Abstract
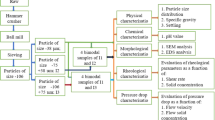
Significant amount of slurry waste is produced from mineral processing plants globally constituting high levels of both kaolin and sand in aqueous suspension. Large quantities of slurry and mine tailings require efficient handling, transportation and storage system. The transportation and treatment of kaolin–sand slurry is dependent on its rheological behaviour which is a function of temperature, total solid concentration and pH. In this study, the effects of total solid concentration, pH and temperature on rheological behaviour of kaolin–sand mixture were investigated. These parameters were varied to analyse the viscosity, yield stress, flow index and shear force requirements of the mixed kaolin–sand suspension as a function of these varying parameters. Experimental rheological investigation conducted on rotational stress-controlled rheometer equipped with Peltier concentric cylinder system showed that the kaolin–sand mixture suspension is shear thickening in nature. The shear stress-rate rheograms for the kaolin–sand suspension can be modelled by the Herschel–Bulkley model with high levels of accuracy for pH range of 4–11, temperature range of 20–50 °C and solid concentration of 5–50 %. Solid concentration of the suspension was found to significantly affect the rheological behaviour of the mixture where higher kaolin–sand slurry concentration resulted in greater viscosity and the trend becoming less predictable for solid concentration greater than 50 % by weight. pH was another factor affecting the rheological behaviour of kaolin–sand slurry. pH of 3 or less resulted in the dramatic increase of viscosity of the suspension possibly due to the isoelectric point of the mixture system found between pH of 3 and 4.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allouche MH, Botton V, Henry D, Millet S, Usha R, Ben Hadid H (2015) Experimental determination of the viscosity at very low shear rate for shear thinning fluids by electrocapillarity. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 215:60–69. doi:10.1016/j.jnnfm.2014.11.003
Au P-I, Leong Y-K (2013) Rheological and zeta potential behaviour of kaolin and bentonite composite slurries. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 436:530–541. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.06.039
Avadiar L, Leong Y-K, Fourie A (2015) Physicochemical behaviors of kaolin slurries with and without cations—contributions of alumina and silica sheets. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 468:103–113. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.12.019
Baroutian S, Eshtiaghi N, Gapes DJ (2013) Rheology of a primary and secondary sewage sludge mixture: dependency on temperature and solid concentration. Bioresour Technol 140:227–233. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.114
Bawa H (2004) Manufacturing processes-II. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
Bezerril LM, de Vasconcelos CL, Dantas TNC, Pereira MR, Fonseca JLC (2006) Rheology of chitosan-kaolin dispersions. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 287(1–3):24–28. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.03.017
Chang S, Ryan M, Gupta R (1993) The effect of pH, ionic strength, and temperature on the rheology and stability of aqueous clay suspensions. Rheol Acta 32(3):263–269
Cheng DC (1980) Viscosity-concentration equations and flow curves for suspensions. Chem Ind 17:403–406
Cohen EGD, Verberg R, de Schepper IM (1997) Newtonian viscosity and visco-elastic behavior of concentrated neutral hard-sphere colloidal suspensions. Int J Multiph Flow 23(4):797–807. doi:10.1016/S0301-9322(96)00074-2
Cruz N, Peng Y, Farrokhpay S, Bradshaw D (2013) Interactions of clay minerals in copper–gold flotation: part 1—rheological properties of clay mineral suspensions in the presence of flotation reagents. Miner Eng 50–51:30–37. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2013.06.003
Cunha FO, Torem ML, D’Abreu JC (2006) On the fundamentals of kaolin rheology applied to the paper industry. Miner Eng 19(14):1462–1464. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2006.03.010
De Noni Jr A, Garcia DE, Hotza D (2002) A modified model for the viscosity of ceramic suspensions. Ceram Int 28(7):731–735. doi:10.1016/S0272-8842(02)00035-4
Güngör N (2000) Effect of the adsorption of surfactants on the rheology of na-bentonite slurries. J Appl Polym Sci 75(1):107–110
He M, Wang Y, Forssberg E (2004) Slurry rheology in wet ultrafine grinding of industrial minerals: a review. Powder Technol 147(1):94–112
Johnston CT, Premachandra GS (2001) Polarized ATR-FTIR study of smectite in aqueous suspension. Langmuir 17(12):3712–3718
Mosa E, Saleh A, Taha A, El-Molla A (2007) A study on the effect of slurry temperature, slurry ph and particle degradation on rheology and pressure drop of coal water slurries. J Eng Sci 35(5):1297–1311
Mular AL, Halbe DN and Barratt DJ (2002) Mineral processing plant design, practice, and control proceedings. SME
Mullineux G (2008) Non-linear least squares fitting of coefficients in the herschel–bulkley model. Appl Math Model 32(12):2538–2551. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2007.09.010
Ndlovu B, Becker M, Forbes E, Deglon D, Franzidis J-P (2011) The influence of phyllosilicate mineralogy on the rheology of mineral slurries. Miner Eng 24(12):1314–1322. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2011.05.008
Otsuki A, Barry S, Fornasiero D (2011) Rheological studies of nickel oxide and quartz/hematite mixture systems. Adv Powder Technol 22(4):471–475. doi:10.1016/j.apt.2011.04.004
Pevere A, Guibaud G, van Hullebusch E, Lens P, Baudu M (2006) Viscosity evolution of anaerobic granular sludge. Biochem Eng J 27(3):315–322. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2005.08.008
Pignon F, Magnin A, Piau J-M (1998) Thixotropic behavior of clay dispersions: combinations of scattering and rheometric techniques. J Rheol (1978-present) 42(6):1349–1373
Rao MA (2010) Rheology of fluid and semisolid foods: Principles and applications: Principles and applications. Springer Science & Business Media
Rutgers IR (1962) Relative viscosity and concentration. Rheol Acta 2(4):305–348
Sanin FD (2002) Effect of solution physical chemistry on the rheological properties of activated sludge. Water SA 28(2):207–212
Schroth BK and Sposito G (1996) Surface charge properties of kaolinite. In: MRS Proceedings. Cambridge University Press pp 87
Senapati PK, Panda D, Parida A (2009) Predicting viscosity of limestone–water slurry. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 8(03):203
Shankar P, Teo J, Leong Y-K, Fourie A, Fahey M (2010) Adsorbed phosphate additives for interrogating the nature of interparticles forces in kaolin clay slurries via rheological yield stress. Adv Powder Technol 21(4):380–385. doi:10.1016/j.apt.2010.02.013
Teh EJ, Leong YK, Liu Y, Fourie AB, Fahey M (2009) Differences in the rheology and surface chemistry of kaolin clay slurries: the source of the variations. Chem Eng Sci 64(17):3817–3825. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2009.05.015
Tombácz E, Szekeres M (2006) Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 34(1–4):105–124. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2006.05.009
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Department of Chemical Engineering of Curtin University, Perth, for providing necessary research infrastructure and equipment/instruments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: N. Atar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, E., Herbert, C.M., Yeneneh, A.M. et al. Rheological characteristics of mixed kaolin–sand slurry, impacts of pH, temperature, solid concentration and kaolin–sand mixing ratio. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 2629–2638 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1090-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1090-4