Abstract
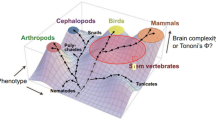
To answer the question of why we have consciousness, I propose the following evolutionary trajectory leading to this feature: Nervous systems appeared for the purpose of orchestrating behavior. As a rule of thumb the challenges facing an animal concern either approach or avoidance. These two options were originally hard-wired as reflexes. Improvements in adaptability of response came with an expansion of the computational aspect of the system and a concomitant shift from simple reflexes to instinctual behavior, learning, and eventually, feelings. The assessment of positive and negative feelings allows organisms to weigh various options, but for this to be a viable strategy, an awareness of hedonic value is required. This was presumably the first neural attribute to evolve that required awareness, and thus the key force in the evolution of consciousness. The attribute first appeared in the early amniotes (the phylogenetic group comprising reptiles, birds and mammals). Support for this model in current accounts of the neurobiology of feelings and consciousness is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkire MT, Miller J (2005) General anesthesia and the neural correlates of consciousness. Prog Brain Res 150:229–244
Alkire MT, Hudetz AG, Tononi G (2008) Consciousness and anesthesia. Science 322:876–880
Baars B (1997) In the theather of consciousness. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Barbano MF, Cador M (2007) Opioids for hedonic experience and dopamine to get ready for it. Psychopharm 191:497–506
Baumeister RF, Masicampo EJ, Vohs KD (2011) Do conscious thoughts cause behavior? Ann Rev Psych 62:331–361
Berridge KC, Kringelbach ML (2011) Building a neuroscience of pleasure and well-being. Psych Well-Being 1:3
Beshkar M (2008) The presence of consciousness in the absence of the cerebral cortex. Synapse 62:553–556
Bittar RG, Kar-Purkayastha I, Owen SL, Bear RE, Green A, Wang S, Aziz TZ (2005) Deep brain stimulation for pain relief: a meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 12:515–519
Borrelli L, Fiorito G (2008) Behavioral analysis of learning and memory in cephalopods. In: Menzel R (ed) Learning theory and behavior. Elsevier, New York, pp 605–628
Butler AB (2008) Evolution of brains, cognition, and consciousness. Brain Res Bul 75:442–449
Butler AB, Cotterill RM (2006) Mammalian and avian neuroanatomy and the question of consciousness in birds. Biol Bul 211:106–127
Buzsaki G (2007) The structure of consciousness. Nature 446:267
Cabanac M (1992) Pleasure: the common currency. J Theor Biol 155:173–200
Cabanac M, Bonniot-Cabanac MC (2007) Decision making: rational or hedonic? Beh Brain Funct 3:45
Cabanac M, Cabanac AJ, Parent A (2009) The emergence of consciousness in phylogeny. Beh Brain Res 198:267–272
Crick F, Koch C (2003) A framework for consciousness. Nat Neurosci 6:119–126
Crick F, Koch C (2005) What is the function of the claustrum? Phil Trans Royal Soc London B 360:1271–1279
Damasio A (1999) The feeling of what happens: body and emotion in the making of consciousness. Harcourt, New York
Denton DA, McKinley MJ, Farrell M, Egan GF (2009) The role of primordial emotions in the evolutionary origin of consciousness. Conscious Cogn 18:500–514
Edelman G (2004) Wider than the sky: the phenomenal gift of consciousness. Yale University Press, Yale
Edelman DB, Seth AK (2009) Animal consciousness: a synthetic approach. Trends Neurosc 32:476–484
Ferrarelli F, Tononi G (2011) The thalamic reticular nucleus and schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bul 37:306–315
Fiorito G, Scotto P (1992) Observational learning in octopus vulgaris. Science 256:545–547
Gould JL, Grant-Gould C (1995) The honey bee. Scientific American Library, New York
Grinde B (2012) The biology of happiness. Springer, Dordrecht
Gvilia I (2010) Underlying brain mechanisms that regulate sleep-wakefulness cycles. Int Rev Neurobio 93:1–21
Hochner B, Shomrat T, Fiorito G (2006) The octopus: a model for a comparative analysis of the evolution of learning and memory mechanisms. Biol Bul 210:308–317
Jones EG (2001) The thalamic matrix and thalamocortical synchrony. Trends Neurosc 24:595–601
Kitchen A, Denton D, Brent L (1996) Self-recognition and abstraction abilities in the common chimpanzee studied with distorting mirrors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7405–7408
Kringelbach ML, Berridge KC (2009) Towards a functional neuroanatomy of pleasure and happiness. Trends Cogn Sci 13:479–487
Kunde W, Kiesel A, Hoffmann J (2003) Conscious control over the content of unconscious cognition. Cognition 88:223–242
Laland KN, Galef BG (2009) The question of animal culture. Harvard University Press, Harvard
Land M, Nilsson D-E (2002) Animal eyes. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lane N (2009) Life ascending: the ten great inventions of evolution. WW Norton, New York
