa, Japonica) rice plants to make a mutant population. Since the EMS mutagenesis depends on target tissue, EMS concentration and EMS exposure time, we fixed the EMS exposure time as 13 h and treated germinating seeds with various levels of EMS dosage (from 0.25 to 2% EMS concentration). EMS treatment clearly showed negative biological influences including low germination and abnormal seedling development of Dongjin rice plants. Based on the standard of about 50% lethal dose, 0.75 and 1% EMS dosage for 13 h was finally selected as the optimal conditions for EMS mutagenesis of Dongjin germinating seeds.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varshney RK, Bansal KC, Aggarwal PK, Datta SK, Craufurd PQ (2011) Agricultural biotechnology for crop improvement in a variable climate: hope or hype? Trends Plant Sci 16:363–371
Shimamoto K, Kyozuka J (2002) Rice as a model for comparative genomics of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:399–419
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1971–1974
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica). Science 296:92–100
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Cao M, Liu J, Sun J, Tang J, Chen Y, Huang X, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong L, Geng J, Han Y, Li L, Li W, Hu G, Huang X, Li W, Li J, Liu Z, Li L, Liu J, Qi Q, Liu J, Li L, Li T, Wang X, Lu H, Wu T, Zhu M, Ni P, Han H, Dong W, Ren X, Feng X, Cui P, Li X, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai W, Xu Z, Zhang J, He S, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhang K, Zheng X, Dong J, Zeng W, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren X, Chen X, He J, Liu D, Tian W, Tian C, Xia H, Bao Q, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao W, Li P, Chen W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hu J, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang G, Xiong Y, Li Z, Mao L, Zhou C, Zhu Z, Chen R, Hao B, Zheng W, Chen S, Guo W, Li G, Liu S, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu L, Yuan L, Yang H (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Indica). Science 296:79–92
Zhang Q, Li J, Xue Y, Han B, Deng XW (2008) Rice 2020: a call for an international coordinated effort in rice functional genomics. Mol Plant 1:715–719
Wei FJ, Droc G, Guiderdoni E, Hsing YI (2013) International consortium of rice mutagenesis: resources and beyond. Rice 6:39
Parry MAJ, Madgwick PJ, Bayon C, Tearall K, Hernandez-Lopez A, Baudo M, Rakszegi M, Hamada W, Al-Yassin A, Ouabbou H, Labhilili M, Phillips AL (2009) Mutation discovery for crop improvement. J Exp Bot 60:2817–2825
Wu JL, Wu C, Lei C, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Madamba MRS, Ramos-Pamplona M, Mauleon R, Portugal A, Ulat VJ, Bruskiewich R, Wang G, Leach J, Khush G, Leung H (2005) Cheminal- and irradiation-induced mutants of Indica rice IR64 for forward and reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 59:85–97
Till BJ, Cooper J, Tai TH, Colowit P, Greene EA, Henikoff S, Comai L (2007) Discovery of chemically induced mutations in rice by TILLING. BMC Plant Biol 7:19
Kim Y, Schumarker KS, Zhu JK (2006) EMS mutagenesis of Arabidopsis. Methods Mol Biol 323:101–103
Kodym A, Afza R (2003) Physical and chemical mutagenesis. Methods Mol Biol 236:189–204
Sikora P, Chawade A, Larsson M, Olsson J, Olsson O (2011) Mutagenesis as a tool in plant genetics, functional genomics, and breeding. Int J Plant Genom 2011:314829
Talebi AB, Talebi AB, Shahrokhifar B (2012) Ethyl methane sulphonate (EMS) induced mutagenesis in malaysian rice (cv. MR219) for lethal dose determination. Am J Plant Sci 3:1661–1665
Comai L, Henikoff S (2006) Tilling: practical single-nucleotide mutation discovery. Plant J 45:684–694
Henikoff S, Comai L (2003) Single-nucleotide mutations for plant functional genomics. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:375–401
Till BJ, Reynolds SH, Greene EA, Codomo CA, Enns LC, Johnson JE, Burtner C, Odden AR, Young K, Taylor NE (2003) Large-scale discovery of induced point mutations with high-throughput tilling. Genome Res 13:524–530
Serrat X, Esteban R, Guibourt N, Moysset L, Nogues S, Lalanne E (2014) EMS mutagenesis in mature seed-derived rice calli as a new method for rapidly obtaining TILLING mutant populations. Plant Methods 10:5
Arisha MH, Shah SNM, Gong ZH, Jing H, Li C, Zhang HX (2015) Ethyl methane sulfonate induced mutations in M2 generation and physiological variations in M1 generation of peppers (Capsicum annuum L.). Front Plant Sci 6:399
Slade AJ, Fuerstenberg SI, Loeffler D, Steine MN, Facciotti D (2005) A reverse genetic, nontransgenic approach to wheat crop improvement by TILLING. Nat Biotechnol 23:75–81
Dolan L, Janmaat K, Willemsen V, Linstead P, Poethig S, Roberts K, Scheres B (1993) Cellular organization of the Arabidopsis thaliana root. Development 119:71–84
Petricka JJ, Winter CM, Benfey PN (2012) Control of Arabidopsis root development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:563–590
Robouillat J, Dievart A, Verdeil L, Escoute J, Giese G, Breitler C, Gantet P, Espeout S, Guiderdoni E, Perin C (2009) Molecular genetics of rice root development. Rice 2:15–34
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Education (NRF-2014R1A6A3A04053795 and NRF-2010-359-F00004), by the International Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2015K1A3A1A21000237) and by the Rural Development Administration under the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (PJ011829012016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, DK., Kim, Y.S. & Kim, JK. Determination of the optimal condition for ethylmethane sulfonate-mediated mutagenesis in a Korean commercial rice, Japonica cv. Dongjin. Appl Biol Chem 60, 241–247 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-017-0273-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-017-0273-0