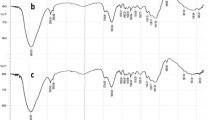
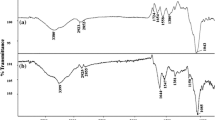
Abstract
The adsorbent properties of dried water hyacinth root biomass towards four polar solvents (dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, diethyl ether and acetone) were studied by inverse gas chromatography between 40 and 70 °C. The enthalpy of adsorption values obtained for the adsorption of the four solvents on untreated root biomass range from −51.234 kJ mol−1 for acetone, an amphoteric solvent, to −74.658 kJ mol−1 for dichloromethane, an acidic solvent. Mineral acid and organic solvent treatment led to reduction in the values of the enthalpy of adsorption for all four solvents. The Lewis acidity parameters calculated from the enthalpy of adsorption values were 0.408, 0.267 and 0.356, while the corresponding Lewis basicity parameters were 3.76, 1.80 and 2.34, respectively, for untreated, mineral acid-treated and organic solvent-treated water hyacinth root biomass. The Lewis basicity parameter-to-Lewis acidity parameter ratios for the untreated, acid-treated and organic solvent-treated biomass were found to be 9.22, 6.74 and 6.57, respectively, indicating (a) that all the surfaces of the untreated, mineral acid-treated and organic solvent-treated water hyacinth root biomass are basic in nature and (b) that for all volatile polar solvents studied, the adsorption interaction involves the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of the solvent as the electron acceptor and the highest occupied molecular orbital of the water hyacinth root biomass surface adsorbent site as the electron donor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askin A, Yacizi DT (2005) Surface characterization of sepiolite by inverse gas chromatography. Chromatographia 61(11–12):625–631
Bistac S, Brogly M (2001) Effect of polymer/solvent acid-base interactions: relevance to the aggregation of PMMA. In: Wypych G (ed) Handbook of solvents. ChemTech Publishing, Toronto
Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (2015) OSH answers fact sheets (a) Acetone, (b) Dichloromethane. Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, Ontario, Canada. www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/chemicals/chem_profiles/….html. Accessed 7 Apr 2016
Cordeiro N, Gouveia C, John MJ (2011a) Investigating of surface properties of physic-chemically modified natural fibres using inverse gas chromatography. Ind Crops Prod 33:108–115
Cordeiro N, Gouveia C, Moraes AGO, Amico SC (2011b) Natural fibers characterization by inverse gas chromatography. Carbohydr Polym 84(1):110–117
El-Khalary MI (2007) Kinetics and mechanism of adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by nitric acid treated water hyacinth. J Hazard Mater 147(1–2):28–36
Fekete E, Moczo J, Pukanszky B (2004) Determination of the surface characteristics of particulate fillers by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution: a critical approach. Colloid Interface Sci 269:143–152
Gamelas JAF (2013) The surface properties of cellulose and lignocellulosic materials assessed by inverse gas chromatography: a review. Cellulose 20(6):2675–2693
Garnier G, Glasser WG (1996) Measuring the surface energies of spherical cellulose beads by IGC. Polym Eng Sci 36(6):885–894
Grob RL (1977) Modern practice of gas chromatography. Wiley, New York, pp 21–30
Gulati D, Sain M (2006) Surface characteristics of untreated and modified hemp fibres. Polym Eng Sci 46(3):269–273
Gutmann V (1977) The donor-acceptor approach to molecular interaction. Plenum Press, New York
Hasan SH, Ranjan D, Talat M (2010) Water Hyacinth biomass (WHB) for the biosorption of hexavalent chromium: optimization of process parameters. Bioresources 5(2):563–575
Heng JYY, Pearse DF, Thielmann F, Lampke T, Bismarck A (2007) Methods to determine surface energies of natural fibers: a review. Compos Interface 14(7–9):581–604
Hudson RF, Klopman G (1967) A general treatment of chemical reactivity. Tetrahedron Lett 12:1103–1108
Ibrahim HS, Ammar NS, Soylak M, Ibrahim M (2012) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution using dried water hyacinth as a biosorbent. Spectrochim Acta A96:413–420
John M, Thomas S (2009) Biofibres and Biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 71(3):343–364
Jorgensen ML, Salem L (1973) The organic chemists’s book of orbitals. Academic Press, New York
Khan MR, Mozumder SI, Islam A, Prasad DMR, Alam MM (2012) Methylene blue adsorption onto water hyacinth: batch and column study. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(6):2943–2953
Kuma BP, Ramanaiah S, Reddy M, Reddy KS (2014) Surface characterization of cellulose acetate propionate by invers gas chromatography. Polym Bull 71(1):125–132
Kunaver M, Zadink J, Planinsck O, Srcic S (2004) Inverse gas chromatography—a different approach to characterization of solids and liquids. Acta Chim Slov 51(3):373–394
Laub RJ, Pecsock RL (1978) Physicochemical applications of gas chromatography. Wiley, New York
Low KS, Lee CK, Heng L (1994) Biosorption of basic dyes by Hydrilla verticillata. Environ Technol 15(2):115–124
Ma XY, Qu XH, Zhang Chen F (2008) Analysis of interfacial action of rectorite thermoplastic polyurethane nano composites by inverse gas chromatography and molecular simulation. Polymer 49(16):3590–3600
Mahamadi C (2011) Water hyacinth as a biosorbent: a review. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 5(13):1137–1145
Mahamadi C, Nharingo T (2010a) Utilization of water hyacinth weed (Eichhornia Crassipes) for the removal of Pb(II), Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aquatic environments: an adsorption isotherm study. Environ Technol 31(11):1221–1228
Mahamadi C, Nharingo T (2010b) Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn (II) ions onto Eichhornia Crassipes in Binary and Ternary systems. Bioresour Technol 101(3):859–864