Leknes S, Tracey I (2008) A common neurobiology for pain and pleasure. Nature Rev Neurosc 9:314–320
Lieberman MD, Eisenberger NI (2009) Neuroscience pains and pleasures of social life. Science 323:890–891
Lou HC (2011) Paradigm shift in consciousness research: the child’s self-awareness and abnormalities in autism, ADHD and schizophrenia. Acta Paediat 101:112–119
Marino L (2007) Cetacean brains: how aquatic are they? Anat Rec 290:694–700
Mather JA (2008) Cephalopod consciousness: behavioural evidence. Conscious Cogn 17:37–48
McFarland DJ, Sibly RM (1975) The behavioural final common path. Philos Trans Royal Soc London B 270:265–293
Merker B (2007) Consciousness without a cerebral cortex: a challenge for neuroscience and medicine. Beh Brain Sci 30:63–81
Miller JW, Ferrendelli JA (1990) Characterization of GABAergic seizure regulation in the midline thalamus. Neuropharma 29:649–655
Mink JW, Blumenschine RJ, Adams DB (1981) Ratio of central nervous system to body metabolism in vertebrates: its constancy and functional basis. Am J Phys 241:R203–R212
Moriyama T, Gunji YP (1997) Autonomous learning in maze solution by octopus. Ethology 103:499–513
Mosley C (2011) Pain and nociception in reptiles. Vet Clin N Am Exotic Ani Prac 14:45–60
Nir Y, Tononi G (2010) Dreaming and the brain: from phenomenology to neurophysiology. Trends Cogn Sci 14:88–100
Noirhomme Q, Soddu A, Lehembre R, Vanhaudenhuyse A, Boveroux P, Boly M, Laureys S (2010) Brain connectivity in pathological and pharmacological coma. Front Syst Neurosci 4:160
Palmiter RD (2011) Dopamine signaling as a neural correlate of consciousness. Neurosci 198:213–220
Panksepp J (1998) Affective neuroscience. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Panksepp J, Normansell L, Cox JF, Siviy SM (1994) Effects of neonatal decortication on the social play of juvenile rats. Phys Behav 56:429–443
Pecina S (2008) Opioid reward “liking” and “wanting” in the nucleus accumbens. Phys Behav 94:675–680
Pessiglione M, Petrovic P, Daunizeau J, Palminteri S, Dolan RJ, Frith CD (2008) Subliminal instrumental conditioning demonstrated in the human brain. Neuron 59:561–567
Prior H, Schwarz A, Gunturkun O (2008) Mirror-induced behavior in the magpie (Pica pica): evidence of self-recognition. PLoS Biol 6:e202
Reiss D, Marino L (2001) Mirror self-recognition in the bottlenose dolphin: a case of cognitive convergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5937–5942
Rose JD (2007) Anthropomorphism and “mental welfare” of fishes. Dis Aqua Org 75:139–154
Rosenthal DM (2008) Consciousness and its function. Neuropsychologia 46:829–840
Rossano MJ (2003) Expertise and the evolution of consciousness. Cognition 89:207–236
Schiff ND, Fins JJ (2007) Deep brain stimulation and cognition: moving from animal to patient. Cur Opin Neurol 20:638–642
Seth AK, Baars BJ, Edelman DB (2005) Criteria for consciousness in humans and other mammals. Conscious Cogn 14:119–139
Smith CU (2010) Darwin’s unsolved problem: the place of consciousness in an evolutionary world. J Hist Neurosci 19:105–120
Smith K, Mahler S, Pecina S, Berridge K (2010) Hedonic hotspots: generating sensory pleasure in the brain. In: Kringelbach M, Berridge K (eds) Pleasures in the brain. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 27–49
Sneddon LU (2009) Pain perception in fish: indicators and endpoints. ILAR J 50:338–342
Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2008) Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and arousal. Ann New York Acad Sci 1129:275–286
Tabibnia G, Satpute AB, Lieberman MD (2008) The sunny side of fairness—preference for fairness activates reward circuitry (and disregarding unfairness activates self-control circuitry). Psychol Sci 19:339–347
Takahashi H, Kato M, Matsuura M, Mobbs D, Suhara T, Okubo Y (2009) When your gain is my pain and your pain is my gain: neural correlates of envy and schadenfreude. Science 323:937–939
Tamietto M, de Gelder B (2010) Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:697–709
Ward LM (2011) The thalamic dynamic core theory of conscious experience. Conscious Cogn 20:464–486
Zhang Y, Lu H, Bargmann CI (2005) Pathogenic bacteria induce aversive olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 438:179–184
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Michel Cabanac (Laval University, Quebec, Canada) and David B. Edelman (The Neurosciences Institute, San Diego, CA, USA) for critical reading of the manuscript and for numerous highly valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grinde, B. The Evolutionary Rationale for Consciousness. Biol Theory 7, 227–236 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13752-012-0061-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13752-012-0061-3