Abstract
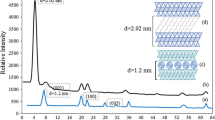
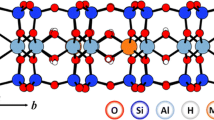
As the uptake of cationic drugs, such as tetracycline (TC), was attributed to cation exchange, the stability of adsorbed TC on a Ca-montmorillonite SAz-2 was studied using cationic solutions of different valence charges under different pH conditions. At the initial loading of 356 mg g−1, the amounts of TC desorbed by 0.05 M AlCl3, CaCl2, and NaCl were 133 ± 4, 83 ± 6, and 50 ± 4 mg g−1, respectively, or 37, 23, and 14 %. However, when the amount or percentage of TC desorbed was normalized to the equivalence of each cation, the values were in the range of 44–50 mg g−1 or 11–14 % per 10 mmol of charge. The kinetics of TC desorption were moderately fast and almost reached equilibrium in 6 h. The results followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model with reaction rate in the order of AlCl3 > CaCl2 > NaCl at a higher initial TC loading level. The total amount of TC desorbed after five desorption cycles followed the order of AlCl3 > CaCl2 > NaCl, too, suggesting that cations with higher positive charges, thus, less hydrated, are preferred to remove adsorbed cationic drugs. The FTIR analyses showed larger band shift when Al3+ was used as the desorbing reagent. The XRD patterns before and after TC desorption revealed no changes in basal spacing, even after five desorption cycles, suggesting that the removal of TC from SAz-2 was largely from the external surfaces.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Y, Zhou Q, Wan Y, Yu Q, Xie X (2010) Effects of soil/solution ratios and cation types on adsorption and desorption of tetracycline in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:1553–1561
Chander Y, Kumar K, Goyal SM, Gupta SC (2005) Antibacterial activity of soil-bound antibiotics. J Environ Qual 34:1952–1957
Chang PH, Li Z, Jiang WT, Jean JS (2009) Adsorption and intercalation of tetracycline by swelling clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 46:27–36
Chen WR, Huang CH (2010) Adsorption and transformation of tetracycline antibiotics with aluminum oxide. Chemosphere 79:779–785
Chen J, Fei Z, Tao W, Zhang G (2011) Adsorption and desorption of tetracycline on activated carbons. Adv Mater Res 233–235:561–566
Figueroa RA, Leonard A, Mackay AA (2004) Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environ Sci Technol 38:476–483
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG (2005) Interaction of tetracycline with aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environ Sci Technol 39:2660–2667
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG (2008) Sorption of the antibiotics tetracycline to humic-mineral complexes. J Environ Qual 37:704–711
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG, Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2007) Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere 66:1494–1501
Halling-Sørensen B, Nors Nielsen S, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Holten Lűtzhøft HC, Jørgensen SE (1998) Occurrence, fate, and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere 36(2):357–393
Hamscher G, Sczesny S, Höper H, Nau H (2002) Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performation liquid chromatograph with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 74:1509–1518
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Jia D An, Zhou DM, Wang YJ, Zhu HW, Chen JL (2008) Adsorption and cosorption of Cu(II) and tetracycline on two soils with different characteristics. Geoderma 146:224–230
Jiang WT, Wang CJ, Li Z (2013) Intercalation of ciprofloxacin accompanied by dehydration in rectorite. Appl Clay Sci (in press) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.07.009
Kay P, Boxall ABA (2000) Environmental risk assessment of veterinary medicines in slurry. SSLRC Contract JF 611OZ; Cranfield University
King AG (2006) Research advances. J Chem Educ 83:186–190
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zauqq SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Kulshrestha P, Giese RF Jr, Aga DS (2004) Investigating the molecular interactions of oxy-tetracycline in clay and organic matter: insights on factors affecting its mobility in soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:4097–4105
Leypold CF, Reiher MG, Brehm G, Schmitt MO, Schneider S, Matousek P, Towrie M (2003) Tetracycline and derivatives—assignment of IR and Raman spectra via DFT calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5:1149–1157
Li Z, Chang PH, Jean JS, Jiang WT, Wang CJ (2010) Interaction between tetracycline and smectite in aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 341:311–319
Loke ML, Tjørnelund J, Halling-Sørensen B (2002) Determination of the distribution coefficient (log Kd) of oxytetracycline, tylosin A, olaquindox and metronidazole in manure. Chemosphere 48:351–361
Mackay AA, Canterbury B (2005) Oxytetracycline sorption to organic matter by metal-bridging. J Environ Qual 34(6):1964–1971
Miller GH, Smith HL, Rock WL, Hedberg S (1977) Antibacterial structure—activity relationships obtained with resistant microorganisms. I: inhibition of R-factor resistant Escherichia coli by tetracyclines. J Pharm Sci 66:88–92
Montero MT, Freixas J, Hernandez-Borrell J (1997) Expression of the partition coefficients of a homologous series of 6-fluoroquinolones. Int J Pharm 149:161–170
Parolo ME, Avena MJ, Pettinari GR, Baschini MT (2012) Influence of Ca2+ on tetracycline adsorption on montmorillonite. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:420–426
Pils JR, Laird DA (2007) Sorption of tetracycline and chlortetracycline on K- and Ca-saturated soil clays, humic substances, and clay-humic complexes. Environ Sci Technol 41:1928–1933
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall AB (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Sassman S, Lee L (2005) Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ Sci Technol 39:7452–7459
Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2008) Interaction of the macrolide antimicrobial clarithromycin with dissolved humic acid. Environ Sci Technol 42:422–428
Wan Y, Bao Y, Zhou Q (2010) Simultaneous adsorption and desorption of cadmium and tetracycline on cinnamon soil. Chemosphere 80:807–812
Wang YJ, Jia DA, Sun RJ, Zhu HW, Zhou DM (2008) Adsorption and cosorption of tetracycline and copper(II) on montmorillonite as affected by solution pH. Environ Sci Technol 42:3254–3259
Wessels JM, Ford WE, Szymczak W, Schneider S (1998) The complexation of tetracycline and anhydrotetracycline with Mg2+ and Ca2+: a spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. B. 102:9323–9331
Wu Q, Li Z, Hong H, Yin K, Tie L (2010) Adsorption and intercalation of ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 50:204–211
Xu XR, Li XY (2010) Sorption and desorption of antibiotic tetracycline on marine sediments. Chemosphere 78:430–436
Yan W, Hu S, Jing CY (2012) Enrofloxacin sorption on smectite clays: effects of pH, cations, and humic acid. J Colloid Interface Sci 372:141–147
Zhao Y, Gu X, Gao S, Geng J, Wang X (2012) Adsorption of tetracycline (TC) onto montmorillonite: cations and humic acid effects. Geoderma 183–184:12–18
Zupancic M, Arcon I, Bukovec P, Kodre A (2002) A physicochemical study of the interaction of cobalt (II) ion with ciprofloxacin. Croat Chem Acta 75:1–12
Acknowledgments
The financial supports from Wisconsin Ground Water Research Council and grant 100-2116-M-006-009 from National Science Council, Taiwan are greatly appreciated. The authors are thankful to the assistance of Chen Yi-Hua and Kao Hsies-Ta for their help in experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, PH., Li, Z., Jean, JS. et al. Desorption of tetracycline from montmorillonite by aluminum, calcium, and sodium: an indication of intercalation stability. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 633–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0215-2