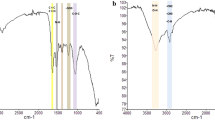
Abstract
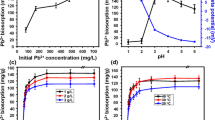
A total of 422 bacterial isolates were obtained from the lead (Pb) ore in north-eastern Iran. The Pb tolerances of these strains were studied using microbroth serial dilution approach and 35 strains could grow up to 3250 ppm Pb concentration. Of these strains, 10 of them represented qualitatively high levels of Pb adsorption and were selected for quantitative studies. Strain AS2 which is phylogenetically related to genus Bacillus showed the highest level of Pb remediation. The effects of different factors, including pH, initial Pb concentration, temperature and inoculum size, were studied on the remediation process. Pb remediation capacity was reached at 74.5 mg/g (99.5 % of initial Pb) at pH 4.5, temperature 30 °C, inoculum size 1.0 % (v/v) and an initial Pb concentration of 500 ppm after 24 h. Pb desorption capacity of strain was 66 %. The novel isolate could remove 98 % of Pb from the contaminated industrial wastes after 24 h. Pb uptaking to the cell surface was proven using scanning electron microscopic micrograph and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis. Most Pb removal efficiency was observed in the active cell culture as compared to the inactive cell and extracellular polymeric substances. The novel strain represents a good candidate for removal of environmental anthropogenic Pb pollutions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batta N, Subudhi S, Lal B, Devi A (2013) Isolation of a lead tolerant novel bacterial species, Achromobacter sp. TL-3: assessment of bioflocculant activity. Indian J Exp Biol 51:1004–1011
Beveridge TJ, Fyfe WS (1985) Metal fixation by bacterial cell walls. Can J Earth Sci 22:1892–1898
Bhakta JN, Munekage Y, Ohnishi K, Jana BB (2012) Isolation and identification of cadmium- and lead-resistant lactic acid bacteria for application as metal removing probiotic. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:433–440
Cabuk A, Akar T, Tunali S, Tabak O (2006) Biosorption characteristics of Bacillus sp. ATS-2 immobilized in silica gel for removal of Pb(II). J Hazard Mater 136:317–323
Chen C, Wang J (2007) Response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to lead ion stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:683–687
Chen QY, Luo Z, Hills C, Xue G, Tyrer M (2009) Precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater using simulated flue gas: sequent additions of fly ash, lime and carbon dioxide. Water Res 43:2605–2614
Deng LP, Su YY, Su H, Wang XT, Zhu XB (2007) Sorption and desorption of lead (II) from wastewater by green algae Cladophora fascicularis. J Hazard Mater 143:220–225
Gabr RM, Hassan SHA, Shoreit AAM (2008) Biosorption of lead and nickel by living and non-living cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ASU 6a. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62:195–203
Halttunen T, Salminen S, Tahvonen R (2007) Rapid removal of lead and cadmium from water by specific lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 114:30–35
Hasnain S, Yasmin S, Yasmin A (1993) The effects of lead resistant Pseudomonads on the growth of Triticum aestivum seedlings under lead stress. Environ Pollut 81:179–184
Hu Q, Qi HY, Zeng JH, Zhang HX (2007) Bacterial diversity in soils around a lead and zinc mine. J Environ Sci 19:74–79
Ismail Z, Salim K, Othman SZ, Ramli AH, Shirazi SM, Karim R, Khoo SY (2013) Determining and comparing the levels of heavy metal concentrations in two selected urban river water. Measurement 46:4135–4144
Jarosławiecka A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2014) Lead resistance in micro-organisms. Microbiology 160:12–25
Johnson KJ, Ams DA, Wedel AN, Szymanowski JES, Weber DL, Schneegurt MA, Fein JB (2007) The impact of metabolic state on Cd adsorption onto bacterial cells. Geobiology 5:211–218
Kabbashi NA, Atieh MA, Al-Mamun A, Mirghami MES, Alam MDZ, Yahya N (2009) Kinetic adsorption of application of carbon nanotubes for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 21:539–544
Landaburu-Aguirre J, García V, Pongrácz E, Keiski RL (2009) The removal of zinc from synthetic wastewaters by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration: statistical design of experiments. Desalination 240:262–269
