Abstract
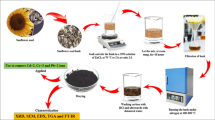
This paper presents a comparative study of the surface chemistry, texture, and adsorption properties of activated carbon and silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon. Activated carbon has been prepared from the pulp of oak cups using a chemical activation method, with silicon carbide nanoparticles used to modify the surface of activated carbon. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, and points of zero charge determination are the methods that have been employed to determine the physicochemical properties of raw material, activated carbon, and silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon, respectively. Results demonstrated that the activated carbon is composed mainly of micropores, with a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area of 1253.92 (m2/g), and that the attachment of silicon carbide nanoparticles changed the surface properties of activated carbon. The adsorption equilibrium of two azo dyes on activated carbon and silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon was investigated using the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherms. Experimental data were fitted to conventional kinetic models, including the pseudo-first-order, second-order, Elovich, and intraparticle diffusion models. For all adsorbents, the removal process follows the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Equilibrium adsorption parameters reveal that a higher adsorption capacity was found for silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon. These features indicate that silicon carbide nanoparticle-activated carbon is a promising and new adsorbent for the removal of acidic dyes during wastewater treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alishavandi Z, Mosallanejad N, Shabani R (2013) Silvernano particle loaded on activated carbon as novel adsorbent for the removal of acid yellow 199 dye. J Chem Health Risks (JCHR) 3:53–68
Ameta SC, Punjabi PB, Vardia J, Madhwani S, Chaudhary S (2006) Use of bromophenol red–EDTA system for generation of electricity in a photogalvanic cell. J Power Sources 159:747–751
Aysu T, Kucuk MM (2015) Removal of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from Ferula orientalis. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:2273–2284
Chatterjee S, Chatterjee S, Chatterjee BP, Guha AK (2007) Adsorptive removal of congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye by chitosan hydrobeads: Binding mechanism, equilibrium and kinetics. colloids surf A. Physicochem Eng Aspects 299:146–152
Chen S, Zhang J, Zhang C, Yue Q, Li Y, Li C (2010) Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange and methyl violet adsorption on activated carbon derived from Phragmites australis. Desalination 252:149–156
Denga S, Niea Y, Dua Z, Huanga Q, Menga P, Wanga B, Huanga J, Yua G (2015) Enhanced adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate by bamboo-derived granular activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 282:150–157
El-Hendawy AA, Alexander AJ, Andrews RJ, Forrest G (2008) Effects of activation schemes on porous, surface and thermal properties of activated carbons prepared from cotton stalks. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 82:272–278
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–470
Ghaedi M, Ghayedi M, Nasiri Kokhdan S, Sahraei R, Daneshfar A (2013a) Palladium, silver, and zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as adsorbent for removal of bromophenol red from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1209–1217
Ghaedi M, Ghayedi M, Nasiri Kokhdan S, Sahraei R, Daneshfar A (2013b) Palladium, silver, and zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as adsorbent for removal of bromophenol red from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1209–1217
Ghaedi M, Golestani Nasab A, Khodadoust S, Rajabi M, Azizian S (2014) Application of activated carbon as adsorbents for efficient removal of methylene blue: kinetics and equilibrium study. Ind Eng Chem 20:2317–2324
Ghazi Mokri HS, Modirshahla N, Behnajady MA, Vahid B (2015) Adsorption of C.I. acid red 97 dye from aqueous solution onto walnut shell: kinetics, thermodynamics parameters, isotherms. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:41401–41408
Giles CH, Smith D (1973) A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm I. Theor J Colloid Interface Sci 47:755–765
Gueu S, Yao B, Adouby K, Ado G (2007) Kinetics and thermodynamics study of lead adsorption on to activated carbons from coconut and seed hull of the palm tree. Int J Environ Sci Tech 4:11–17
Hu C, Zhou J, He S, Luo Z, Cen K (2009) Effect of chemical activation of an activated carbon using zinc chloride on elemental mercury adsorption. Fuel Process Technol 90:812–817
Hwang HJ, Nishihara A (1998) Perovskite-type BaTiO3 ceramics containing particulate SiC: part II Microstructure and mechanical properties. J Mater Sci 33:549–558
Kannan N, Sundaram MM (2001) Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—a comparative study. Dyes Pigments 51:25–40
Khaled A, Nemr AE, El-Sikaily A, Abdelwahab O (2009) Spent tea leaves: a new non conventional and low cost adsorbent for removal of basic dye from aqueous solutions. Desalination 238:210–232
Kim M, Kim J (2014) Development of high power and energy density microsphere silicon carbide-MnO2 nanoneedles and thermally oxidized activated carbon asymmetric electrochemical supercapacitors. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(23):11323–11336
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. part i. solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Lavrenko VA, Desmaison-Brut M, Panasyuka AD, Dasmaison J (1999) Mechanisms of deformation of silicon nitride and silicon carbide at high temperatures. J Eur Ceram Soc 18:2339