Mall ID, Srivastava VC, Agarwal NK, Mishra IM (2005) Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis. Chemosphere 61(4):492–501
Martina M, Jozefa F, Aleksander P (2004) Decoloration of the diazo dye reactive black 5 by immobilized Bjerkandera adusta in a stirred tank bioreactor. Acta Chim Slov 51(4):619–628
Mayer UA (1979) Semi empirical model for the description of solvent effects on chemical reactions. Pure Appl Chem 51(8):1697–1712
Mills RH, Gardner DJ, Wimmer R (2008) Inverse gas chromatography for determining the dispersive surface free energy and acid–base interactions of sheet molding compound-Part II 14 ligno-cellulosic fiber types for possible composite reinforcement. J Appl Polym Sci 110(6):3880–3888
Mukaratirwa-Muchanyereyi N, Kugara J, Zaranyika MF (2015) Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of volatile n-alkane hydrocarbons on water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) root Biomass: effect of organic solvent and mineral acid treatment. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 9(3):282–291. doi:10.5897/AJEST2014.1817
Mukaratirwa-Muchanyereyi N, Kugara J, Zaranyika MF (2016) Surface composition and surface properties of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) root biomass: effect of mineral acid and organic solvent treatment. Afr J Biotechnol. 15(21):897–909. doi:10.5897/AJB2015.15068
Mutuana LM, Woodhams RT, Balatinecz JJ, Park CB (1998) Influence of interfacial interactions on the properties of PVC/Cellulosic fiber composites. Polym Comp 19(4):446–455
National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (2014) Diethyl ether. International Chemical Safety Card (ICSC): 0355. Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Resources, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0355.html. Accessed 7 Apr 2016
Nyananyo BL, Gijo AH, Ogamba EN (2007) The physico-chemical distribution of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipies) on the river Nun in the Niger Delta. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 11(3):133–137
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (2012) Chemical Sampling Information: Ethyl Acetate. US Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Washington, DC 20210. https://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_239500.html. Accessed 7 Apr 2016)
Onjia AE (2002) Inverse gas chromatography of chromia, part II. Finite surface coverage. J Serb Chem Soc 67(3):165–178
Rajamohan N (2009) Equilibrium studies on sorption of an anionic dye onto acid activated water hyacinth roots. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3(11):399–404
Riddle FL Jr, Fawkes FM (1990) Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry.1. van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers. J Am Chem Soc 112(9):3259–3264
Rjiba N, Nardin M, Drean J, Frydrych R (2010) Comparison of surfaces properties of different types of cotton fibers by inverse gas chromatography. J Polym Res 17(1):25–32
Rouessac F, Rouessac A (2007) Chemical analysis. Modern instrumentation methods and techniques, vol 2. Wiley, West Sussex
Santos J, Gil MH, Portugal A, Guthrie J (2001) Characterization of cellulosic multi-purpose office paper by inverse gas chromatography. Cellulose 8(3):217–224
Shi B, Qi D (2012) A method for improving the calculation accuracy of acid base constants by inverse gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1231:73–76
Spinace MAS, Lambert CS, Fermoselli KKG, De Paoli MA (2009) Characterization of lignocellulosic curaua fibres. Carbohyd Polym 77(1):47–53
Tarawou T, Horsfall M Jr, Vicente JL (2007) Adsorption of methyl red by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Biomass Chem Biodivers 4(9):2236–2245
Tshabalala MA, Han JS (1999) Effect of solvent extraction on surface energy of kenaf powder. In: Sellers T, Reichert NA (eds) Kenaf properties, processing and products. Mississippi State University, Mississippi, pp 121–131
van Asten A, van Veenendaal N, Koster S (2000) Surface characterization of industrial fibers with inverse gas chromatography. J Chromatography A 888(1):175–196
Voelkel A, Strzemiecka B, Adamska K, Milczewska K (2009) Inverse gas chromatography as a source of physicochemical data. J Chromatogr A 1216(10):1551–1566
Widegren JA, Bruno TJ (2011) Enthalpy of adsorption for hydrocarbons on concrete by inverse gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(28):4474–4477
Woverton BC, McKown MM (1976) Water Hyacinth for removal of phenols from polluted water. Aquat Bot 2:191–201
Wypych G (2001) General concept of acid-base interactions. In: Wypych G (ed) Handbook of solvents. Chemtech, Toronto
Zaranyika MF, Ndapwadza T (1995) Uptake of Ni Zn Fe Co Cr Pb, Cu and Cd by water hyacinth (Eicchornia Crassipes) in Mukuvisi and Manyame Rivers. Int J Environ Sci Health Part A Environ Sci Eng A 30(2):281–297
Zhao L, Boluck Y (2010) XPS and IGC characterization of steam treated triticale straw. Appl Surf Sci 257(1):180–185
Zheng JC, Feng HM, Lama MH, Lama PK, Ding YW, Yua HQ (2009) Removal of Cu (II) in aqueous media by biosorption using water hyacinth roots as a biosorbent material. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):780–785
Zhou W, Zhu D, Langdon A, Li L, Liao S, Tan L (2009) The structure characterization of cellulose xanthogenate derived from the straw of Eichhornia crassipes. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5366–5369
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out with financial support from the Research Board of the University of Zimbabwe.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukaratirwa-Muchanyereyi, N., Kugara, J. & Zaranyika, M.F. Adsorption of volatile polar organic solvents on water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) root biomass: thermodynamic parameters and mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 1941–1950 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1016-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1016-1