Lane DJ, Pace B, Olsen GJ, Stahl DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (1985) Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6955–6959
Leung WC, Chua H, Lo W (2001) Biosorption of heavy metals by bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 91:171–184
Li L, Liu H, Shi Z, Wang G (2013) Sphingobium cupriresistens sp. nov., a copper-resistant bacterium isolated from copper mine soil, and emended description of the genus Sphingobium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:604–609
Macek T, Mackova M (2011) Potential of biosorption technology. In: Kotrba P, Mackova M, Macek T (eds) Microbial biosorption of metals. Springer, London, pp 1–17
Maiti SK (2004) Handbook of Methods in Environmental Studies Vol. 1: Water and Wastewater Analysis, 2nd edn. ABD Publishers
Naik MM, Dubey SK (2011) Lead-enhanced siderophore production and alteration in cell morphology in a Pb-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 4EA. Curr Microbiol 62:409–414
Naseem R, Tahir SS (2001) Removal of Pb (ii) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent. Water Res 16:3982–3986
Pérez MPJA, García-Ribera R, Quesada T, Aguilera M, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Monteoliva-Sánchez M (2008) Biosorption of heavy metals by the exopolysaccharide produced by Paenibacillus jamilae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2699–2704
Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cycoń M, Kozdrój J (2005) Metal-tolerant bacteria occurring in heavily polluted soil and mine spoil. Appl Soil Ecol 28:237–246
Pümpel T, Pernfub B, Pigher B, Diels L, Schinner F (1995) A rapid screening method for the isolation of metal-accumulating microorganisms. J Ind Microbiol 14:213–217
Roane TM, Kellogg ST (1996) Characterization of bacterial communities in heavy metal contaminated soils. Can J Microbiol 42:593–603
Saad B, Pok FW, Sujari ANA, Saleh MI (1998) Analysis of anions and cations in drinking water samples by Capillary Ion Analysis. Food Chem 61:249–254
Saǧ Y, Özer D, Kutsal T (1995) A comparative study of the biosorption of lead (II) ions to Z. ramigera and R. arrhizus. Process Biochem 30:169–174
So NW, Rho JY, Lee SY, Hancock IC, Kim JH (2001) A lead-absorbing protein with superoxide dismutase activity from Streptomyces subrutilus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 194:93–98
Sparks DL (2005) Toxic metals in the environment: the role of surfaces. Elements 1:193–197
Sun F, Shao Z (2007) Biosorption and bioaccumulation of lead by Penicillium sp. Psf-2 isolated from the deep sea sediment of the Pacific Ocean. Extremophiles 11:853–858
Trajanovska S, Britz ML, Bhave M (1997) Detection of heavy metal ion resistance genes in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria isolated from a lead-contaminated site. Biodegradation 8:113–124
Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS (2008) Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol Adv 26:266–291
Zanardini E, Andreoni V, Borina S, Cappitellia F, Daffonchio D, Talottaa P, Sorlinia C, Ranallib G, Brunic S, Cariatic F (1997) Lead-resistant microorganisms from red stains of marble of the Certosa of Pavia, Italy and use of nucleic acid based techniques for their detection. Int Biodeter Biodegrad 40:171–182
Zhang J, Wang R, Jiang P, Liu Z (2002) Production of an exopolysaccharide bioflocculant by Sorangium cellulosum. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:178–181
Zhang Q, Pan B, Zhang W, Pan B, Lv L, Wang X, Wu J, Tao X (2009) Selective removal of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) ions from waters by an inorganic exchanger Zr(HPO3S)2. J Hazard Mater 170:824–828
Zhu H, Guo J, Chen M, Feng G, Yao Q (2012) Burkholderia dabaoshanensis sp. nov., a heavy-metal-tolerant bacteria isolated from Dabaoshan mining area soil in China. PLoS One 7:1–6
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad (23889/3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cephidian, A., Makhdoumi, A., Mashreghi, M. et al. Removal of anthropogenic lead pollutions by a potent Bacillus species AS2 isolated from geogenic contaminated site. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 2135–2142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1023-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1023-2