Li W, Peng J, Zhang L, Xia H, Li N, Yang K, Zhu X (2008) Investigations on carbonization processes of plain tobacco stems and H3PO4-impregnated tobacco stems used for the preparation of activated carbons with H3PO4 activation. Ind Crop Prod 28:73–80
Lopez-Ramon MV, Stoeckli F, Moreno-Castilla C, Maring-Carrasco F (1999) On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques. Carbon 37:1215–1221
Lu C, Chung YL, Chang KF (2006) Adsorption thermodynamic and kinetic studies of trihalomethanes on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 138:304–310
Manoj Kumar Reddy P, Krushnamurty K, Mahammadunnisa SK, Dayamani A, Subrahmanyam CH (2015) Preparation of activated carbons from bio-waste: effect of surface functional groups on methylene blue adsorption. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(4):1363–1372
Mezohegyi G, Vander Zee FP, Font J, Fortuny A, Fabregat A (2012) Towards advanced aqueous dye removal processes: a short review on the versatile role of activated carbon. J Environ manage 102:148–164
Neill CO, Hawkes FR, Hawkes DL, Lourenco N, Pinheiro HM, Delee W (1999) Colour in textile effluents–sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:1009–1018
Pezzotti G, Sakai M (1994) Effect of silicon carbide “nano dispersion” on the mechanical properties of silicon nitride. J Am Ceram Soc 77:3039–3041
Pham-Huu C, Estournes C, Heinrich B, Ledoux MJ (1998) High temperature H2S removal over high specific surface area [beta]-SiC supported iron oxide sorbent part 1 preparation and characterization. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 18:435–442
Poinern GEJ, Senanayake G, Shah N, Thi-Le X, Parkinson GM, Fawcett D (2011) Adsorption of the aurocyanide, Au(CN)2–complex on granular activated carbons derived from macadamia nut shells—a preliminary study. Miner Eng 24:1694–1702
Pourreza N, Naghdi T (2014) Silicon carbide nanoparticles as an adsorbent for solid phase extraction of lead and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Ind Eng Chem 20:3502–3506
Rengaraj S, Kim Y, Joo CK, Yi J (2004) Removal of copper from aqueous solution by aminated and protonated mesoporous aluminas: kinetics and equilibrium. J Colloid Interface Sci 273:14–21
Rudnik E (2013) Incorporation of ceramic particles into nickel and cobalt electroless deposits. Adv Mater Sci Appl 2:1–8
Strachowski P, Bystrzejewski M (2015) Comparative studies of sorption of phenolic compounds onto carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes and activated carbon. Colloids Surf A 467:113–123
Subramonian W, Wu TY (2014) Effect of enhancers and inhibitors on photocatalytic sunlight treatment of methylene blue. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(4):1–15. doi:10.1007/s11270-014-1922-0
Temkin MJ, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physiochim RSS 12:217–222
Timura S, Cem Kantarlib I, Onenca S, Yanika J (2010) Characterization and application of activated carbon produced from oak cups pulp. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 89:129–136
Tutem E, Apak R, Unal CF (1998) Adsorptive removal of chlorophenols from water by bituminous shale. Water Res 32:2315–2324
Ubago-Perez R, Carrasco-Marin F, Fairen-Jimenez D, Moreno-Castilla C (2006) Granular and monolithic activated carbons from KOH-activation of olive stones. Micropor Mesopor Mater 92:64–70
Vargas AMM, Garcia CA, Reis EM, Lenzi E, Costa WF, Almeida VC (2010) NaOH activated carbon from flamboyant (Delonix regia) pods: optimization of preparation conditions using central composite rotatable design. Chem Eng J 162:43–50
Vargas AMM, Cazetta AL, Kunita MH, Silva TL, Almeida VC (2011) Adsorption of methylene blue on activated carbon produced from flamboyant pods (delonix regia): study of adsorption isotherms and kinetic models. Chem Eng J 168:722–730
Wang Z (2015) Efficient adsorption of dibutyl phthalate from aqueous solution by activated carbon developed from phoenix leaves. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1923–1932
Wu FC, Tseng RL, Juang RS (2005a) Preparation of highly microporous carbons from fir wood by KOH activation for adsorption of dyes and phenols from water. Sep Purif Technol 47:10–19
Wu FC, Tseng RL, Juang RS (2005b) Comparisons of porous and adsorption properties of carbons activated by steam and KOH. J Colloid Interface Sci 283:49–56
Wu TY, Mohammad AW, Lim SL, Lim PN, Hay JXW (2013) Recent advances in the reuse of wastewaters for promoting sustainable development. In: Sharma SK, Sanghi R (eds) Wastewater reuse and management. Springer, Netherlands, p 47. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-4942-9_3
Zabaniotou A, Stavropoulos G, Skoulou V (2008) Activated carbon from olive kernels in a two-stage process: industrial improvement. Bioresour Technol 99:320–326
Zakaria ZA, Suratman M, Mohammed N, Ahmad WA (2009) Removal aqueous solution by untreated rubber wood of methylene blue from waste stream by fly sawdust. Desalination 244:109–121
Zolfaghari G, Esmaili-Sari A, Anbia M, Younesi H, Ghasemian MB (2013) A zinc oxide-coated nanoporous carbon adsorbent for lead removal from water: optimization, equilibrium modeling, and kinetics studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(2):325–340
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support (Grant number: 32/1012) from the Research Councils of Ilam University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemian, E., Palizban, Z. Comparisons of azo dye adsorptions onto activated carbon and silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 501–512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0875-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0875-1